Alesis QSR
Introduction
Page
Contents
Editing Mixes
Editing Effects
Index
Chapter
AC Power Hookup
Unpacking and Inspection
Line Conditioners and Protectors
Basic Audio Hookup
About Audio Cables
Playing the Demo Sequences
Powering UP
WHAT’S a PROGRAM?
About Sound Groups
WHAT’S a MIX?
Whats a BANK?
Auditioning Internal Programs
Program Mode and MIX Mode
Playing the QSR
Selecting the Midi Channel in Program Mode
Selecting Program Banks
Realtime Performance Functions
Auditioning MIX Play Mode
Selecting MIX Banks
Play Mode Active Midi Channels
Choosing Programs in a MIX
Save Mix to
Enabling General Midi Mode
Storing AN Edited MIX
Using the Pcmcia Expansion Card Slots
Word about the QSR CD-ROM
Sound Bridge
Connections
Basic Midi Hookup
Using AN External Sequencer
PC31.25Kbd
Using a Computer
PC 38.4Kbd
MAC 1MHz
IBM PCS and Compatibles
Digital AUDIO/OPTICAL Hookup
Recording Digital Audio
KHZ
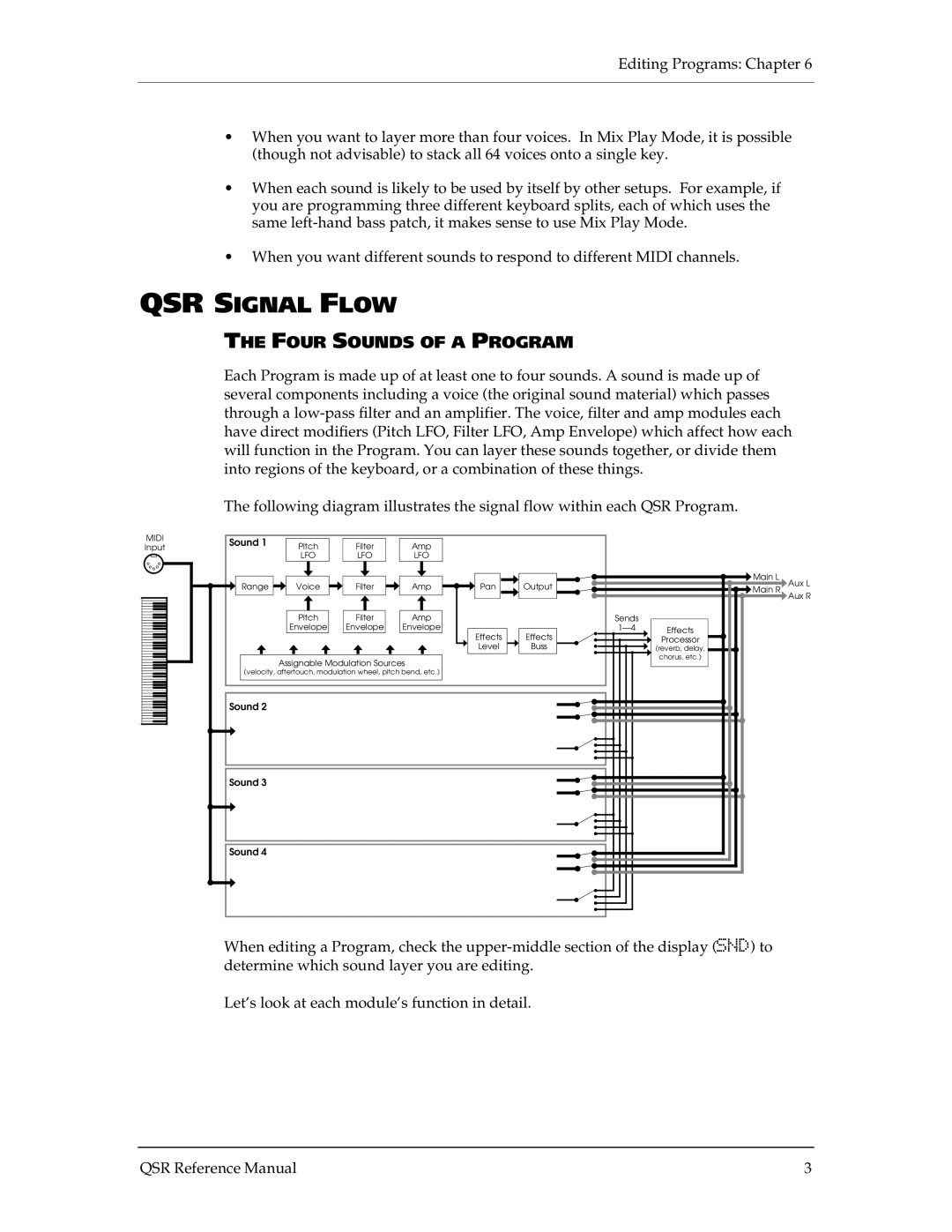
Basic Architecture
QSR Polyphony
Program Edit Mode
Program Play Mode
MIX Play Mode
Modes
Global Edit Mode
MIX Edit Mode
Effects Edit Mode
Store Mode
User Interface DISPLAY, FUNCTIONS, Pages and Parameters
About the Display
SND1VOICE πå Snd EnableON
Parameter Editing Overview
Midi CH Buttons
Editing Values
Preset Memory and User Memory
Comparing Edited and Stored Versions
Save Program to User
Storing
Store a Program or MIX
To Audition Programs Before Storing
Program is now stored
This selects Mix Play Mode
Prog
Copying Sounds Between Programs
Copying Effects Between Programs
Initializing the PROGRAM/MIX Buffers
Initializing Sounds
Overview Chapter QSR Reference Manual
Program Assign for Each Midi Channel
What is a MIX?
MIX Edit Mode
Understanding the Edit Buffers
Level Setting for Each Program
KEYBOARD/MIDI
Pitch
Effect
Aftertouch On or Off
Controllers
Pitch-bend and Modulation Wheels On or Off
Sustain Pedals On or Off
Lower Limit Midi note 000 to 127/ C-2 to G8
Setting the Range and Midi Switches
Naming a MIX
High Limit Midi note 000 to 127/ C-2 to G8
Polyphony in MIX Play Mode
Playing a Group of Channels in a MIX
You will see Midi Group in the middle of the display
Overview
Normalized Synth Voice
HOW the QSR Generates Sound
Program Sound Layers
QSR Signal Flow
Four Sounds of a Program
Cutoff Frequency
Voice
Lowpass Filter
