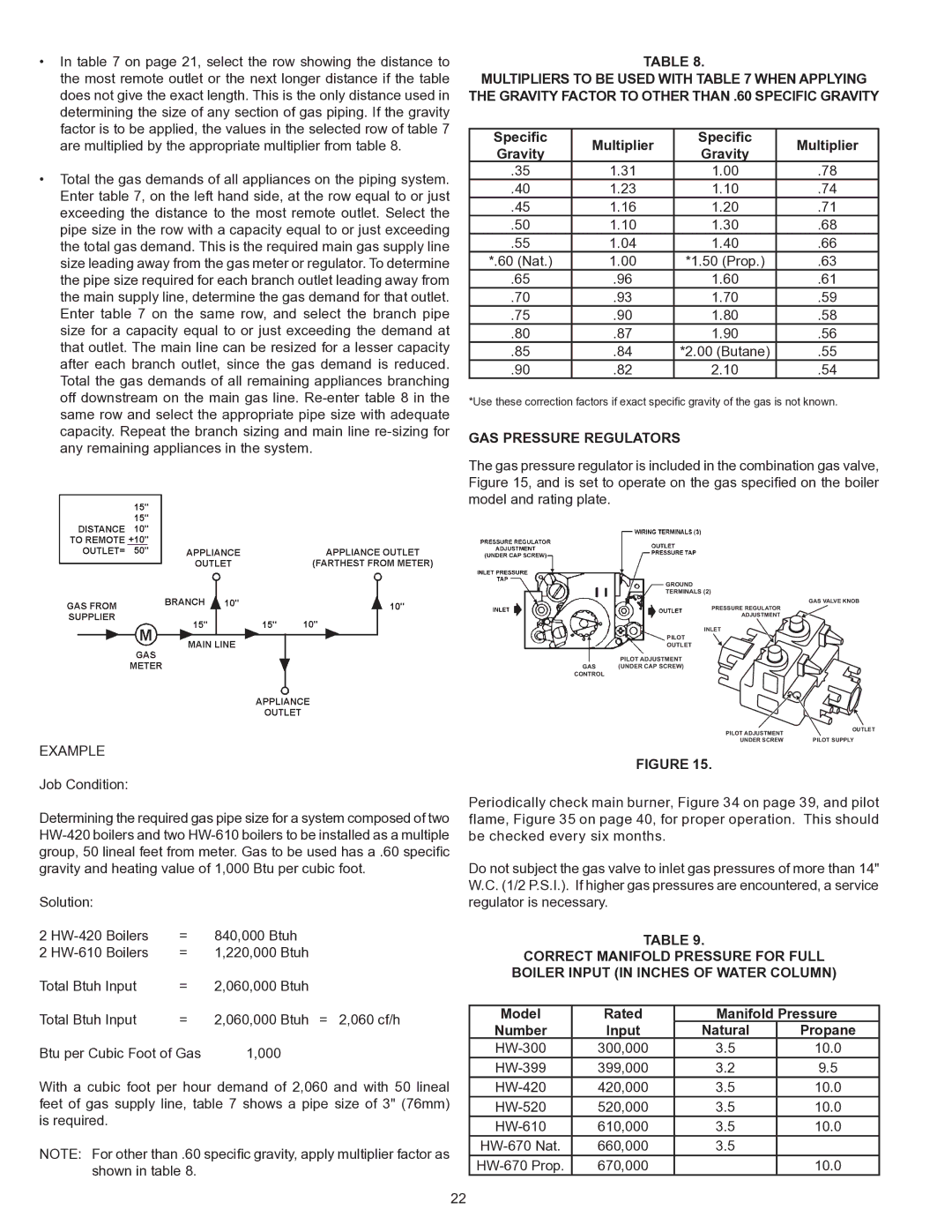
•In table 7 on page 21, select the row showing the distance to the most remote outlet or the next longer distance if the table does not give the exact length. This is the only distance used in determining the size of any section of gas piping. If the gravity factor is to be applied, the values in the selected row of table 7 are multiplied by the appropriate multiplier from table 8.
