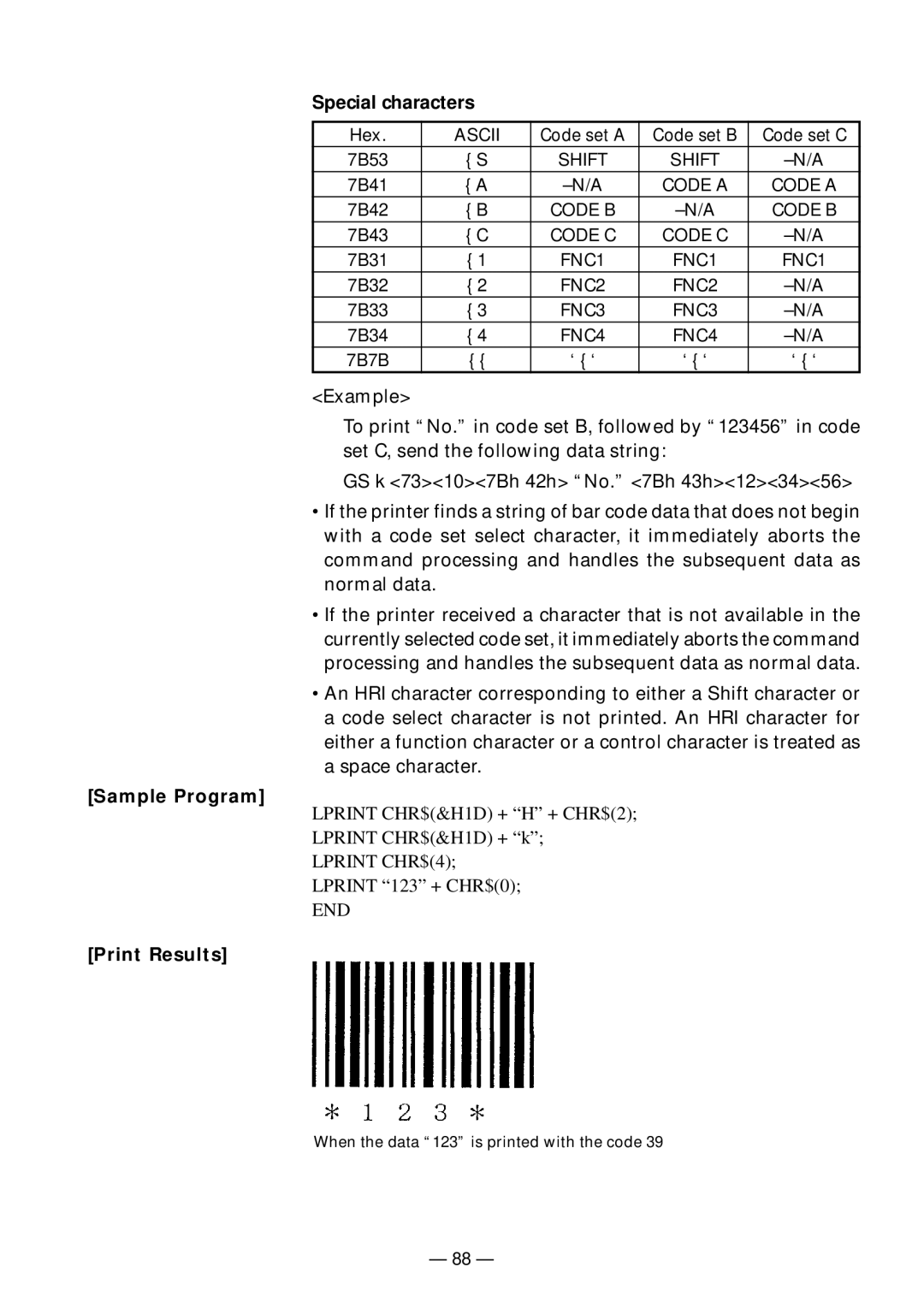
Special characters
Hex. | ASCII | Code set A | Code set B | Code set C |
7B53 | { S | SHIFT | SHIFT | |
7B41 | { A | CODE A | CODE A | |
7B42 | { B | CODE B | CODE B | |
7B43 | { C | CODE C | CODE C | |
7B31 | { 1 | FNC1 | FNC1 | FNC1 |
7B32 | { 2 | FNC2 | FNC2 | |
7B33 | { 3 | FNC3 | FNC3 | |
7B34 | { 4 | FNC4 | FNC4 | |
7B7B | { { | ‘ { ‘ | ‘ { ‘ | ‘ { ‘ |
<Example>
To print “No.” in code set B, followed by “123456” in code set C, send the following data string:
GS k <73><10><7Bh 42h> “No.” <7Bh 43h><12><34><56>
•If the printer finds a string of bar code data that does not begin with a code set select character, it immediately aborts the command processing and handles the subsequent data as normal data.
•If the printer received a character that is not available in the currently selected code set, it immediately aborts the command processing and handles the subsequent data as normal data.
•An HRI character corresponding to either a Shift character or a code select character is not printed. An HRI character for either a function character or a control character is treated as a space character.
[Sample Program]
LPRINT CHR$(&H1D) + “H” + CHR$(2);
LPRINT CHR$(&H1D) + “k”;
LPRINT CHR$(4);
LPRINT “123” + CHR$(0);
END
[Print Results]
When the data “123” is printed with the code 39
— 88 —