Key Features
Applications
Product Description
Table of contents
RF Data Buffering
Ordering Information General Information
Abbreviations
ITU-T
References
Features
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Operating Conditions
Parameter Min Max Units Condition
Parameter Min Typ Max Units Condition
Electrical Specifications
Overall
Transmit Section
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Condition / Note
Receive Section
Rssi / Carrier Sense
If Section
Frequency Synthesizer Section
Digital Inputs/Outputs
VDD
Battery Monitor
Power Supply
Voltage Regulator
CC2420
Pin Assignment
Pin Pin Name Pin type Pin Description
Avddadc
CC2420 simplified block diagram
Circuit Description
CC2420
Power supply decoupling and filtering
Application Circuit
Input / output matching
Bias resistor
Overview of external components
Description
Transceiver
Transceiver
Bill of materials for the application circuits
Symbol Chip sequence C0, C1, C2, … , C31
Ieee 802.15.4 Modulation Format
Configuration Overview
Phase
Evaluation Software
SmartRF Studio user interface
13 4-wire Serial Configuration and Data Interface
Pin configuration
Register access
SPI timing specification Status byte
Parameter Symbol Min Max Units Conditions
RAM access
Configuration registers write and read operations via SPI
CC2420 RAM Memory Space Fifo access
Multiple SPI access
Address Byte Ordering Name Description
Configuration interface
Microcontroller Interface and Pin Description
Receive mode
Rxfifo overflow
Pin activity examples during receive
Demodulator, Symbol Synchroniser and Data Decision
Demodulator Simplified Block Diagram
Frame Format
Transmitted Synchronisation Header Length field
MAC protocol data unit
Format of the Frame Control Field FCF Frame check sequence
Buffered transmit mode
Buffered receive mode
RF Data Buffering
Unbuffered, serial mode
Fifop
Address Recognition
Acknowledge Frames
Acknowledge frame format
Radio control state machine
Radio control states
MAC Security Operations Encryption and Authentication
Keys
Nonce / counter
Ieee 802.15.4 Nonce
CC2420 Security Flag Byte Stand-alone encryption
In-line security operations
CTR mode encryption / decryption
CBC-MAC
21.7 CCM
Linear if and AGC Settings
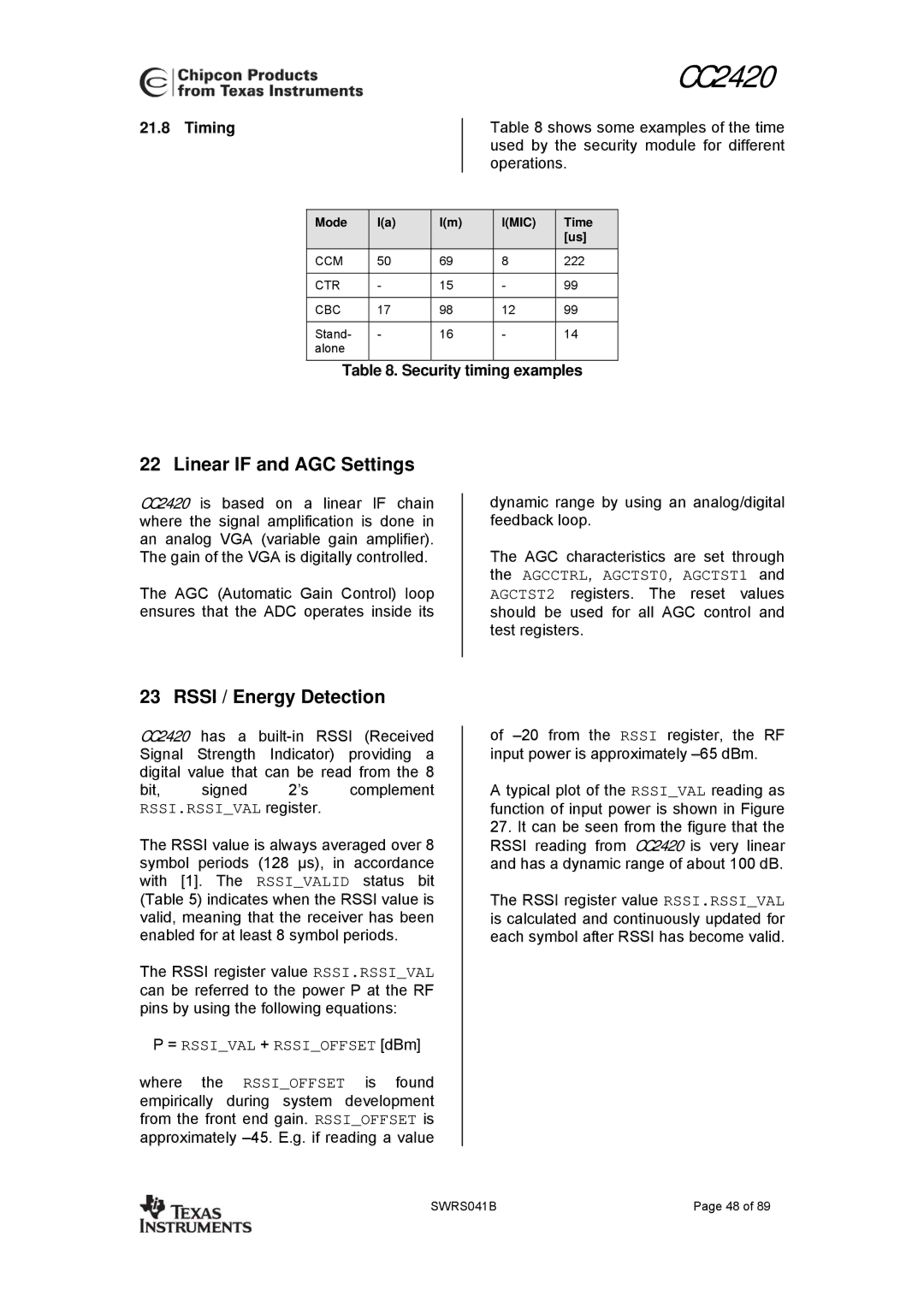
Mode LMIC Time
Rssi / Energy Detection
Timing
Link Quality Indication
Value
RF Level dBm
Clear Channel Assessment
Frequency and Channel Programming
Output Power Programming
VCO and PLL Self-Calibration
Voltage Regulator
27.1 VCO
Battery Monitor
Voltage regulator, simplified schematic
Crystal Oscillator
Input / Output Matching
Transmitter Test Modes
Crystal oscillator component values
Unmodulated carrier
CC2420
Modulated spectrum plot
System Considerations and Guidelines
Battery operated systems
