Corporate Headquarters
Cisco ONS 15600 Reference Manual
Cisco ONS 15600 Reference Manual, Release
Iii
N T E N T S
TSC Network-Level Indicators
SFP Modules
TSC Card Database
Vii
Path Protection Circuits
Viii
Two-Fiber Blsr to Four-Fiber Blsr
10.1 Any Service Any Port Card Application 10.2
Snmp
Bandwidth
Xii
Environmental Specifications A-4
Xiii
CTC Default Settings C-39
Xiv
Bay Label
Xvi
Legal Disclaimer Tab
Xvii
Path-Protected Mesh Network Ppmn Virtual Ring
Xviii
OSI/IP Scenario 5 GNE Without an OSI DCC Connection
Xix
B L E S
Link Icons
Xxi
Alarm Window
Xxii
Power and Noise Limited Performances A-14
Xxiii
About this Manual
Related Documentation
Revision History
Document Objectives
Audience
Document Conventions
Convention Application
Xxv
Xxvi
Warnung Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise
Avvertenza Importanti Istruzioni Sulla Sicurezza
Aviso Instruções Importantes DE Segurança
Xxvii
Xxviii
Xxix
GEM Disse Anvisninger
Xxx
Xxxi
Where to Find Safety and Warning Information
Obtaining Optical Networking Information
Cisco Optical Networking Product Documentation CD-ROM
Xxxii
Shelf and Backplane Hardware
Installation Overview
Bay Installation
ONS 15600 with Dollies Installed
ONS 15600 Front Door
Front Door
Front door also has a Class I laser warning Figure
Rear Covers
6shows the bus bar covers
Cable Routing
Customer Access Panel
Rear of the ONS 15600, Including the CAP
8shows the CAP faceplate
Alarm, Timing, LAN, and Craft Pin Connections
External Alarm and Control Contact Installation
Visual and Audible Alarms
Alarm Cutoff and PDU Alarms
Timing Installation
LAN Installation
4 TL1 Craft Interface Installation
See , Timing, for more information
Power and Ground Description
Power Distribution Unit
11 Front and Rear Bay Ground Holes
Air Filter
Fan-Tray Assembly
13 Air Filter and one Fan Tray Pulled Out
Fan Speed and Failure
157
Cards and Slots
Card Slot Requirements
Condition Watts Amps BTU/Hr
Card Ports Line Rate per Port
Asap Card Cables
17show the OGI pin breakout for the OC-48 card
OGI Cables
Optical Card Cable Routing
Card Replacement
Page
Page
Card Overview
Card Summary
Card Description For Additional Information
Card R1.0 R1.x.x R5.0 R6.0 R7.0 R7.2
Card Compatibility
TSC Card
TSC Slots and Connectors
TSC
TSC Faceplate and Block Diagram
TSC Card-Level Indicators
TSC Network-Level Indicators
Indicator Color Definition
Push-Button Function
TSC Push-Button Switches
Ssxc Switch Matrix
Ssxc Card
Ssxc Faceplate and Block Diagram
Ssxc Slots and Connectors
Ssxc Card-Level Indicators
1 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Slots and Connectors
OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card
OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Faceplate and Block Diagram
2 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Faceplate and Block Diagram
Indicator Color Description
3 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card-Level Indicators
4 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Network-Level Indicators
5 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Card OGI Connector Pinout
OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card
1 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Slots and Connectors
OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Faceplate and Block Diagram
2 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Faceplate and Block Diagram
12lists the OC48/STM16 SR/SH card OGI connector pinouts
3 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card-Level Indicators
4 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Network-Level Indicators
5 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Card OGI Connector Pinout
OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card
1 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Slots and Connectors
OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Faceplate and Block Diagram
2 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Faceplate and Block Diagram
3 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card-Level Indicators
4 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Network-Level Indicators
5 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Card OGI Connector Pinout
OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card
1 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Slots and Connectors
3 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card-Level Indicators
2 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Faceplate and Block Diagram
4 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Network-Level Indicators
5 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Card OGI Connector Pinout
Asap Card
OC3
Asap Connectors
SFP on STS192
STS3c STS6c STS9c STS12c STS18c STS24c STS36c STS48c
Asap Covers and Plugs
Asap Card Faceplate and Block Diagram with 4PIOs Installed
9shows the 1PIO module faceplate
5 1PIO Module Faceplate
Asap Card Port-Level Indicators
Asap Card-Level Indicators
Port PPM Slot
Asap Card Port Numbering 4PIO Installed
SFP Modules
Asap Card Port Numbering 1PIO Installed
ONS-SE-Z1
Card
ONS 15600 SONET/SDH
ONS-SE-2G-L2
XFP Description
Asap 1PIO only
ONS-XC-10G-S1 ONS-XC-10G-L2
PPM Provisioning
Filler Card
17shows the Filler card body and faceplate
Page
Optical Port Protection
Card Protection
Type Ports Description
ONS 15600 in a 1+1 Protected Configuration
Unprotected Ports
External Switching Commands
Card Protection External Switching Commands
CTC Software Delivery Methods
CTC Software Installed on the TSC Card
CTC Software Installed on the PC or Unix Workstation
CTC Installation Overview
PC and Unix Workstation Requirements
Area Requirements
RAM
CTC Login
Legal Disclaimer Tab
Legal Disclaimer
CTC Window
Login Node Group
Card Color Status
Port Color Service State Description
Node View
CTC Card Colors
IS-NR
Node View Card Shortcuts
Node View Tabs
OOS-MA,DSBLD
Tab Description Subtabs
Network View
Color Alarm Status
CTC Node Colors
Node icon colors indicate the node status Table
Icon Description
Network View Tabs
Link Consolidation
6lists the tabs and subtabs available in the network view
