Page
Contents
NB714 User Guide
Package Contents
Features
Introduction
Security
Specification
Routing
Bridging
WAN Interface
Indicators
ATM QoS
AAL5 Encapsulation
Product Information
Application
Physical/Electrical
Memory
Firewall
Packet Filtering
Types of Firewall
There are three types of firewall
Circuit Gateway
Denial of Service Attack
Application Gateway
UDP Flood
Ping of death
SYN Flood
Icmp Flood
Frame Specification
Vlan Virtual Local Area Network
VID uniquely identifies the Vlan to which the frame belongs
Applications
Front Panel
Getting to know the router
LED status
LAN 1,2,3,4
Rear Panel
Check the Ethernet Adapter in PC
Connecting your G.SHDSL Modem Router
Check the Terminal Access Program
Determine Connection Setting
Bridge EoA Route EoA IPoA PPPoA
Port router with network topology
Install the Shdsl Router
PPPoE
Cross-over Ethernet cables can be used
Configuration via Web Browser
Router, which will lose any previous configuration
System error or disconnection
Basic Setup
Click Basic for basic installation
LAN Parameters
Bridge Mode
Enter Host Name
Enter VPI Enter VCI Click LLC Click Next
WAN1 Parameters
Routing Mode
Dhcp Client
Click Next to setup WAN1 parameters
LAN IP Type
Subnet Mask
Dhcp Server
IP type
IP Address
DNS Server
Trigger Dhcp Service
Relay
Dhcp relay
For more information, refer to the section on NAT/DMZ
PPPoE or PPPoA
AAL5 Encap
Protocol
Idle Time
Password
Password Confirm
Username
Eprom
Gateway
IPoA or EoA
Eprom
Advanced Setup
Data Rate
Annex Type
Link Type
Data rate
Reconnect for better line connection
Shdsl SNR margin
Margin range is from 0 to
Margin, the better the line connection
WAN
PCR Peak Cell Rate in kbps
QoS Quality of Service
UBR Unspecified Bit Rate
CBR Constant Bit Rate
Bridge
Eprom
Vlan
Packets
Pvid
Press Modify
RIP Mode
Route
Auto RIP Summary
RIP Version
Authentication required
Poison Reverse
NAT/DMZ
Count Global Start IP Address
Multi-DMZ
Multi-NAT
Virtual Start IP Address
Virtual Server
Basic Firewall Security
Firewall
Automatic Firewall Security
Connections and will be unresponsive
Advanced Firewall Security
Click Advanced Firewall Security and then press Finish
SYN Attack
Ping of death attack attempts to crash your system by
Addresses originating from your network
Dest. IP Address
Direction
Description
Src. IP Address
Filtering rule will be configured as follow
Filtering Rule for Smtp connection
Filtering Result
Update Filtering Rule
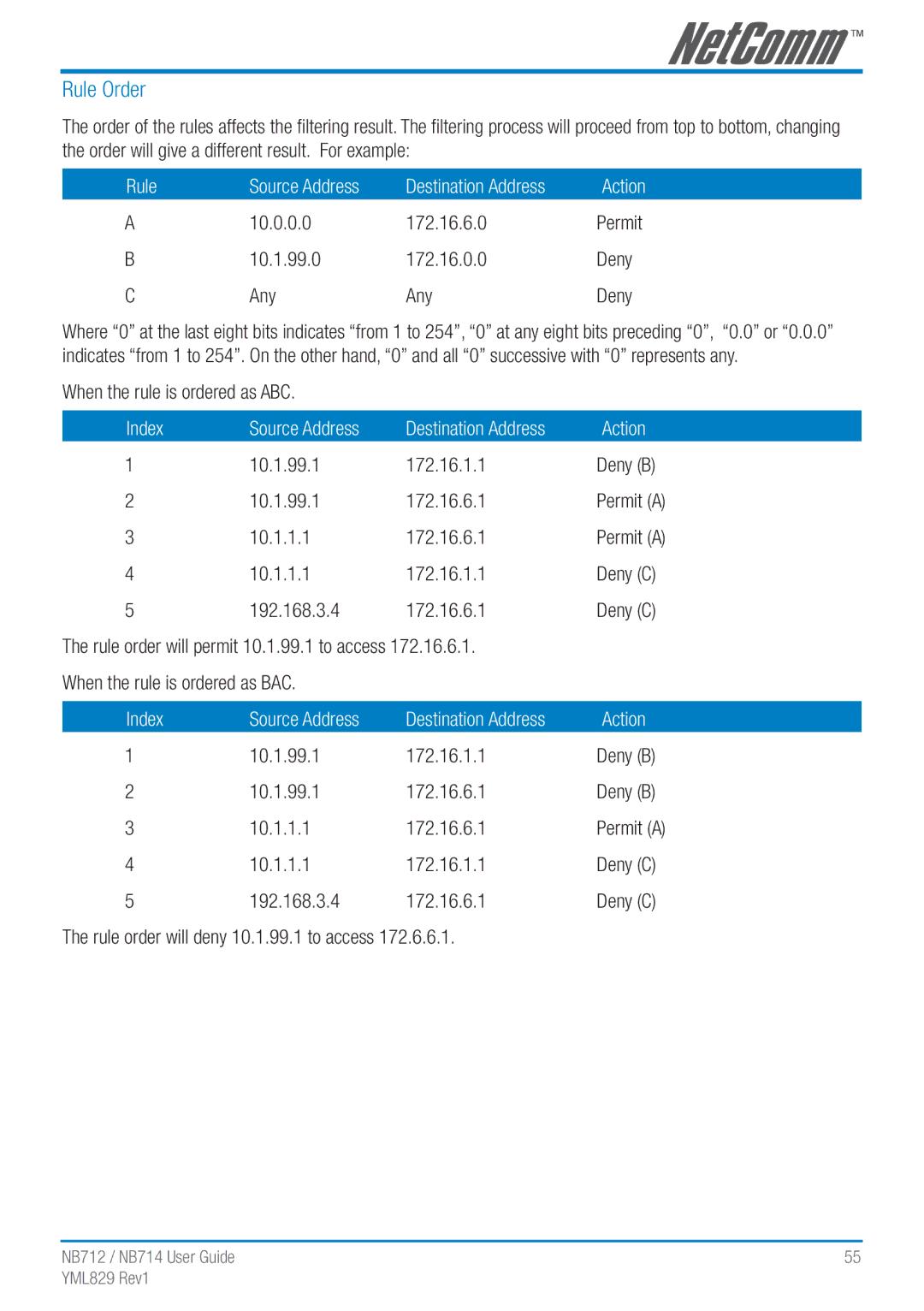
Rule Order
When the rule is ordered as ABC
10.0.0.0 172.16.6.0 Permit 10.1.99.0 172.16.0.0 Deny Any
IP QoS
NB714 User Guide
Administration
Security
NB712 / NB714 User Guide
MIB
Snmp
Community
Snmp status
Version Community
Click on Time Sync