About Modulation
AMP
Envelopes
About Signal Processing
LFO LOW Frequency Oscillator
Drum Mode
Sound
Sound Type
Sound Enable
Program Edit Functions
Sound Group 17 options
Sound
Noise
Sound Output Main, Aux, or Off
Sound Volume 00 to
Sound Pan 3 to
Effect Level 00 to
Detune Type Normal or Equal
Semitone -24 to +24 semitones
Detune -99 to +99 cents
Pitch Wheel Range 0 to 12 semitones
Portamento Rate 0 to
Keyboard Mode Mono, Poly, 1-Pitch or 1-PMono
Portamento Exponential, Linear, 1 Speed
Velocity -99 to +99
Filter Frequency 00 to
Keyboad Track On or Off
Filter
Filter Envelope Depth -99 to +99
Modulation Wheel Depth -99 to +99
Filter LFO Depth -99 to +99
Velocity Curve 13 choices
AMP/RANGE
Amp LFO Depth -99 to +99
Sound Overlap 00 to
Decay & Sustain 00 to Pages 2
Pitch Envelope
Attack 00 to
Release 00 to 99, Hold
Sustain Decay 00 to
Delay 00 to 99, Hold
Trigger Normal, Freerun, Reset, Reset-Freerun
Time Tracking On or Off
Velocity Modulation 00 to
Sustain Pedal On or Off
Level 00 to
Release 00 to
Filter Envelope
Delay 00 to
AMP Envelope
Release 00 to
Name
Modulation Source
About General Purpose Modulation
Selecting the Modulator 1 to
Page
Modulation Destination
Gate Mode Off or On 4 Mods 1 3 Only
Quantize Mode Off or On 4 Mods 4 6 Only
Modulation Level -99 to +99
Pitch LFO
Shape 8 choices
Speed 00 to
Trigger Mono, Poly, Key Mono, or Key Poly
Mod Wheel Depth -99 to
Filter LFO
Aftertouch Depth -99 to
Wave 8 choices
AMP LFO
Trigger Mono, Poly, Key Mono, Key Poly
Tracking Generator
Tracking Input
Tracking Points 0 10 Pages
Programming Drum Sounds
Kick
Tune -12.00 to +12.00
VelocityPitch 0 to
VelocityFilter 0 to
Decay 0 to 99, Gate00 to Gate99
Page
Copying Sounds
Mute Group Off, 1, 2, or
Copying Effects
Editing Effects
Effect πß Midi Chan
Selecting AN Effects Patch in MIX Mode
Setting Effects Send Levels
Prg Change0N
Editing Effects
Send1CONFIG πå
Clip
Navigating
Page
Copying Effect Patches
Storing Effect Patches in Program Mode
Storing Effect Patches in MIX Mode
Configurations
Configuration #1 1 Reverb
Pitch Delay Reverb
Page
Configuration #2 2 Reverbs
Configuration #3 Lezlie and Reverb
Configuration #4 Reverb and EQ
Configuration #5 Overdrive and Lezlie
Lo EQ Gain 0dB to +12dB
MOD
Lo EQ Frequency 30Hz to 180Hz
Hi EQ Frequency 3kHz to 10kHz