•Total the gas demands of all appliances on the piping system. Enter table 7, on the left hand side, at the row equal to or just exceeding the distance to the most remote outlet. Select the pipe size in the row with a capacity equal to or just exceeding the total gas demand. This is the required main gas supply line size leading away from the gas meter or regulator. To determine the pipe size required for each branch outlet leading away from the main supply line, determine the gas demand for that outlet. Enter table 7 on the same row, and select the branch pipe size for a capacity equal to or just exceeding the demand at that outlet. The main line can be resized for a lesser capacity after each branch outlet, since the gas demand is reduced. Total the gas demands of all remaining appliances branching off downstream on the main gas line.
EXAMPLE
Job Condition:
Determining the required gas pipe size for a system composed of two
Solution: |
|
|
2 | = | 840,000 Btuh |
2 | = | 1,220,000 Btuh |
Total Btuh Input | = | 2,060,000 Btuh |
Total Btuh Input | = | 2,060,000 Btuh = 2,060 cf/h |
Btu per Cubic Foot of Gas | 1,000 | |
With a cubic foot per hour demand of 2,060 and with 50 lineal feet of gas supply line, table 7 shows a pipe size of 3" (76mm) is required.
NOTE: For other than .60 specific gravity, apply multiplier factor as shown in table 8.
TABLE 8.
MULTIPLIERS TO BE USED WITH TABLE 7 WHEN APPLYING THE GRAVITY FACTOR TO OTHER THAN .60 SPECIFIC GRAVITY
Specific | Multiplier | Specific | Multiplier | |
Gravity | Gravity | |||
|
| |||
.35 | 1.31 | 1.00 | .78 | |
.40 | 1.23 | 1.10 | .74 | |
.45 | 1.16 | 1.20 | .71 | |
.50 | 1.10 | 1.30 | .68 | |
.55 | 1.04 | 1.40 | .66 | |
*.60 (Nat.) | 1.00 | *1.50 (Prop.) | .63 | |
.65 | .96 | 1.60 | .61 | |
.70 | .93 | 1.70 | .59 | |
.75 | .90 | 1.80 | .58 | |
.80 | .87 | 1.90 | .56 | |
.85 | .84 | *2.00 (Butane) | .55 | |
.90 | .82 | 2.10 | .54 |
*Use these correction factors if exact specific gravity of the gas is not known.
GAS PRESSURE REGULATORS
The gas pressure regulator is included in the combination gas valve, Figure 15, and is set to operate on the gas specified on the boiler model and rating plate.
GROUND
TERMINALS (2)
GAS VALVE KNOB
PRESSURE REGULATOR
ADJUSTMENT
INLET
PILOT
OUTLET
PILOT ADJUSTMENT
GAS (UNDER CAP SCREW)
CONTROL
PILOT ADJUSTMENT | OUTLET |
| |
UNDER SCREW | PILOT SUPPLY |
FIGURE 15.
Periodically check main burner, Figure 34 on page 39, and pilot flame, Figure 35 on page 40, for proper operation. This should be checked every six months.
Do not subject the gas valve to inlet gas pressures of more than 14" W.C. (1/2 P.S.I.). If higher gas pressures are encountered, a service regulator is necessary.
TABLE 9.
CORRECT MANIFOLD PRESSURE FOR FULL BOILER INPUT (IN INCHES OF WATER COLUMN)
Model | Rated | Manifold Pressure | |
Number | Input | Natural | Propane |
300,000 | 3.5 | 10.0 | |
399,000 | 3.2 | 9.5 | |
420,000 | 3.5 | 10.0 | |
520,000 | 3.5 | 10.0 | |
610,000 | 3.5 | 10.0 | |
660,000 | 3.5 |
| |
670,000 |
| 10.0 | |
22