Time Sync
Time Server
Sntp service
Time Zone
Utility
System Info
Lose all the configured parameters
Restore Configuration
Backup Configuration
10.2 Config Tool
Upgrade
To logout the router, press logout
Logout
Restart
You can monitor the following
Status
CO side
LAN-to-LAN connection with bridge Mode
LAN Parameters
Enter VPI Enter VCI Encap
WAN1 Parameters
Enter IP 192.168.1.1 Enter Subnet Mask
Enter Gateway 192.168.1.1 Enter Host Name
Host Name Enter Soho
CPE Side
VCI32 EncapLLC
IP Address 192.168.20.1 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 Host Name
LAN to LAN Connection with Routing Mode
Dhcp Service
Click Route and CO Side then press Next
WAN Parameters
Click Next to setup the IP parameters
IP Address 192.168.10.1 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 Host Name
Click Route and CPE Side then press Next
192.168.30.2
Baudrate 9600 Data Bits Parity Check Stop Bits Flow-control
Useradmin Password
Serial Console
Telnet
Operation Interface
Window structure
To choose another parameters
Menu Driven Interface Commands
Ctrl + C To quit the configuring item Ctrl + Q For help
Menu Tree
14.7 Configuration
Exit Quit system
Ping Packet internet groper command Admin
Done via utility command
Utility
Status
Script
Show
System
Config
Ping
Reboot
Administration
Write
User Profile
Edit Community Entry List Show
Snmp
Supervisor Password and ID
Move the cursor to timeserver1 and press enter
Move the cursor to service and press enter
Sntp
Move the cursor to sntp and press enter
Move the cursor to list and review the setting
Mode
Setup
Utility
Exit
Shdsl
14.16.3 WAN
After enter add menu, the screen will prompt as follow
Bridge
Move the cursor to vlan and press enter
Vlan
Follow the following steps to configure 802.11q Vlan
14.16.6 802.11Q Vlan
For each VLAN, Vlan ID is a unique number among 1~4095
Screen will display the following
Generic command can setup RIP mode and auto summery mode
You can review the list of RIP parameters via list command
Route
IP share
14.16.8 LAN
You can configure NAT parameters in nat menu
14.16.10 NAT
Mapping
After key in enter, the screen will prompt as below
14.16.11 PAT
Firewall
You can enable the demilitarized zone via active command
firewall security level can configure via level command
14.16.12 DMZ
Active
DoS Protection
IPQoS
Dhcp
You can view the Dhcp configuration via list command
DNS proxy
Default
Host name
100Mbps
Appendix a Cable Information
RJ-45 Network Ports
10Mbps
Straight-Through Cabling
Straight and crossover cable configuration
Cross-Over Cabling
TxD
Shdsl Line Connector Console Cable
No connection
RxD O
Contact Information
Appendix B Registration and Warranty Information
Product Warranty