IBM
Page
IBM
Edition
1998
Contents
With
Utility
PFD
Print Format Utility
Format Utility
Definitions
Chapter
Introduction to
Vii
Work with Fonts
Management Utility
AFP Utilities for AS/400
Cvtpcdpags
Function
AFP
Limitations and Restrictions
Utilities
Box
GDFs
Task
EIA
Portability
Aiag
128
Index Xii AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Xiii
Page
Service
Marks
Xvi AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Xvii
Utilities For
IBM Advanced Function
AS/400
Who Should Use This Book
Are
Utilities For AS/400
Function
Utilities for AS/400
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
For
Chapter
Utilities
Advanced
Database files. The Print Format Utility
With
Utilities for AS/400
Query For
Ipds
Conventional Letter Preparation
Using Overlays
Letter Preparation Using AFP Utilities
Using Overlays
Using Graphics
Using Images
Using Bar Codes
GDF. GD
Overlay Utility
Sample Overlay Created by the Overlay Utility
Print Format Utility
Sample Label Created by the Print Format Utility
Print Sample Labels
Labels
Product descriptions
Application Are
Resource
On AS/400. These images are normally
AFP Resource
AS/400
Requirements for Use
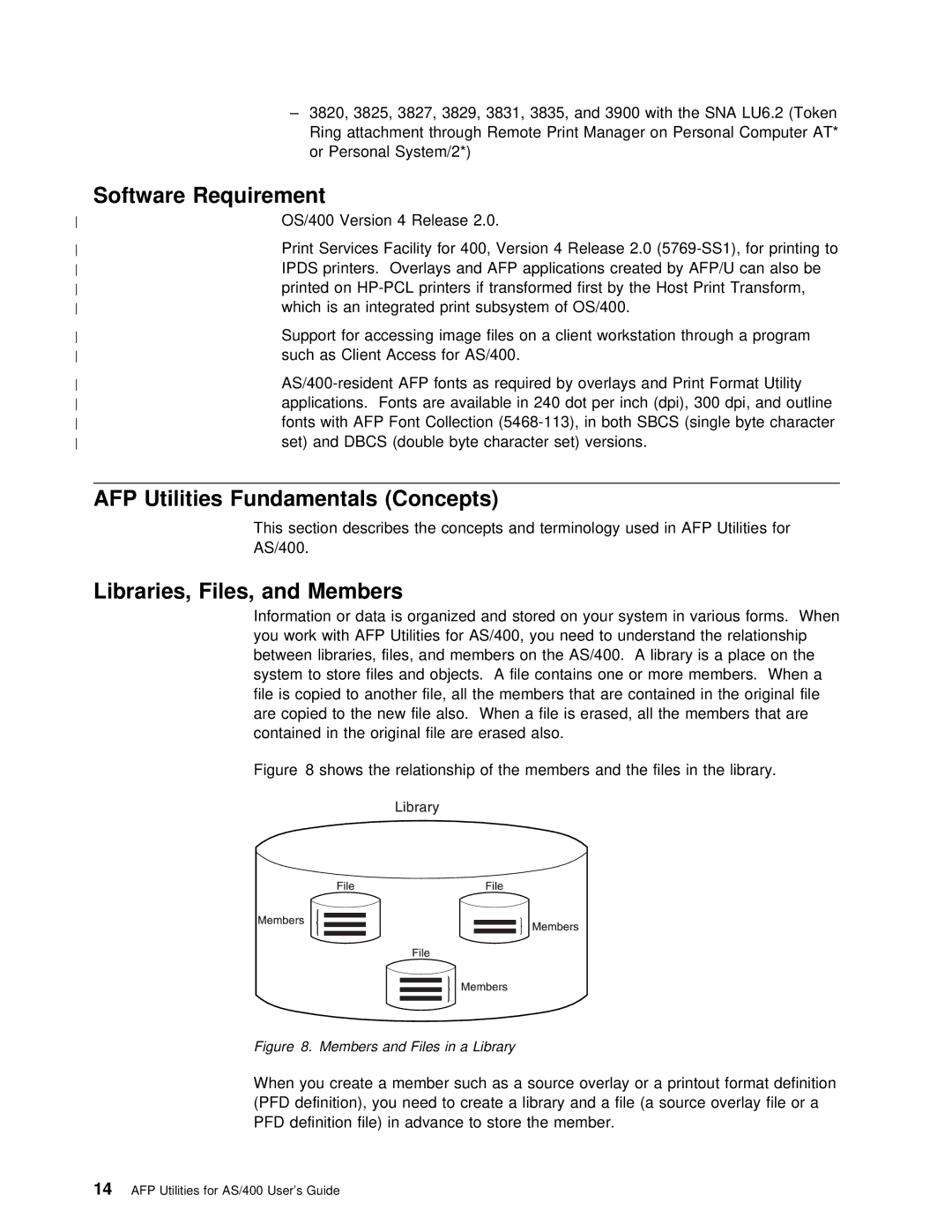
For
Members
Software Requirement
AFP Utilities Fundamentals Concepts
Dbcs
Menu Display
Elements
AFP Utilities for AS/400 Displays
With Display
Screen View Approximate Print Image is Displaye Upper part
When you Define Change Element Follows
Design display
Area
Design Overlay
Function Keys
List View on For More info
Define Text
Station
Information for this display or another Message Roll Down
Summary of AFP Utilities Function Keys
Description
InfoSeeker
Help for Control Language Commands
For Displays
Related Online Information
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Overlay Utility
With Overlay Utility
Files
Showing Source Overlay
Print Form and Overlay
Utility
Overlay
Utility is
Overlay Fonts
Overlay Specifications
Source Overlay
Design Overlay
Segment
Operation Flow
Graphic
Overview of Overlay Utility Operation
Introduction to the Overlay27 Utility
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
With the Overlay Utility
They Not exist Copy Segment
Option Function
Starting the Overlay Utility
Line Pressing the Enter key
Source Overlay File is
Creating a Source Overlay File
Ovllib
Because no Source Overlay File
Create
This step Overlay is Designed by creating a source overlay
Creating
Overlay
Type Create Optthecolumn First Line List
Defining
Text
More
Press the Enter key Following display appears
More Define Text
On the Text data