Mod Level 3 Mod 1 & Page 6 Mod
Mod Source 1 Mod 1 & Page 4 Mod
Mod Destination 2 Mod 1 & Page 5 Mod
Lezlie
Pitch Type
Send1PITCH πå Type MN Chorus
DRY Signal
Delay Input 99 to 0 to 2 Config Only
Depth 00 to
Resonator Tuning 00 to 2 Resonator only
Waveform Shape Sine or Square
Feedback 00 to
Time 0 to 799ms total Pages 3 & 4 and 6 & 7 in Stereo Delay
Delay
Delay Type 3 types
Feedback 00 to 5 and Page 8 in Stereo Delay
Input Balance 99 to 0 to 3 Config 1, 3, 4
Input 1 Config 1, 3, 4
Input 2 Config 1, 3, 4
Input level 00 to 4 Config 1
Send1REVERB πå Chrs In Lev03
Chorus Input Level 00 to 1 Config 2 Only
Send Input Levels 99 to 0 to 1 Sends 2 through
Send4REVERB πå RvbSN430DEL
Reverb Parameters
Pre-Delay Time 0 to 299ms Pages 6
Reverb Type 7 types
Decay 00 to
Pre-Delay Mix 99 to 0 to
Input Filter 00 to
Low Decay and High Decay 00 to Pages 11
Overdrive Threshold 00 to
Overdrive
Overdrive Type Hard or Soft
Overdrive Brightness 00 to
Lezlie Level 00 to 1 Config Page 5 Config
Pitch Level 00 to 99 Page 1Config 1 and 4 Page 2 Config 2
Reverb Level 00 to 99 Page 3 Config 4 Page 4 Config
Overdrive Level 00 to 1 Config Only
Editing Effects Chapter QSR Reference Manual
Master Pitch
General Midi Mode
Editing Global Parameters
Master Tune
Controllers a D Assignment
Pedals 1 and 2 Assignment
Midi Program Select
RECEIVING/TRANSMITTING Bank Change Messages
Midi and MAC 1MHz
INPUT/OUTPUT Mode
Midi , PC 38.4kbaud and PC31.25kb
Midi OUT
MIX Group Channel
Clock
Save User to CrdABnk1 STR
Using Pcmcia Expansion Cards
Saving the User Bank to a Pcmcia Card
Load User from CrdABnk1 STR
Loading a Bank from AN External Card
Storing AN Individual Program or MIX
Page
Loading AN Individual Program or MIX
Card Storage Ramifications
Page
Saving Programs VIA Midi SYS EX
PRG 000? STR
Sequence Playback
Play CardA Seq01 Store
Midi Transfer and Storage Operations QSR Reference
Appendix a
TROUBLE-SHOOTING Index
RE-INITIALIZING
Obtaining Repair Service
MAINTENANCE/SERVICE
Cleaning
Checking Software Version
Customers outside the USA
Page
Midi Hardware
Appendix B
Channel Messages Voice Messages
Channel Messages Mode Messages
Midi Message Basics
Page
General Midi
System Common Messages
Page
Midi Implementation Chart
Appendix C
Program Edit Parameters
Parameter
MIX Edit Parameters
Index