Low-cost systems
BER / PER measurements
PCB Layout Recommendations
Antenna Considerations
CC2420
Configuration Registers
Address Register Register type Description
Configuration registers overview
Saes
Bit Field Name Reset
Main 0x10 Main Control Register
XOSC16MBYPASS
MDMCTRL0 0x11 Modem Control Register
Reservedframemode Pancoordinator Adrdecode
CCAHYST20 CCAMODE10 Autocrc Autoack Preamblelength
MDMCTRL1 0x12- Modem Control Register
Rssi 0x13 Rssi and CCA Status and Control Register
CORRTHR40 Demodavgmode Modulationmode
RSSIVAL70
Syncword 0x14 Sync Word
Txctrl 0x15 Transmit Control Register
RXCTRL0 0x16 Receive control register
RXMIXBUFCUR10
RXCTRL1 0x17 Receive control register
Fsctrl 0x18 Frequency Synthesizer Control and Status
Caldone Calrunning Locklength Lockstatus
SECCTRL0 0x19 Security Control Register
SECMODE10
Battmon 0x1B Battery Monitor Control register
SECCTRL1 0x1A Security Control Register
Sectxl Secrxl
Battmonok Battmonen Battmonvoltage
IOCFG0 0x1C I/O Configuration Register
IOCFG1 0x1D I/O Configuration Register
Manfidl 0x1E Manufacturer ID, Lower 16 Bit
HSSDSRC20 SFDMUX40 CCAMUX40
Manfidh 0x1F Manufacturer ID, Upper 16 Bit
Fsmtc 0x20 Finite state machine time constants
Manand 0x21 Manual signal and override register1
Isused = is * Isandmask + Isormask
Manor 0x22 Manual signal or override register
Agcctrl 0x23 AGC Control
Vgagainoe
Lnamixgainmodeo
AGCTST0 0x24 AGC Test Register
AGCTST1 0x25 AGC Test Register
AGCTST2 0x26 AGC Test Register
FSTST0 0x27 Frequency Synthesizer Test Register
FSTST1 0x28 Frequency Synthesizer Test Register
FSTST2 0x29 Frequency Synthesizer Test Register
FSTST3 0x2A Frequency Synthesizer Test Register
Rxbpftst 0x2B Receiver Bandpass Filters Test Register
Fsmstate 0x2C Finite state machine information
Adcclockdisable
Adctst 0x2D ADC Test Register
Dactst 0x2E DAC Test Register
Oscillator must be running for accessing the Rxfifo
Toptst 0x2F Top Level Test Register
Txfifo 0x3E Transmit Fifo Byte register
Rxfifo 0x3F Receive Fifo Byte register
Test Output Signals
CCA test signal select table
Signal output on CCA pin Description
SFD test signal select table
Signal output on SFD pin Description
Package Description QLP
Quad Leadless Package QLP
Recommended layout for package QLP
Package thermal properties
Soldering information
Thermal resistance
40.3 Plastic tube specification
40.4 Carrier tape and reel specification
Tube Specification
Tape and Reel Specification
General Information
42.1 Document History
Revision Date Description/Changes
Data Sheet Identification Product Status Definition
Product Status Definitions
Address Information
TI Worldwide Technical Support Internet
Product Information Centers
2007, Texas Instruments. All rights reserved
Important Notice