Prompt Key Entry area Press Enter Following Display Appears
Defining a Line Element
Specify opposite end of line and press F9
Changes to *L003 Display Show That Line Corr Defined
Defining a Box Element
Specify opposite corner of box and press F1ð
Specify Opposite Corner Box, press
More Define Box
Defining a Bar Code Element
Move the cursor to position Across 43, Down
Now, place a graphics element at the bottom of the overlay
Placing a Graphics Element
Specify opposite corner of graphics block and press F6
Type2 in theSource object typeprompt
With
Viewer
Qgpl
Opt Action
Saving the Source Overlay
Press the F3 key to exit from this display
Exit Overlay Utility
Save Source Overlay
\CURLIB
Opt File
Source overlay file OVLFILE, which Contains Overlay
Source overlay file Ovlfile created in library Ovllib
Step Changing a
Source Opt
Text Changed
Press Key
Press F6 or F9 to place graphics or page segment
Getting Started with the Overlay51 Utility
Change Source Overlay
Press Enter Key Create Overlay display appears
TypeY for Createthe overlayprompt Press the Enter key
Work with Source Overlays
File
Using the Printer File
Step
Advanced Function Presentation and Print
Definition Panel. Then, specify the o Name Library
Overlays Can be Printed Using
For Front Side Overlay Back Side overlay
Option
Starting and Ending the Overlay Utility
Copyright IBM Corp
Option 2 Work with source overlay files
Option 1 Work with source overlays
Ending the Overlay Utility
Work with Source Overlays
Work with Source Overlays
Prompts
Source Opt Overlay Text Changed
Name
Options
Library-name
Partial
Columns
Thethat listthere Are More Items After
Showing a Source Overlay List
Selecting a Source Overlay from a List
Beside Source Overlay
Create Source Overlay
Create Source Overlay Following Display Type1
First line List Type Source Overlay
Opt Action
Define Overlay Specifications
Define Overlay Specifications
More Define Overlay Specifications
Yes
Field Name
Specifications
Width gets
Cause of a Message and Its Results
Cause Result
Module widthorLine widthgets
Position Mark Name Across Down
Confirm Delete of Elements
Confirm Delete Elements
Bottom
Field Name Description
Work with Source Overlay Fonts
Not supported by printer type
Save Exit allows
Using Exit Overlay Utility Display You can Specify to
Saving a Source Overlay
Resume overlay utility sessionallows you to return to
Save Source Overlay Display You can Specify Followi
Save Source Overlay
=Change a Source Overlay
Change Source Overlay
For Receiving File
Source Overlay
Copy Source Overlay
Delete Source Overlay Following Work with
=Delete a Source Overlay
