OPERATION | ||
|
|
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
Return to Master TOC
OUTPUT LIMITATIONS
The maximum output current as specified in the instal- lation section of this manual is derated in two situa- tions; alternate AC Wave Forms and elevated AC Frequencies.
• Alternate AC Wave Forms (See Set Up Menu)
Square | 200 amps max. output |
Sinusoidal | 150 amps max. output |
Triangular | 120 amps max output |
• Elevated AC Frequencies
Above 85Hz (AC output) the square wave out- put is limited to 170 amps. Elevated AC Frequencies do not effect the output of Sinusoidal and Triangular Waveforms.
These derated values have been programmed into the Invertec
DC TIG WELDING (see FIGURE B.3)
The TIG (Tungsten lnert Gas) welding process is based on the presence of an electric arc between a
To avoid inclusions of tungsten in the joint, the elec- trode should not contact the workpiece. For this reason the arc is started through a Hi. Freq. generator.
For situations requiring no Hi. Freq., Touch Start Tig reduces the
To improve weld bead quality at the end of the weld it is important to carefully control the downslope of cur- rent and ensure proper gas coverage over the weld.
WELDING POLARITY
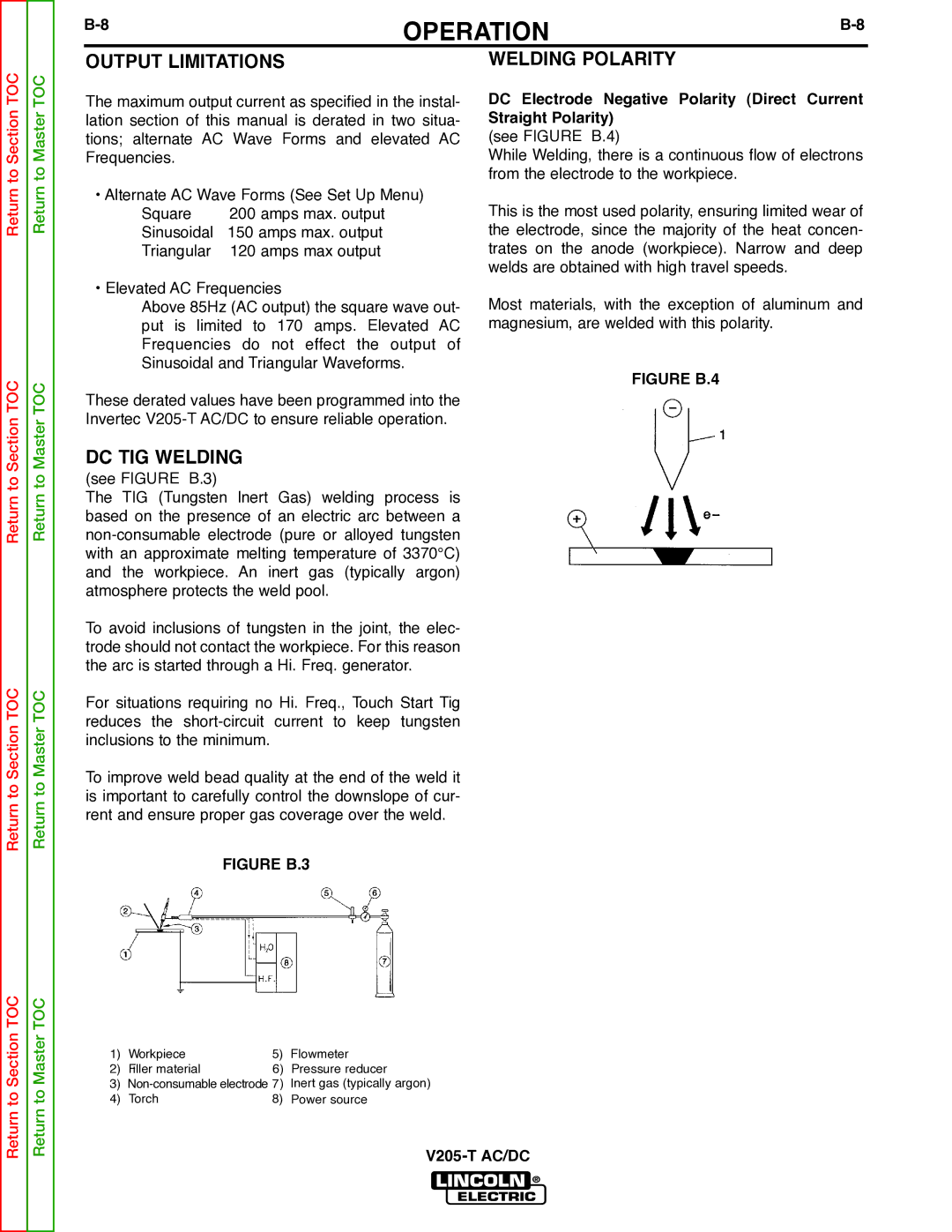
DC Electrode Negative Polarity (Direct Current Straight Polarity)
(see FIGURE B.4)
While Welding, there is a continuous flow of electrons from the electrode to the workpiece.
This is the most used polarity, ensuring limited wear of the electrode, since the majority of the heat concen- trates on the anode (workpiece). Narrow and deep welds are obtained with high travel speeds.
Most materials, with the exception of aluminum and magnesium, are welded with this polarity.
FIGURE B.4
Return to Section TOC
Return to Master TOC
FIGURE B.3
1) | Workpiece | 5) | Flowmeter |
2) | Filler material | 6) | Pressure reducer |
3) | lnert gas (typically argon) | ||
4) | Torch | 8) | Power source |