PPC icon Server Trail icon
Card View
CTC Card View Showing an OC-192 Card
View or Card Tab Subtabs
Export and Print CTC Data
TSC Card Database
CTC Card Reset
Software Load Revert
User Privileges and Policies
Users IDs and Security Levels
User Privileges by Security Level
OSI
Blsr
Snmp
Edit/Reset
Subtab Actions Retrieve Maintenance Provisioning Superuser
Idle User Timeout
Security Policies
Superuser Privileges for Provisioning Users
Superuser Password and Login Privileges
Default Idle Time
Audit Trail
Audit Trail Capacities
Radius Authentication
Radius Security
Audit Trail Log Entries
Shared Secrets
Group Examples
Page
Timing Parameters
Timing
Network Timing
STU
Synchronization Status Messaging
Message Quality Description
PRS
ST4
ST2
ST3
SMC
Circuits and Tunnels
Circuit Properties
Overview
ONS 15600 Circuit Window in Network View
Starting
Concatenated STS Time Slot Assignments
109
100
103
106
Circuit Status
Circuit States
DRI
Circuit Protection Types
2F Blsr
2F-PCA
Circuit Information in the Edit Circuit Window
Port Color Service State
Purple
Cyan Blue
Detailed Circuit Map Showing a Terminal Loopback
Sonet Bytes
Cross-Connect Card Bandwidth
DCC Tunnels
Traditional DCC Tunnels
Multiple Destinations for Unidirectional Circuits
Path Protection Circuits
IP-Encapsulated Tunnels
Editing Path Protection Selectors
Viewing Path Protection Switch Counts
Protection Channel Access Circuits
Blsr STS Squelch Table
Blsr STS and VT Squelch Tables
Blsr VT Squelch Table
Path Trace
Card Receive Transmit
Automatic Circuit Routing
Secondary Sources and Destination
Bandwidth Allocation and Routing
Two-way
Manual Circuit Routing
No. of Sources No. of Drops Connection Type
Double path
Drop and continue
Constraint-Based Circuit Routing
One-way
Head end
Rolls Window
Bridge and Roll
State Description
Roll Status
Single Destination Roll
Single and Dual Rolls
12illustrates a dual roll on the same circuit
Merged Circuits
Two Circuit Bridge and Roll
Protected Circuits
Server Trails
Reconfigured Circuits
Circuits and Tunnels Server Trails
Sonet Topologies and Upgrades
Point-to-Point and Linear ADM Configurations
Bidirectional Line Switched Rings
Two-Fiber BLSRs
Four-Node, Two-Fiber Blsr
Four-Node, Two-Fiber Blsr Traffic Pattern Sample
Four-Fiber BLSRs
Four-Node, Four-Fiber Blsr
Four-Fiber Blsr Span Switch
OC-48 STS N 1 PT OC-192 N PT
Blsr Bandwidth
OC-48 STS 1-48 Fiber N 1 PT OC-192 STS 1-192 Fiber N PT
Blsr Fiber Connections
Connecting Fiber to a Four-Node, Two-Fiber Blsr
Path-Protected Mesh Networks
10 Connecting Fiber to a Four-Node, Four-Fiber Blsr
11 Path-Protected Mesh Network
In-Service Topology Upgrades
Point-to-Point or Linear ADM to Two-Fiber Blsr
Two-Fiber Blsr to Four-Fiber Blsr
Add or Remove a Node from a Topology
IP Networking Overview
Management Network Connectivity
ONS 15600 IP Addressing Scenarios
Scenario 1 CTC and ONS 15600s on the Same Subnet
What to Check
Sonet Ring
Scenario 2 CTC and ONS 15600s Connected to Router
ONS 15600 Proxy Server section on
Scenario 3 Using Proxy ARP to Enable an ONS 15600 Gateway
Scenario 3 Using Proxy ARP