Press Enter Key After You Type Choices
Display Type 4 a
Press the Enter key to delete source overlays
Confirm Delete of Source Overlays
=Rename
=Create Overlay
TheN w member prompt
Create Overlay
That You Are
Authorization-list-name
ValueReturnof tothesource overlaypromptlistin
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Work with Source Overlay Files
Work with Source Overlay Files
Library Name
Following table Explains Each Field on this Display
Overlay File Name
Opt File Library Text Changed
Prompt Description
Prompt
Option Description
Showing a Source Overlay File List
Column
Are More Items After
Selecting a Source Overlay
Beside Source Overlay File
First line of the list Type 1a
=Create Source Overlay
Librarycolumn
Create Source Overlay File
Press the Enter key after you specify the choices
=Change Source Overlay File
Description
Change Source Overlay File
=Copy Source Overlay
File
Copy Source Overlay File
Press Enter Key After You Specify Choices
Press F12 Cancel. If yo
=Delete Source Overlay
Press F12 You Return Work With Source Overlay Files Display
Selections Still shown, and you can remove From
Press Enter Key Delete Them F12 Cancel
=Display Description
=Rename Source Overlay
Print
Print
Start Printing From Work With PFD Definitions . .Display
Work
=Display Description PFD
With PFD Definition Files
Enables You Develop
PFD Specifications
Printout Format Definition PFD Definition
Record Layout
PFD Definition Fonts
Database File
Layout
Text data on a
Layout
Character strings Which
Text element or Box Element
Mapping Object Name
Printout Specifications
Record Selection
Calledinthe text
Based
Using Different printout Format Definitions
Utility
Shown Below From One Database File
Shows the overview of the print format utility operation
Overview of Print Format Utility Operation
Introduction to Print Format101Utility
Definition Rename
Definition Copy
Definition Delete
Definition Print
Definition file in a library
Print Format Utility
103
Definition in a PFD definition file that you c
Toa store
Starting Print
Start AFP Utilities For
Selection Function
Definition Files Display Appears to Create a PFD d
Creating a
Definition 12 file,Work typewith
Library name that you Used Last
Mylib
Work with PFD Definitions
For example, the following describes How to Create a
Opt Definition Text Changed
Press the Enter key Specify Database File display appears
Type 1 inOptthecolumn besideDefine printout specifications
Specifying a Database File
Specify Database File
Select Database File
File Text
Record Layout
Bar
Text Data
Fixed Data
Data
Area .
