User Guide
3CR990 Family of EtherLink NICs
EtherLink 10/100 PCI Network Interface Card with 3XP processor
Published August
Clara, California
3Com Corporation
5400 Bayfront Plaza Santa
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND
2 3CR990 NICS
CONTENTS
3 NIC INSTALLATION
1 BEFORE YOU BEGIN
6 IP SECURITY
4 WINDOWS DRIVERS
5 NETWARE DRIVERS
Multiple NICs
7 UPGRADING DRIVERS
8 CONFIGURATION
9 TROUBLESHOOTING
Accessing the 3Com KnowledgeBase
D UNINSTALLING NIC SOFTWARE
E MBA BOOT ROM
A SPECIFICATIONS
B TECHNICAL SUPPORT
DynamicAccess Features
F DYNAMICACCESS TECHNOLOGY
INDEX WARRANTY AND REGULATORY COMPLIANCE INFORMATION
Configuring DynamicAccess Technology
Page
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
2 Click Register Product, and then Register Online
Go to Auto Insert Go to Root Subdirectories
1 Right-click the My Computer icon, and then select Properties
Go to NIC Installation
click NIC Software, Drivers and Diagnostics, NIC Preinstallation
NIC Installation with Windows 2000, and then Done
Minimum System
to install these drivers
DOS-Bootable
Diskette Installation
about installation diskettes
Installations \ Diskette.pdf To make installation diskettes
3CR990 NICS
NIC Overview
3CR990 NICs support up to
NIC Features
Encryption chip Remote Wake-Up RWU connector 3XP processor
168-bit 3DES encryption
Remote Wake-Up cable installed
NOTE The 3CR990 NICs provide a network connection with or without the
Upgrading software Scanning for viruses
Offline Diagnostics
Offload Features
DynamicAccess Technology, and Install 3Com DMI Agent now
Windows
NOTE The default hex value is F all offloads enabled
2 Click the Local Area Connection icon
3 Click Configure
20 CHAPTER 2 3CR990 NICS
your system
NIC INSTALLATION
Installing the NIC
For more information
22 CHAPTER 3 NIC INSTALLATION
Installing the NIC
Remote Wake-Up Cable
TX ACT
24 CHAPTER 3 NIC INSTALLATION
DATA
L N K
Go to NetWare Drivers
What do you want to do?
Go to Windows Go to Windows Go to Windows NT Go to Windows NT
Go to Multiple NICs
Page
4 Click NIC Preinstallation
Windows 2000 and installed the NIC, go to step 7 in this procedure
3 Click Drivers and Diagnostics
5 Click NIC Installation with Windows 2000, and then click Done
Go to 3Com DOS Configuration Program
Go to Verifying Successful Installation
NOTE You must restart your computer to complete the installation
To verify that the installation was successful
Go to New Hardware Found Go to Update Device Driver Wizard
Go to Verifying Successful Installation
Driver Wizard
Update Device
Windows NT
Windows NT
PC or server running Windows NT
a Select the Enable Automatic DHCP Configuration check box
4 Click Add Adapter
6 Click Continue
Installation
Verifying Successful
34 CHAPTER 4 WINDOWS DRIVERS
5 Click NIC Installation with Windows 2000, and then Done
Multiple NICs
operating system
Windows 95 and
36 CHAPTER 4 WINDOWS DRIVERS
5 Click Have Disk
Page
NETWARE DRIVERS
NOTE 3CR990 NICs do not support NetWare 3.11 and 4.0x servers
4.11, and
Go to Verifying the PCI Slot Number
For NetWare
a Select Reinitialize System
Verifying the PCI Slot Number
load c\nwserver\3c99x.lan
IP SECURITY
Overview Creating a Security Policy
7 Clear the Activate the default response rule check box
5 Select IP Security Policy Management, and then click Add