Scenario 4 Default Gateway on CTC Computer
Scenario 4 Default Gateway on a CTC Computer
Scenario 5 Using Static Routes to Connect to LANs
81205
Scenario 5 Static Route with Multiple LAN Destinations
Scenario 6 Using Ospf
Scenario 6 Ospf Enabled
Scenario 6 Ospf Not Enabled
Scenario 7 Provisioning the ONS 15600 Proxy Server
Proxy Server Gateway Settings
Firewall Not Enabled
Ospf LAN
Setting ONS 15600 GNE ONS 15600 ENE
GNE
ENE
81209
Firewall Enabled
Packets Arriving At Accepts Rejects
13 Nodes Behind a Firewall
Scenario 8 Dual GNEs on a Subnet
15 Scenario 8 Dual GNEs on the Same Subnet
16shows a network with dual GNEs on different subnets
Provisionable Patchcords
OC-192
Routing Table
MXP2.5G10G MXP2.5G10E
TXPPMR2.5G
Entry Destination Mask Gateway Interface
6shows sample routing entries for an ONS
Http
External Firewalls
Port Function Action
FTP
3082 Raw TL1 3083
TL1
Management Network Connectivity Open GNE
Open GNE
18 Proxy and Firewall Tunnels for Foreign Terminations
19 Foreign Node Connection to an ENE Ethernet Port
TCP/IP and OSI Networking
OSI Model IP Protocols OSI Protocols IP-OSI Mediation
Point-to-Point Protocol
OSI Connectionless Network Service
Link Access Protocol on the D Channel
Field Definition Description
SEL
OSI Routing
Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System
End System-to-Intermediate System Protocol
Field Abbreviation Size bytes Description
Tarp
Type Description Procedure
Tarp Processing
PDU
Default Range Timer Description Seconds
Tarp Loop Detection Buffer
Process General Tarp Flow
6 TCP/IP and OSI Mediation
Manual Tarp Adjacencies
Manual TID to Nsap Provisioning
TD Protocol Flow
OSI Virtual Routers
Is L1/L2
Routing Mode Router Router 2 Per area Per is
IP-over-CLNS Tunnels
FT-TD
25 IP-over-CLNS Tunnel Flow
Provisioning IP-over-CLNS Tunnels
Step Purpose
IP-Over-CLNS Tunnel Scenario 1 ONS Node to Other Vendor GNE
CTC
IP-Over-CLNS Tunnel Scenario 2 ONS Node to Router
IP Over Clns Tunnel Scenario 2 ONS Node to Router
Management Network Connectivity IP-over-CLNS Tunnels
9 OSI/IP Networking Scenarios
CTC/CTM IP DCN ONS GNE
CTC/CTM IP OSS IP DCN ONS GNE
OSI GNE
CTC/CTM IP OSS
9.4 OSI/IP Scenario 4 Multiple ONS DCC Areas
33 OSI/IP Scenario 4 Multiple ONS DCC Areas
9.5 OSI/IP Scenario 5 GNE Without an OSI DCC Connection
34 OSI/IP Scenario 5 GNE Without an OSI DCC Connection
OSI/IP Scenario 7 -36 shows an example of a European network
ONS NE
Cisco ONS 15600 Reference Manual, R7.2
OSI/LAP-D
Tab Actions
OSI Provisioning in CTC
Any Service Any Port Card Application
GE LX
10-1
Transport Functionality
GFP
10-2
ONS 15600 Ethernet Frame Transport
10-3
Path and Circuit Sizes
Ethernet Rates and Mapping
Frame Size
Encapsulations
PPP Half Bridge
Protocols over Ethernet
Oversubscription
Bridge Control Protocol
Buffering and Flow Control
Vlan
10-6
10-7
Autonegotiation
10-8
Gigabit EtherChannel/IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation
11-1
Alarms, Conditions, and History
11-2
1describes in the information in the Alarms window
Description Description of the alarm
Column Information Recorded