Thekey entry area
Image area Shows you an Approximate Printout
Data
Select Field Record Format display appears
Cursor to Textthe dataprompt and press the F4 key
Type1 in theOpt column besideNAME Press the Enter key
Text dataprompt
Press Enter Key Following Display Appears
Specifying a Page Segment
Getting Started with Print Format117Utility
Specifying a Bar Code Element
More Define Bar Code
Specifying a Box Element
Control PFD definition
Cursor Position Across Down Line Press Key An element
Line
You Can Draw Line Record Layout
Appears Message prompts you Press
Press the Enter Key Line is Defined
Designing a Page Layout
Definitions For More Information
Getting Started with Print Format123 Utility
Design Page Layout
Example Action Press the F11 key to place a record
You Can Type Desired choices Detail list
More Place Record Layout
Type Value Repetition Across
To print a title on the page, do the following
126
Defining Printout Specifications
Define Printout Specifications
Type2 TheCopies Prompt Press Down Key
Exiting from Defining
Second Define Printout Specifications display appears
Definition
You Can Save PFD definition Exit From Defining
Exit PFD Definition
Type PFD exercise in the Text descriptionprompt, and press
Enter Key Following display appears
Save PFD Definition
From this display, you can print a database file
PFD definition Productlbl saved in file Pfdfile successfully
You can print a database file in the following procedures
Printing a Database File
Print
Ending
Format
To print only the tutorial overview
Printing
Tutorial
Print Database File Member
Definition Display Appears
Qafctutpfd
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
135
Starting and Ending the Print Format Utility
Starting the Print Format Utility
Definitions Work With
Utilities Tutorial
Definitions
Option 12 Work with PFD definition files
Option
File, Create Change
Command, t
Data Copy
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Definition, you need Create
Work with PFD Definitions
139
Definitions Display
ABC
=Create Creates
Showing a PFD Definition List
List
=Create PFD Definitions
Create PFD Definition
Following Explains Each field Create PFD Definition
With PFD definition fonts
Specifications
Define printout specifications
Specify database file
Define PFD Specifications
Define PFD Specifications
Specif
Define PFD Specifications display Allows You
Specificati
This Value Used to decide vertical positions when the measu
Row/Column is
Specifications to
PFD Specifications
Utility Finds Any Mismatched Elements Print
Another type and the Colorvalue for
Correct Printer Typechanged From Value\DEFAULT is used
Cause of Message and Its Result
Or 3=3916/4ð28, or7=3935 and the value for
Specific
Specifications Displa
Confirm Delete of Record Layout Elements
Confirm Delete of Page Layout Elements
Confirm Delete Layout Elements display Shows List
Layout Deleted Due Change
Position Mark Name Across Down Reason
Key, Design Record Layout List Database Files
Work with PFD Definition Fonts
Specify Database File
Specify Database File
Select Database File
Select Database File
Opt File Text
Select Record Format
Select Record Format
Record Opt Format Text
Specify Break Fields
Fields
Opt Field Length
Referred As a
Design Record Layout
Record
Design Record Layout
TheText
Data in Record Layout
Libraryprompt
Name of the member to be printed
Name Database File to Be printed
Library Name Database File
Then Press F11 key Following display appears
Images
Boxes
Graphics
Bar code
Utility allows you to specify an edit code with wh
Editing
More Define Text
This display You Can Specify Edit Code An edit
Edit Numeric
Select Fields to Edit Numeric
Design Page Layout
From the following display you can specify the design
Opt Field
Productlbl
First Input Field o Follows
% indicates the cursor position. a
More Place Record Layout
Repetition of the Record
Sample of repeating records vertically
Place Record Layout Detail
Following figure shows the above choices
Work with PFD Definitions171
F11
F10
F13 Then
S005 remains Since This Last element You Can
Work with PFD Definitions173
Branch Sales
Text data . . . . &SALES\TOTAL
Last Value
Data Strings First
Count
Break
Data display appears. You can select fields
Function Specify an edit code on the display Define
Field For Each Page, specify Prompts as Follows
