Chapter 2 Provisioning
Solution Architecture
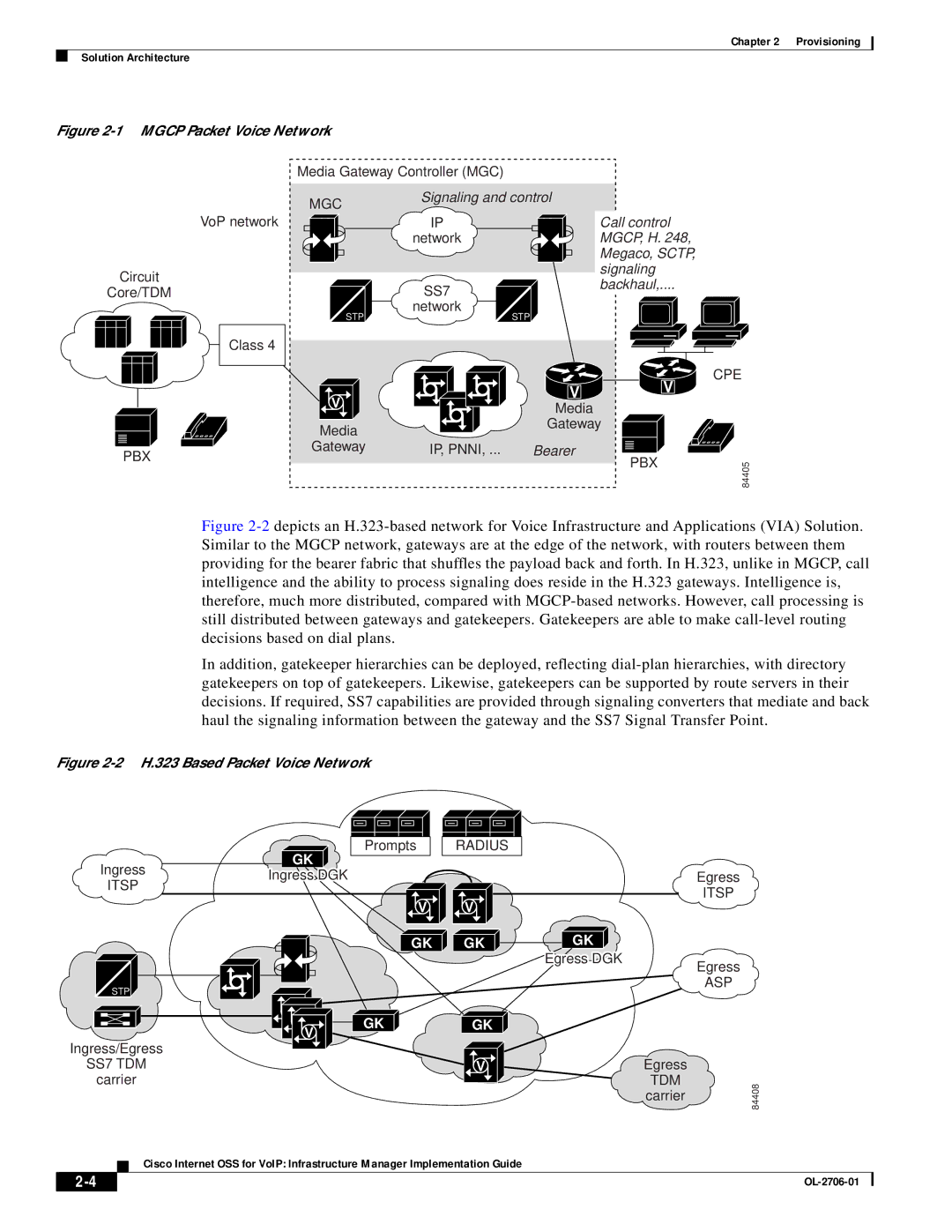
Figure 2-1 MGCP Packet Voice Network
VoP network
Circuit
Core/TDM
Class 4
PBX
Media Gateway Controller (MGC) |
|
|
| |
MGC | Signaling and control |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
| IP |
| Call control |
|
| network |
| MGCP, H. 248, |
|
|
|
| Megaco, SCTP, |
|
|
|
| signaling |
|
| SS7 |
| backhaul,.... |
|
|
|
|
| |
STP | network | STP |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
| V | CPE |
V |
| V |
| |
|
|
| ||
| Media |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Media |
| Gateway |
| |
|
|
|
| |
Gateway | IP, PNNI, ... | Bearer | PBX |
|
|
|
| 84405 | |
|
|
|
| |
Figure 2-2 depicts an H.323-based network for Voice Infrastructure and Applications (VIA) Solution. Similar to the MGCP network, gateways are at the edge of the network, with routers between them providing for the bearer fabric that shuffles the payload back and forth. In H.323, unlike in MGCP, call intelligence and the ability to process signaling does reside in the H.323 gateways. Intelligence is, therefore, much more distributed, compared with MGCP-based networks. However, call processing is still distributed between gateways and gatekeepers. Gatekeepers are able to make call-level routing decisions based on dial plans.
In addition, gatekeeper hierarchies can be deployed, reflecting dial-plan hierarchies, with directory gatekeepers on top of gatekeepers. Likewise, gatekeepers can be supported by route servers in their decisions. If required, SS7 capabilities are provided through signaling converters that mediate and back haul the signaling information between the gateway and the SS7 Signal Transfer Point.
Figure 2-2 H.323 Based Packet Voice Network
Ingress
ITSP
Prompts | RADIUS |
GK |
|
Ingress DGK | Egress |
| ITSP |
V | V |
STP
Ingress/Egress
SS7 TDM
carrier
V |
V |
V |
GK 
 GK
GK
GK | GK |
V |
GK
Egress DGK
Egress
ASP
Egress
TDM
carrier
84408
Cisco Internet OSS for VoIP: Infrastructure Manager Implementation Guide
| ||
|