11-3
Color Description
Button Action
Alarm Window
Alarm-Affected Circuits
MON Object Optical Syntax and Examples
11-5
Conditions Window
Retrieve Filter
Conditions Window Actions
5shows the actions you can perform in the Conditions window
Button
History Window
Description Description of the condition
11-7
11-8
7describes the information in the History window
11-9
Alarm Profiles
Alarm History Actions
Alarm Profile Window
Alarm Profile Buttons
Button Description
11-10
Row Display Options
Alarm Profile Editing
Alarm Severity Option
Alarm Profile Applications
Alarm Filter
Alarm Suppression
11-12
11-13
External Alarms and Controls
Alarms Suppressed for Maintenance
Alarms Suppressed by User Command
11-14
External Alarm Input
Virtual Wires for External Alarms in Mixed Networks
External Control Output
11-15
Virtual Wires Seen from an ONS
11-16
12-1
Threshold Performance Monitoring
Intermediate-Path Performance Monitoring
Line Terminating Equipment
12-2
12-3
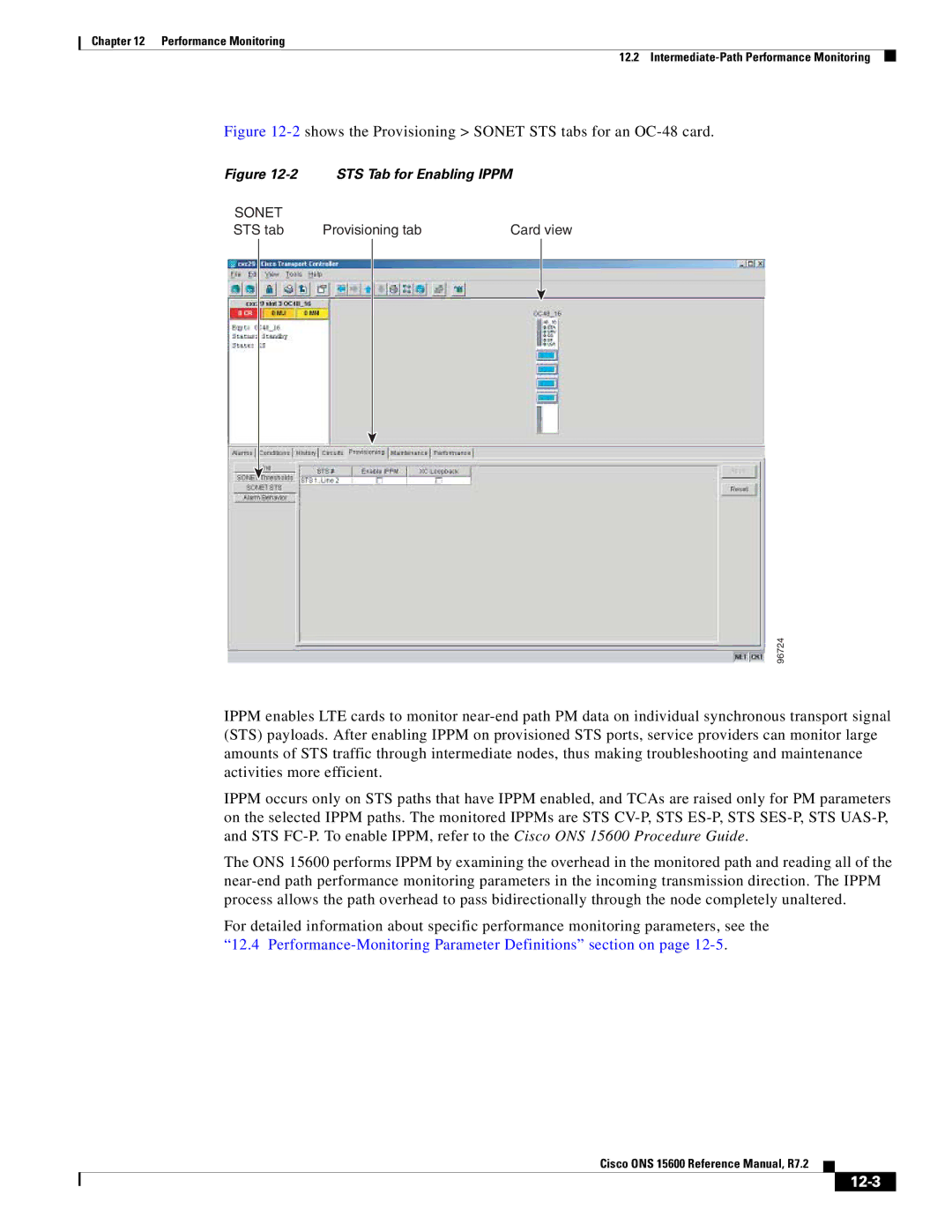
2shows the Provisioning Sonet STS tabs for an OC-48 card
12-4
Pointer Justification Count
Performance-Monitoring Parameter Definitions
Parameter Definition
12-5
12-6
12-7
12-8
12-9
Optical Card Performance Monitoring
PSC 1+1
3lists the near-end and far-end section layer PMs
Section NE Line NE
Line FE Optics NE 3 STS Path FE
STS SES-P
Asap Card Performance Monitoring
Physical Layer Parameters
Asap Card Optical Performance Monitoring Parameters
12-12
Asap Card Ethernet Performance Monitoring Parameters
Asap Card Ether Port Statistics Window
Parameter Meaning
12-13
12-14
12-15
Asap Card Ether Ports Utilization Window
Time Interval Number of Intervals Displayed
Asap Card Ether Ports History Window
Asap Card POS Ports Statistics Parameters
MaxBaseRate
Asap Card POS Ports Utilization Window
Asap Card POS Ports History Window
12-17
12-18
13-1
Snmp Overview
13-2
Basic Snmp Components
Example of the Primary Snmp Components
13-3
Operation Description
Snmp External Interface Requirement
Snmp Version Support
Snmp Message Types
Number Module Name Title/Comments
Snmp Management Information Bases
IETF-Standard MIBs for ONS
This section contains the following information
13-6
Snmp Trap Content
Proprietary ONS 15600 MIBs
HC-RMON-MIB
Generic and Ietf Traps
Variable Trap Bindings
13-7
EntConfigChange from RFC AuthenticationFailure From RFC
RFC
13-8
13-9
13-10
13-11
Proxy Over Firewalls
Row Creation in MediaIndependentTable
Remote Monitoring
13.8.2 64-Bit Rmon Monitoring over DCC
HC-RMON-MIB Support
History Control Rmon Group
Ethernet Statistics Rmon Group
Ethernet History Rmon Group
Alarm Rmon Group
Row Creation in historyControlTable
Row Deletion in historyControl Table
Event Table
Alarm Table
Row Deletion in alarmTable
Event Rmon Group
13-16
Shelf Specifications
Bandwidth
Slot Assignments
Cisco Transport Controller
Configurations
Dimensions
Cards
Modem Interface
Alarm Interface
External LAN Interface
8 TL1 Craft Interface
Card Type Card Name Watts
Environmental Specifications
Power Specifications
Database Storage
Specification Type Description