SALES\TOTAL
Five
Specify Record Selection
You can specifyup to
Specify Record Selection
Records Are Selected Field
Correct Incorrect Reason
ColumnDescription
Value
Define Printout Specifications
Define Printout Specifications
More Define Printout Specifications
Number-of-copies
PromptDescription
Form-type
Source Drawer Envelopes are fed from the envelope drawer
Mapping
Specify Mapping Object Name
Can Segment name Qfclogo and a file name
When Variable data is specified for Segments Graphics
Searches Specified mapping For Object type
Segment Display
Following table explains each field
Mapping Page Segment Name
Exit PFD Definition
Mapped
Type all choices and press the Enter key
Without
Save PFD Definition
=Change PFD Definition
PFD definition Pfdnew saved in file Pfufile successfully
Definition. See the 1=Create PFD For More Information
Change PFD Definition
Definition Display You Can Copy
Using the Copy
192
Definition Disp
=Delete PFD Definition
Confirm Delete of PFD Definitions
=Rename PFD Definition
=Print PFD Definition
=Print Database File
Definition File Deleting
Work with PFD Definition Files
195
Definition File Renaming
ABC
Prompt that You want to list and work With Along Library
InLibrarythe prompt to locate the file Values
Cause Long Response Time Until Work With
Definition File. OptTypecolumn,1 in andthethe Name
Showing a PFD Definition File List
First Line List Type
Library where the PFD definLibrarytion file res
Display Type
Inn the first Line List Type
When You Press Enter,
Display on 197
Definition Files display on
Change PFD Definition File
=Copy PFD Definition
=Delete PFD Definition
12=Work with PFD Definitions
=Rename PFD Definition
Display
File
Start
207
Print Database File Member
END
Output-bin
Select Database File Member
Position toprompt
Opt Member Text
Such as ‘Fields used
Definitions Display by Pressing
Start Printing from the AFP Utilities Menu
Select PFD Definition
You Can Also
Select PFD Definition File
Opt Definition Text
Start Printing with
Line Display Press Key. This command allows you to
Following Command prompt Appears
Print Database file member fro
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Design Operation and Fonts
217
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Design Operation
Enter Advanced Function Printing Utilities
Graphics
Defining Elements on the Design Display
New Source Overlay
Screen View
Design Display
List View
Screen View Design display is shown
Defining Elements in the Screen View
View
Following table Explains Each Field Above Display
Key
Mark
Indication on
F13
Four Can Assigned Element Name Even Length
Hide
Refresh
Hide
Scroll
Key Function Description
Rep
Element Operations
Element Operation
Define
This function key cannot be used List View
Function Keys on the Design Display
Edit Operation
Left Moves Image Area Toward First
Image Area Toward Top line Down
Roll Up Forward
Image Area Toward Bottom line Down Roll Backward
Function Keys for Base Operation on the Design Display
You Can Use Following Function Keys When Are Editing
Elements Press F21 Key F22 Twice
Text Line Box F10 Box Bar Code
Defining or Changing an Element
Any element
Bar Code on
Segment
All Elements This Display
Text
Following Explains Each Field This Display
More Change Text
Change Text Detail
For Record Layout of the printout format definition
Vertical Right to Left
Horizontal
Vertical
Data
238
YesUserfor specifiedthe
You Can Show Select Source Overlay Font display or
Definition Font display Positioning Fontthe Cursorthe
Type option, press Enter
Line
Select Source Overlay Font
=Select Font Opt Number Text
Control You May
Following table Explains Each Field This Display
Define Line Detail
Middle
Box
Border
Image area window by entering one of the fo
Define Box Detail
Design Operation245
Press the Roll Up Page Down Key See Next Def Display
For Element
Shading Patternis
=Screen
Shading patternprompt
Text Placementprompts
Vertical, right to left
250
Errors May Occur
Horizontal
LPI
Bar Code
Vertical Right
Cðð2
MHI/AIM
Change Bar Code Detail
Define Bar Code Detail
Mark Shows Element mark. a
HRI
Upca
MSI
UPC
Postnet
CODE128
Ascii
ZIP+4
Jpbc
Segment
F3=Exit F6=Place graphics F9=Place page segment F12=Cancel
You May move the image area Window by entering one
Place Page Segment Detail
