i n t e l l i g e n t | w i r e l e s s | p l a t f o r m | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
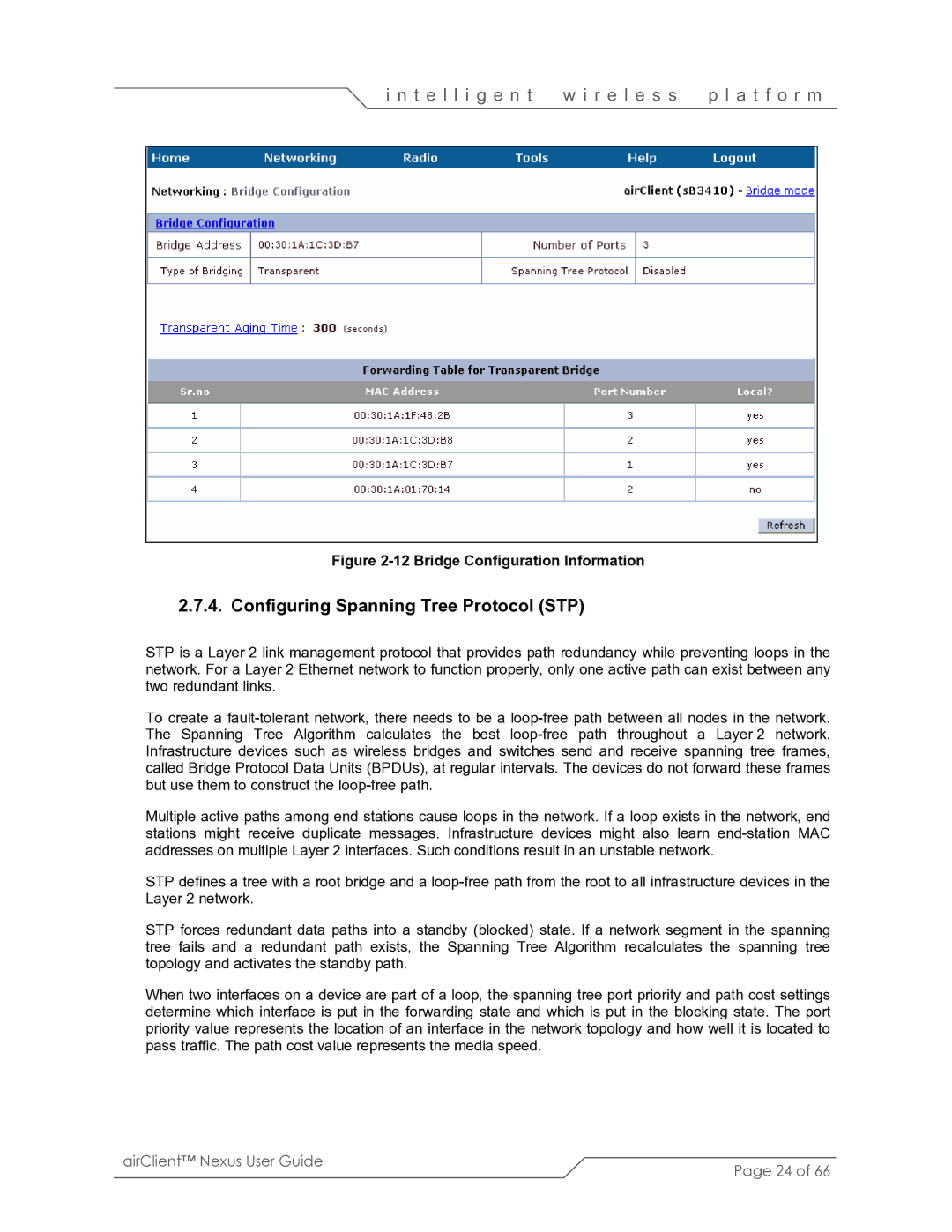
Figure 2-12 Bridge Configuration Information
2.7.4. Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
STP is a Layer 2 link management protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing loops in the network. For a Layer 2 Ethernet network to function properly, only one active path can exist between any two redundant links.
To create a
Multiple active paths among end stations cause loops in the network. If a loop exists in the network, end stations might receive duplicate messages. Infrastructure devices might also learn
STP defines a tree with a root bridge and a
STP forces redundant data paths into a standby (blocked) state. If a network segment in the spanning tree fails and a redundant path exists, the Spanning Tree Algorithm recalculates the spanning tree topology and activates the standby path.
When two interfaces on a device are part of a loop, the spanning tree port priority and path cost settings determine which interface is put in the forwarding state and which is put in the blocking state. The port priority value represents the location of an interface in the network topology and how well it is located to pass traffic. The path cost value represents the media speed.
airClient™ Nexus User Guide | Page 24 of 66 |
|