1 In the left pane, click IP Security Policies on Local Machine
Filter Action
Creating a Security Policy
2 Select Un-assign
46 CHAPTER 6 IP SECURITY
UPGRADING DRIVERS
8 Click Have Disk
Go to Windows 95 Version A Build
Go to Windows 98 and Windows
7 Click Have Disk
6 Click Close
Windows NT 4.0
6 Click Restart Now
50 CHAPTER 7 UPGRADING DRIVERS
CONFIGURATION
Provides the ability to boot a PC
100BASE-TX 100 Mb/s
3Com DOS
If you do not have a DOS-bootable diskette
Go to Making a DOS-Bootable Diskette
Configuration
3Com NIC
Diagnostics Program
Diagnostics Program
Go to To Run the Network Test
5 Repeat the process for each setting that you want to change
Troubleshooting
TROUBLESHOOTING
Accessing the
the Installation
Go to 10BASE-T Description Go to 100BASE-TX Description
Running Diagnostics
Programs
Go to Technical Support
General Tab
For more information about how to make a DOS-bootable diskette
4 Click 3Com NIC Doctor
Configuration Tab
Flash Update Tab
Diagnostics Tests
Diagnostics Tab
Accessing the 3Com
To run the NIC test, Network test, or Remote Wake-Up test
2 Click Perform NIC Test
Go to Troubleshooting Remote Wake-Up
Accessing 3Com
Support Services
Go to 3Com NIC Diagnostics Program
3Com Tray Icon
Remote Wake-Up
connection between the NIC and the network
Troubleshooting a
Network Connection
NOTE For more information on PCI specifications and Remote Wake-Up
2 Connect a straight-through cable from the PC to the hub
PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision
SPECIFICATIONS
NIC Specifications
Hardware
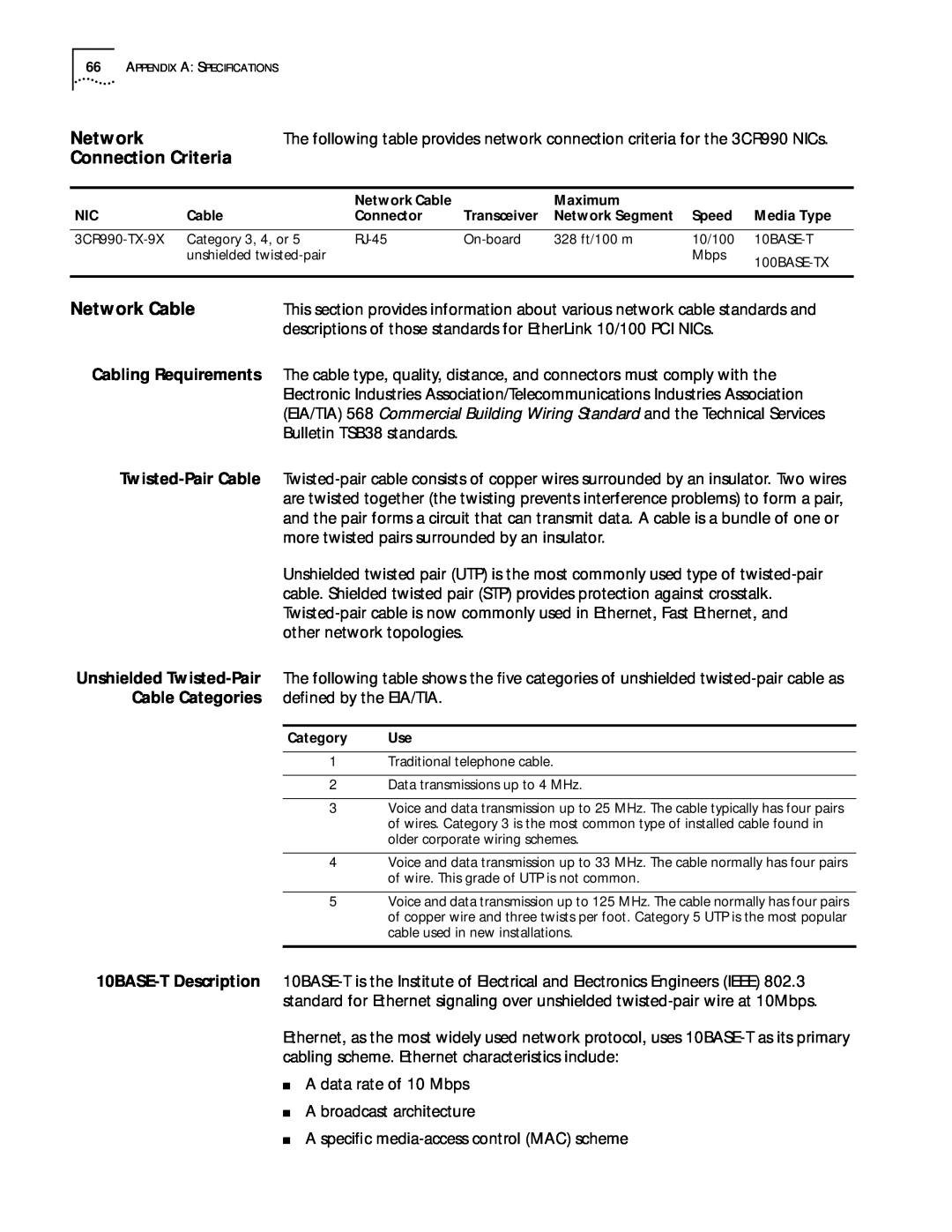
Network
Connection Criteria
Network Cable
Assignments
1 TD+ 2 TD 3 RD+ 6 RD
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Flow Control
Pause Frames
Link Negotiation
Register this Product
Services
TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Online Technical
1 847
1 408 727
day, 7 days a week
Support from 3Com
Country
Telephone Number
To obtain an RMA number, call or fax
Additional Drivers
over-the-network installations
SUPPORTED DRIVERS
NOTE DOS drivers are not supported for 3CR990 NICs. However, they are
Page
UNINSTALLING NIC SOFTWARE
Windows 98 and
or Windows
76 APPENDIX D UNINSTALLING NIC SOFTWARE
Booting with the
MBA BOOT ROM
the Boot ROM Setting
MBA Boot ROM
MBA boot ROM, see the documentation that came with MBA on the EtherCD
Non-BBS
Features
DYNAMICACCESS TECHNOLOGY
DynamicAccess
Failure to install the patch will result in system failure
you install the NIC software
Installing
Technology
To install DynamicAccess technology
NOTE You must restart your PC to complete the installation
Configuring
management tools for an Ethernet network
Removing
1 Double-click the Add/Remove Programs icon in the Control Panel
2 Select the DAPassThru Driver Transport protocol
Page
INDEX
Numbers
uninstalling NIC software 76 unshielded twisted pair UTP
YEAR 2000 WARRANTY
3Com Corporation Limited Warranty
WARRANTY AND REGULATORY COMPLIANCE INFORMATION
OBTAINING WARRANTY SERVICE
DISCLAIMER
Regulatory Compliance Information
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
GOVERNING LAW
EMISSION COMPLIANCE
3COM END USER SOFTWARE IMPORTANT Read Before Using This Product
INDUSTRY CANADA CLASS B
STATEMENT
3Com Corporation 5400 Bayfront Plaza P.O. Box
Santa Clara, CA 95052-8145 408