Following Display, you can select a
Prompt, the following display appears Select a Segment
Column Pressing Enter
Opt Segment Library Text
Graphics
Following table explains each field in these displays
More Place Graphics
Field Help For f Information Restrictions
Following table Explains Each Field These Displays
Place Graphics Detail
As that shown on
Switch
Record Layout
Where nnn Through
Press F11 Key To select Record
You May
Specificatio
Position and Distance of the Record in the Page Layout
Element is copied, moved, or removed, and the element edi
Element
Element Edit
Operation Is complete
One element copied
280
Block Edit
Specify opposite corner of block and press F22
Step Remove Elements Press F10 Copy Move
Design Operation281
Elements Creating New
List
Changing
Be easier To do View Which Shows Approximate Image
Parameters column
Parameters
Unit Measure
Unit
Inch
Text Line Box
Create or Change the Element
Create
F13 Then
Sort Element List
Copy, Move, Remove, or Restore
Change
Down
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Work with Source Overlay Fonts
Work with Fonts
289
Font Opt Number Text
290
Fgid
Old
Definition Fonts Display
New Font Printer
You System
Definition Font Display
=Change Font
292
Fonts Reside Syst Downloaded Printer. To use
Coded Font Name
Font Character Set Names Use
Has an Object Type
Sysval
All libraries in your library list
Beside Font number you want to display Press Enter
=Display Font
Display PFD Definition Font
Display Font Font Type=2
=Set Initial Font
Display Font Font Type=3
299
Resource Management
=Convert Overlay to Physical File Member
With Page Segments Function
Resource
Converting to an AS/400 Page Segment
To a
301
Segment created and stored in the resource library by
PC Document
Segment from
Process of Converting to Page Segment
An Overlay
Working with Overlays
Copying
File
Working with Page Segments
Overlay
Displays Segment Description
Description
File Member
Changes Segment Description
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
307
Getting Started with the Resource Management Utility
Starting Resource Management Utility
Convert to Segment Work with Overlays
Crtflr
PC Document
Imds
Ioca
Printing an Overlay
Rotation prompt if
Work with Overlays
Opt Overlay Library Text
You Should See Name
Press the Enter key.
Printing a Page Segment
Beside Segment Name
Type Name
Type6
Press Enter Key Print Segment Display Appears
Print Page Segment
Starting
Command
Starting and Ending the Resource Management Utility
Resource Management Utility with
Function
Utility With Cvtpcdpags Command
Option Convert to
With Overlays Function
Convert PCD to Page Segment Cvtpcdpags
Press the Enter key and the following display appears
Convert PCD to Page Segment Cvtpcdpags
Command Press Key Following display Appears
When you start the Resource Management Utility with
Convert PFM to Page Segment Cvtpfmpags
This Display You Can Convert Member Database file to See
Resource Management Utility
Convert Overlay to PFM Cvtovlpfm
Cvtpagspfm
Convert Page Segment to PFM Cvtpagspfm
Resource
For More Information
Function
Convert
323
Object
Typeprompt When You Segment
When You Type Segment Name
TheSource Object
Following Describes Fields Convert
\CURLIB
Resource Management Utility Determines Output
Replace Existing Segment Not
Center-and-trim
Change Image
Scale-to-fit
Image point-to-pel
Convert to Page Segment Function329
Example of Center-and-Trim Mapping
Example of Rotating the Image Block
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Work
With
333
Partial Name
=Copy Overlay Object
CommandCRTDUPOBJ
=Delete Overlays
=Print Overlay
Confirm Delete of Overlays
JOB
Output-queue-name
=Display Overlay Description
=Rename Overlay
Physical
Convert Overlay to PFM
File-name
Library-name
13=Change Overlay Text
Description
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
343
Work with Page Segments Function
316 Press Enter. Work With Segments display Appear
TOP
=Copy Page Segment
=Delete Page Segments
Called Following Describes Confirm Delete Segments Displa
=Print Page Segment
Confirm Delete of Page Segments display appears
Confirm Delete of Page Segments
Segment Shows Name
Will be called
=Rename Page Segment
=Display Page Segment Description
Member
Prompt Press enter
Type data in the prompts Press Enter
Text
Convert Page Segment to PFM