Card Specifications
TSC Card Specifications
Table A-3shows the TSC card specifications
Ssxc Specifications
3 OC48/STM16 LR/LH 16 Port 1550 Specifications
Table A-4shows the Ssxc card specifications
Specification Type Description
4 OC48/STM16 SR/SH 16 Port 1310 Specifications
OGI
5 OC192/STM64 LR/LH 4 Port 1550 Specifications
6 OC192/STM64 SR/SH 4 Port 1310 Specifications
Table A-9shows the Asap card specifications
Asap Specifications
Min/Max dBm
SFP/XFP Specifications
Filler Card Specifications
Transmitter Output Receiver Input Power
Interface Wavelength
Table A-13lists the available Dwdm SFPs
Wavelength Fiber Type Cable Distance
PRBS23
OOS-AUMA
Service States
State Qualifier Definition
OOS-AU
Secondary State Definition
Administrative States
Service State Transitions
Card Service State Transitions
Current Service State Action Next Service State
OOS-AUMA,MT & Swdl
OOS-AU,MEA
OOS-AU,MEA & MT
OOS-AUMA,MT & UEQ
Port and Cross-Connect Service State Transitions
OOS-AU,AINS & FLT
OOS-AUMA,FLT & Lpbk
OOS-MA,LPBK & MT
Loopback Alarm/condition is raised
OOS,MT
OOS,DSBLD Put the port or cross-connect
Page
Network Element Defaults Description
Network Element Defaults
Configuration Defaults
Card Default Settings
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Threshold Defaults
Defaults by Card
3.1 OC1924 Card Default Settings
LBC-LOW, LBC-LOW + 1, LBC-LOW
OPR-LOW, OPR-LOW + 1, OPR-LOW
OPT-LOW, OPT-LOW + 1, OPT-LOW
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
OPT-LOW, OPT-LOW +
3.2 OC4816 Card Default Settings
LBC-LOW, LBC-LOW +
OPR-LOW, OPR-LOW +
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Asap Card Default Settings
OOS,DSBLD IS, OOS,DSBLD, OOS,MT IS,AINS
IS,AINS IS, OOS,DSBLD, OOS,MT
ASAP4.config.oc3.line.SyncMsgIn
ASAP4.config.oc192.line.State
ASAP4.config.oc192.line.SyncMsgIn
ASAP4.config.oc192.sts.IPPMEnabled
ASAP4.physicalthresholds.oc12.warning.1day.LBC-HIGH 200 %
ASAP4.physicalthresholds.oc3.alarm.OPR-HIGH 200 %
ASAP4.physicalthresholds.oc48.warning.15min.OPT-HIGH 120 %
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Default Name Default Value Default Domain
Node Default Settings
False True
Default Default Name Value Domain
NODE.circuits.State
IS,AINS OOS,DSBLD OOS,MT
ProxyOnlyNo
NODE.network.general.AlarmMissingBackplaneLAN
NODE.general.UseDST
True False
NODE.osi.tarp.PDUsL2Propagation
NODE.osi.tarp.L2DataCache
NODE.osi.tarp.LANStormSuppression
NODE.osi.tarp.LDB
NODE.protection.blsr.SpanRevertive
NODE.security.passwordAging.EnforcePasswordAging
ESF ESF, D4
B8ZS B8ZS, AMI
Tncress
ST3EREST
RES=DUS
Time Zones
NODE.timing.general.Revertive
NODE.timing.general.SSMMessageSet Generation
GMT Greenwich Mean Time
GMT
CTC Default Settings
True TRUE, False
Default Default Name Value Default Domain
IN-1
IN-2
Bits
Corba
CTC
IN-3
Dwdm
DCC
DCN
Dhcp
IN-5
IN-6
Iiop
JRE
LAN
IN-7
IN-8
Viewing popup information NPJC-Pdet parameter
NPJC-Pgen parameter
Nsap
Radius
Power requirements Timing
PM read points
Cable breakout
SSM
PIM
LAP-D OSI
Sntp
PST B-1 Pstq B-1
Rmon
IN-11
Sonet
SSM SST
IN-12
IN-13
TCA
IN-14