WebView Switches
Path Cost. Indicates the port contribution to the root path cost. The path cost is adjusted to a higher or lower value, and is used to forward traffic when a path being rerouted.
Default Path Cost. When selected the default path cost is implemented.
Priority. Priority value of the port. The priority value influences the port choice when a bridge has two ports connected in a loop. The priority value is between 0
Designated Bridge ID. Indicates the bridge priority and the MAC Address of the designated bridge.
Designated Port ID. Indicates the selected port’s priority and interface.
Designated Cost. Indicates the cost of the port participating in the STP topology. Ports with a lower cost are less likely to be blocked if STP detects loops.
Forward Transitions. Indicates the number of times the port has changed from the Blocking state to Forwarding state.
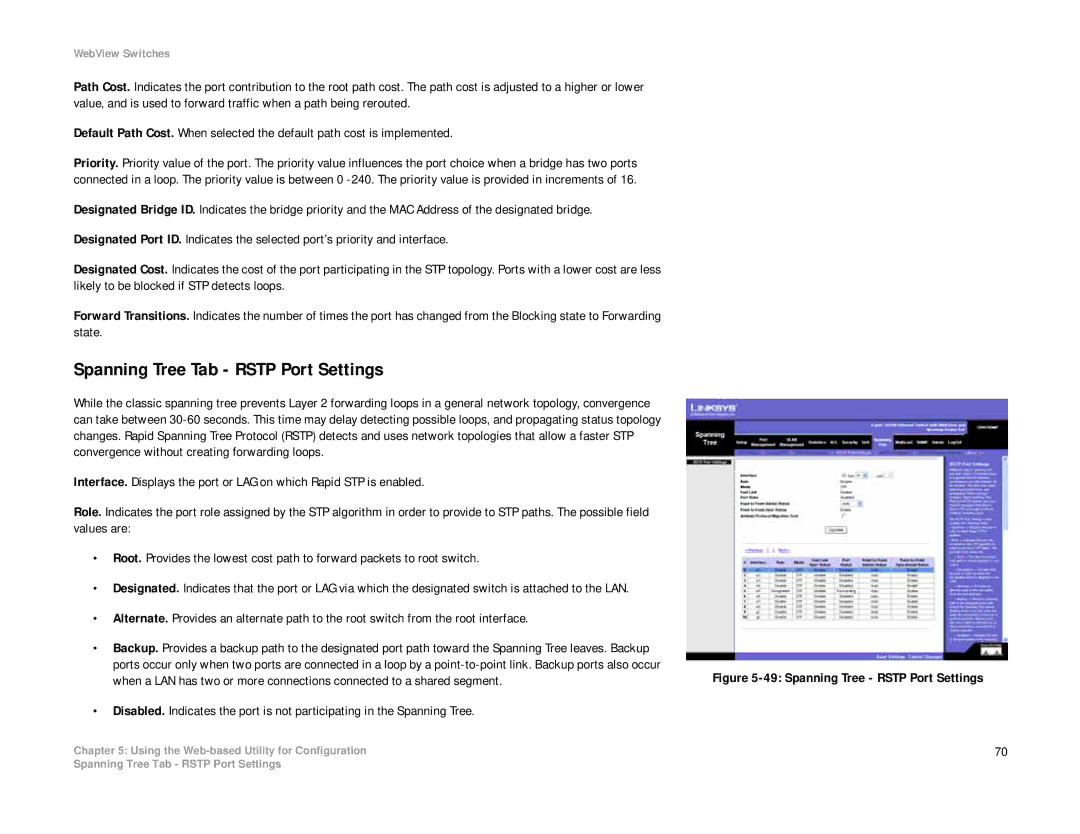
Spanning Tree Tab - RSTP Port Settings
While the classic spanning tree prevents Layer 2 forwarding loops in a general network topology, convergence can take between
Interface. Displays the port or LAG on which Rapid STP is enabled.
Role. Indicates the port role assigned by the STP algorithm in order to provide to STP paths. The possible field values are:
•Root. Provides the lowest cost path to forward packets to root switch.
•Designated. Indicates that the port or LAG via which the designated switch is attached to the LAN.
•Alternate. Provides an alternate path to the root switch from the root interface.
•Backup. Provides a backup path to the designated port path toward the Spanning Tree leaves. Backup ports occur only when two ports are connected in a loop by a
•Disabled. Indicates the port is not participating in the Spanning Tree.
Chapter 5: Using the
Figure 5-49: Spanning Tree - RSTP Port Settings
70
Spanning Tree Tab - RSTP Port Settings