Converted Phy Member Library
13=Change Page Segment
Segment field Description
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Strovlu
AFP Utilities for AS/400 Commands
353
Imds Ioca
Problem
Chapter
Strovlu Start Overlay Utility Command
Provide Following Eight commands
355
Source-overlay-file-name
Source overlay file File
Library-name
Strpfu Start Print Format Utility Command
PFD file Pfdfile
Following describes the parameters for Strpfu command
PFD-definition-file-name
PFD-definition-name
PFD definition Pfdmbr
=Print database file
Command
Prtpfddta Print PFD
Command Syntax for Prtpfddta Command
Database file File
Following describes the parameters for Prtpfddta command
Specify the name of the PFD-definition you want to use
File-name
Include grid Grid
Member MBR
Member-name
YES
Specifies Source Drawer Used
Value specified in the printout specification is used
Default
Single-cut Sheets are Printer. Possible Values Are
Output-queue-name
Form-definition-name
Specify the library where the form definition is located
Shows Command syntax for
Specifies the qualified
Following describes the parameters for Cvtpcdpags command
Segment Pagseg
Segment to be cr
Folder-name
Page-segment-name
From folder Frmflr
PC-document-name
Mapping option Mapping
Image area size Imgsize
Unit of measure
PAT Position Trim
Pel
STF Scale to fit
CAT Center and trim
Pel with
Parameter Change New Value Will Not Affect This Segment
Authorization-list-name
Crtaut
Text description Text
Replace Replace
File Member
Description
Cvtpfmpags Convert Physical
Following Describes Parameters For
Segment To be cr Required Parameter
From file File
From member MBR
Specify the member name that is to be converted
Specify the length value in the selected unit of me
PAT Position
AFP Utilities for AS/400 Commands377
Specifies whether or not Segment replaces the exist Same
Syntax for Cvtovlpfm command
Cvtovlpfm Convert Overlay
Already Exists Library Possible Values Are
Overlay OVL
Following describes the parameters for Cvtovlpfm command
Specify the library where the overlay is located
Library list is used to locate the overlay
To file File
To member MBR
Crtfile
Create file Crtfile
Description
Following describes the parameters for Cvtpagspfm command
File Member Command
Cvtpagspfm Convert Page Segment
One record has one structured field. The padding charact
Specify the library where the page segment is located
Library List is Used Locate Segment
Used. It will Be a Val Type For Segment System
File
Specify the member name to fill the page segment data
Create
AFP Utilities for AS/400 Commands385
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Dotted Lines
Limitations and Restrictions
Overlay Utility Limitations
Overlay Size
Font
Restrictions
Source Overlay File
DDM
Text Box
Correct Segment Library
Print Format Utility Limitations
Line Width and Page Size
Dashed and Dotted Lines
Element Position
IO1
PFD Definition File
Format Images. IM1 Images may Not Printed Desired Resol
Limitations and Restrictions393
Resource Management Utility Limitations
Sending Source Overlays
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Identifying Problems
Problem Analysis
How to Use This Procedure
Problem Analysis
0100
Did
Yes 012
013
Task?
Indicate a Status HELD? Yes 020
019
Does Job
Parameter Value
Use
Installed
Can
AS/400 system?
For Current
Common Symptoms
Have All
Utilities for
Possible Causes
Symptom
Sbcs
Messages sent Queue Printer Writer
Sense Codes and Possible Causes
Sense Data Applicable. For Example
Code Color prompt
Bytes
Color
Text Element and Position
Contacting Your Service Representative
Element Type and Position
Is Row/Column
Top Horizontal Line Positioned Row Left Side Vertical
Line Element and Position
Center Horizontal Line Top Positioned Column Row. Left Edge
Box Element and Position
Is Inch Centimeter
Bar Code Element
Segment Element and Position
Inch or Centimeter
Measurement Method is Inch or Centimeter
Row/Column
Record Layout Element and Position
Graphics Element and Position
Top left corner of the page segment is positioned
Measurement Method is Inch or Centimeter
413
Appendix A. Printer Characteristics
Supported Printers
Only 300-pel 3116
Limitations for Each Printer
Printable Area
Printer Storage Limitations
Printer
GDF
Printer
3930 Printers
Col f or
