P-2000W_V2 User’s Guide
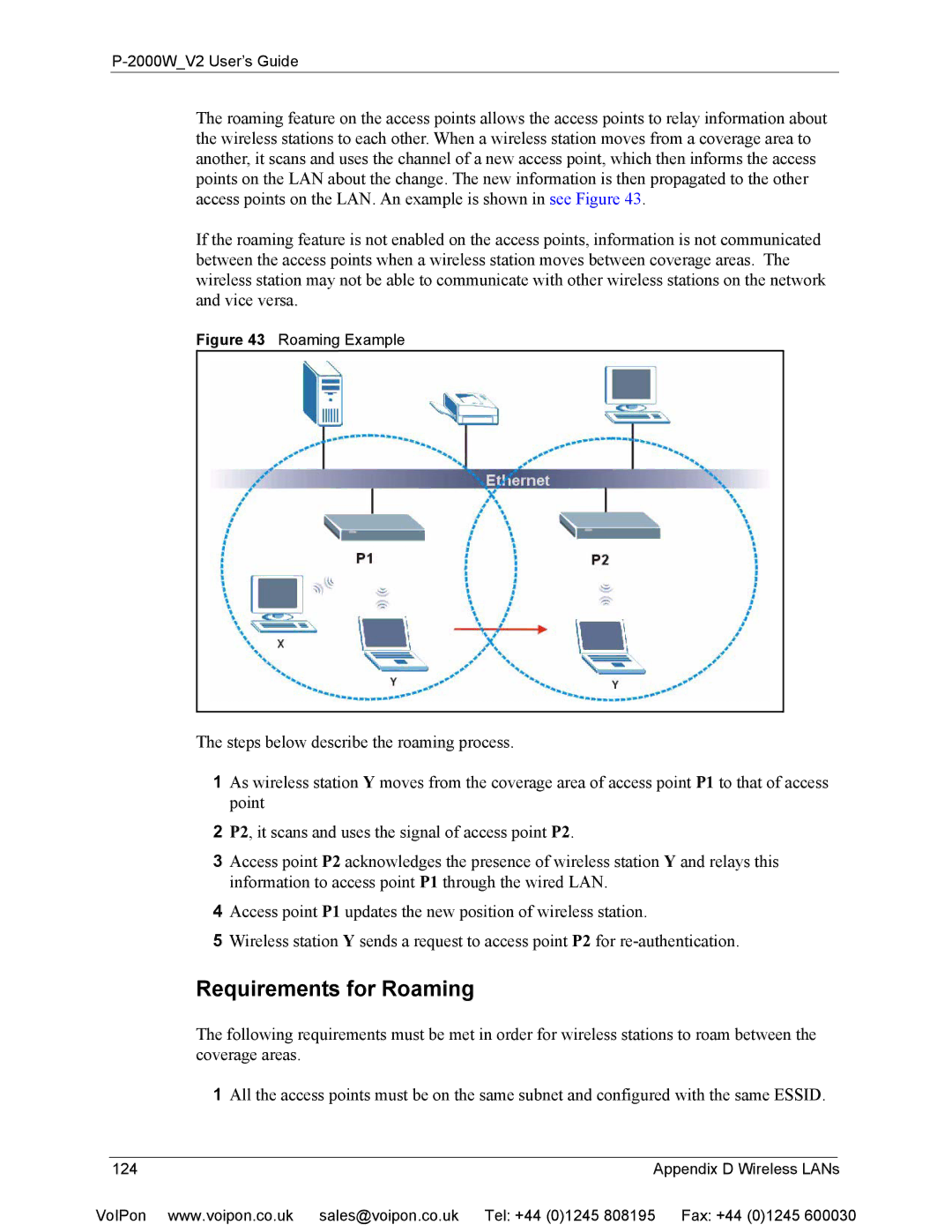
The roaming feature on the access points allows the access points to relay information about the wireless stations to each other. When a wireless station moves from a coverage area to another, it scans and uses the channel of a new access point, which then informs the access points on the LAN about the change. The new information is then propagated to the other access points on the LAN. An example is shown in see Figure 43.
If the roaming feature is not enabled on the access points, information is not communicated between the access points when a wireless station moves between coverage areas. The wireless station may not be able to communicate with other wireless stations on the network and vice versa.
Figure 43 Roaming Example
The steps below describe the roaming process.
1As wireless station Y moves from the coverage area of access point P1 to that of access point
2P2, it scans and uses the signal of access point P2.
3Access point P2 acknowledges the presence of wireless station Y and relays this information to access point P1 through the wired LAN.
4Access point P1 updates the new position of wireless station.
5Wireless station Y sends a request to access point P2 for
Requirements for Roaming
The following requirements must be met in order for wireless stations to roam between the coverage areas.
1All the access points must be on the same subnet and configured with the same ESSID.
124 | Appendix D Wireless LANs |
VoIPon www.voipon.co.uk | sales@voipon.co.uk Tel: +44 (0)1245 808195 Fax: +44 (0)1245 600030 |