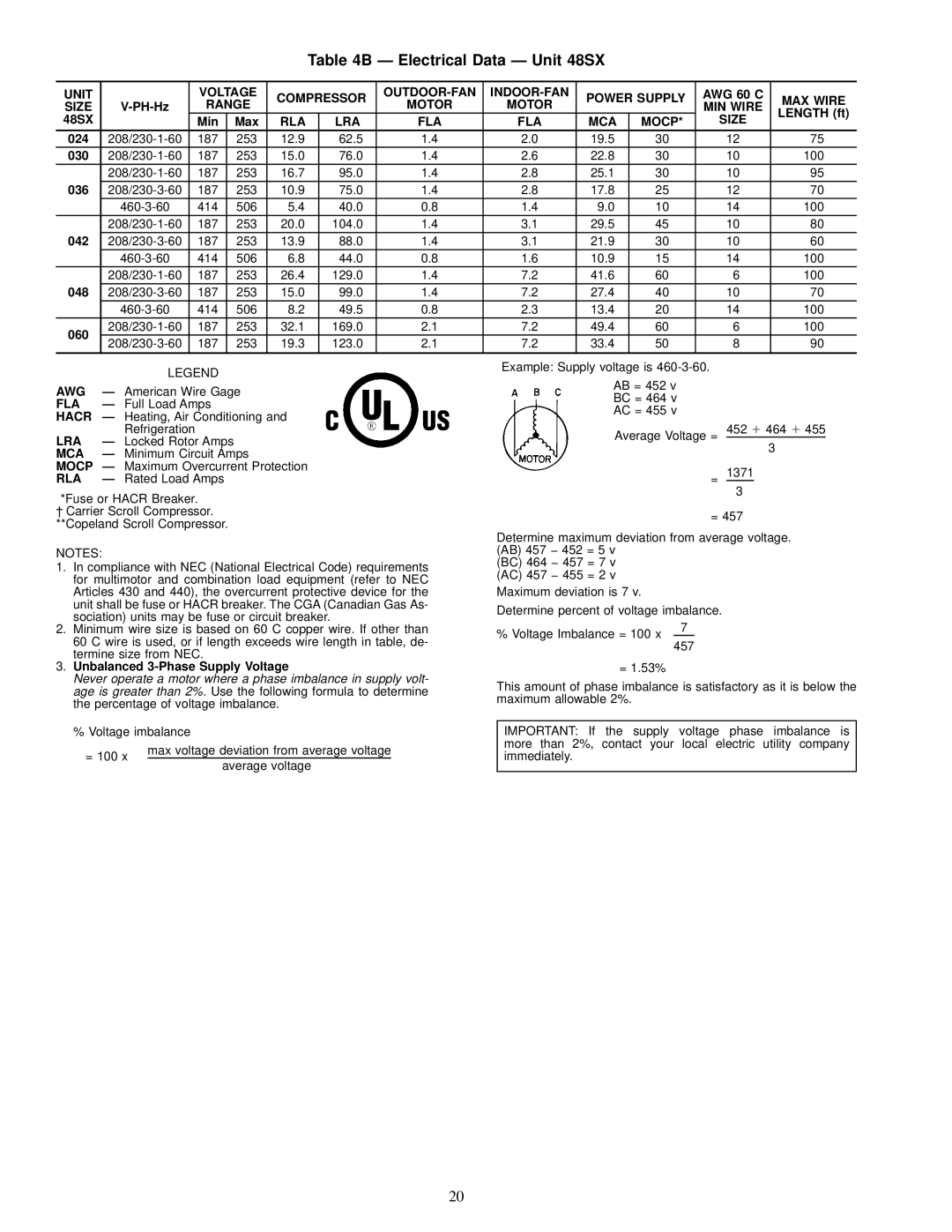
Table 4B Ð Electrical Data Ð Unit 48SX
UNIT |
| VOLTAGE | COMPRESSOR | POWER SUPPLY | AWG 60 C | MAX WIRE | ||||||
SIZE | RANGE | MOTOR | MOTOR | MIN WIRE | ||||||||
|
|
|
| LENGTH (ft) | ||||||||
48SX |
| Min | Max | RLA | LRA | FLA | FLA | MCA | MOCP* | SIZE | ||
|
| |||||||||||
024 | 187 | 253 | 12.9 | 62.5 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 19.5 | 30 | 12 | 75 | ||
030 | 187 | 253 | 15.0 | 76.0 | 1.4 | 2.6 | 22.8 | 30 | 10 | 100 | ||
| 187 | 253 | 16.7 | 95.0 | 1.4 | 2.8 | 25.1 | 30 | 10 | 95 | ||
036 | 187 | 253 | 10.9 | 75.0 | 1.4 | 2.8 | 17.8 | 25 | 12 | 70 | ||
| 414 | 506 | 5.4 | 40.0 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 9.0 | 10 | 14 | 100 | ||
| 187 | 253 | 20.0 | 104.0 | 1.4 | 3.1 | 29.5 | 45 | 10 | 80 | ||
042 | 187 | 253 | 13.9 | 88.0 | 1.4 | 3.1 | 21.9 | 30 | 10 | 60 | ||
| 414 | 506 | 6.8 | 44.0 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 10.9 | 15 | 14 | 100 | ||
| 187 | 253 | 26.4 | 129.0 | 1.4 | 7.2 | 41.6 | 60 | 6 | 100 | ||
048 | 187 | 253 | 15.0 | 99.0 | 1.4 | 7.2 | 27.4 | 40 | 10 | 70 | ||
| 414 | 506 | 8.2 | 49.5 | 0.8 | 2.3 | 13.4 | 20 | 14 | 100 | ||
060 | 187 | 253 | 32.1 | 169.0 | 2.1 | 7.2 | 49.4 | 60 | 6 | 100 | ||
187 | 253 | 19.3 | 123.0 | 2.1 | 7.2 | 33.4 | 50 | 8 | 90 | |||
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| LEGEND |
AWG | Ð American Wire Gage |
FLA | Ð Full Load Amps |
HACR | Ð Heating, Air Conditioning and |
| Refrigeration |
LRA | Ð Locked Rotor Amps |
MCA | Ð Minimum Circuit Amps |
MOCP Ð Maximum Overcurrent Protection | |
RLA | Ð Rated Load Amps |
*Fuse or HACR Breaker.
²Carrier Scroll Compressor. **Copeland Scroll Compressor.
NOTES:
1.In compliance with NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements for multimotor and combination load equipment (refer to NEC Articles 430 and 440), the overcurrent protective device for the unit shall be fuse or HACR breaker. The CGA (Canadian Gas As- sociation) units may be fuse or circuit breaker.
2.Minimum wire size is based on 60 C copper wire. If other than 60 C wire is used, or if length exceeds wire length in table, de- termine size from NEC.
3.Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply volt- age is greater than 2%. Use the following formula to determine the percentage of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage imbalance
= 100 x | max voltage deviation from average voltage | |
average voltage | ||
|
Example: Supply voltage is
AB = 452 v BC = 464 v AC = 455 v
Average Voltage = 452 1 464 1 455 3
= 1371
3
= 457
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage. (AB) 457 − 45 2 = 5 v
(BC) 464 − 45 7 = 7 v
(AC) 457 − 45 5 = 2 v Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x |
| 7 | |
457 | |||
| |||
= 1.53%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the maximum allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is more than 2%, contact your local electric utility company immediately.
20