Image Is not supported Only
3829 Printers
Print fidelity, because graphics
Double Byte Character Sets are not Supported
4028 Printers
Has Color Orders which Are Not Supported
Image Is not Supported Vertical format is not supported
Corresponding Font Exists
Not Supported Only
Specifications display,
Printout Is printed Black Error occurs You Can Graphics With
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Appendix B. Rotation, Format, and Shading Pattern in Box
Format, Text Placement and Rotation
Text Placement
Format
Degree of Rotation
Box
Print Example
Print Example
Appendix B. Rotation, Format, and Shading Pattern425 in Box
Print Example
Appendix B. Rotation, Format, and Shading Pattern427 in Box
Print Example
Appendix B. Rotation, Format, and Shading Pattern429 in Box
Print Example
Appendix B. Rotation, Format, and Shading Pattern431 in Box
Print Example
Appendix B. Rotation, Format, and Shading Pattern433 in Box
Print Example
Appendix B. Rotation, Format, and Shading Pattern435 in Box
Print Example
Shading Pattern in Box
Shade type Value %
Light 24.00 Medium 48.00 DARK72.00
Appendix C. Rotation of Graphics
439
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Indsn
Appendix D. Using GDFs in AFP Utilities
441
Outdsn
Supported Process Specific Control Ignored
Characteristics Supported
Operation Ignored
Set Character Box Supported 2Ignored
Attribute Modify Supported Ignored
Set Character Mode Supported Ignored
Attribute Supported Ignored
Set Character Angle Supported Ignored
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Tasks Related to Source Overlays
Appendix E. How to Do a Task
How to Use This Chapter
445
Following description
Files
Tasks Related to Source
That You are on Display With
Tasks Related to Overlay Objects
Following Description Assumes That You are Display Wit
Tasks Related to Screen
View
Defining an Element
Design Display
Handling Existing Elements
Task How to Do
Define Box Detail display Change Box Detail display
Tasks Related to Each Element Text Element
Rotation prompt
Bar Code Element
Line Element
Box Element
Define Line Detail display Change Line Detail display
Segment Element
Graphics Element
Narrow
Range
Record Layout Element
Tasks Related to Record Selection
Value Valuein theField, number, or charactecolumn or show
Per inch
Tasks Related to Font
Display Work With PFD Definition Fonts
Spacing prompt
Assumes That You are on Specify Map Object
456
Overlay prompt
Overstrike
Appendix F. Portability to Other Systems
Restrictions Ipds Towers
PT2 Tower Underline
Fonts
PSF Print Service Facility
Segments
Dmas Forms
Appendix G. Sample Overlays and Sample PFD Definitions
Sample Overlays
459
Definitions From library
MAPICS/DB Forms
Some Samples
Some Sample
Action Group
Labels
AFP Utilities
Tutorial
File Name Record Format Description
Character
Set
463
Character Hex
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Times New Roman Medium
Appendix I. Font Samples
465
Helvetica Roman Bold
Helvetica Roman Bold
Courier
Courier Font Samples
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Glossary
469
Area
470
Point
Compatibility
Diagnostic
Edit
Library
File List
File Type
Font Generic
For
IO1
Client
Identifier
474
Panel
Owner
Utility PFU
Parity
476
Syntax
Use
System Unit
AFP Utilities for AS/400 User’s Guide
Numerics
Index Special Characters
479
List View 286
Detail
256
Font 292
279
390
323
Object 335
345
Display 147
Text Design
189
Text Element Display Font Type=3
Display Font
Display font Font Type=1 296 Text 219 Type=2
Type 219 Display Overlay object
Form type 182 format
Identifying problems 397 image area Imds Ioca data stream
251 Font character set 293
From PC document 325 front side overlay 182 function design
Ipds towers JAN-short JAN-standard Jpbc Key entry area Line
Overlay Specifications
Ioca data stream
Line Type
209 337
260 Numeric editing
Omit
Override a printer file
Tasks 446
Restrictions 392
Tasks 447
Characters Per Inch 147
Record selection 179
PSF Print Service Facility
PT2 towers
Record selection in PFD definition 98 refresh function
Sample label Sample overlay 9, 24
Strpfu command
Symptoms
Sample PFD definition
Text Font
What is
Test 179
421
333
Source Overlay Files Fonts
289
195
Page
Series
Wed
Readers
User’s Guide
Boulder
Readers Comments Wed Like to Hear from You
S544-5349-01
80301-9817
Page
IBM