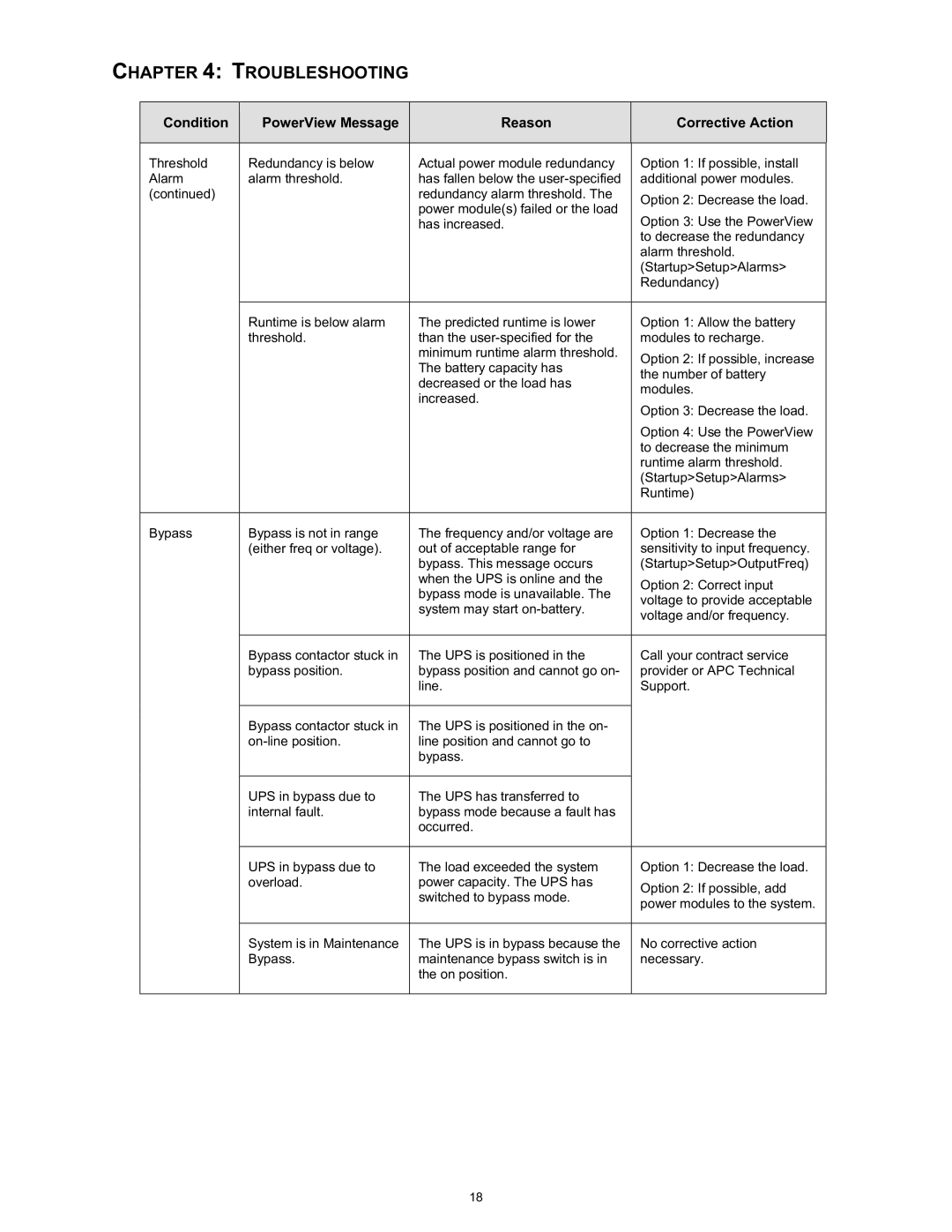
CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING
Condition | PowerView Message |
| Reason |
| Corrective Action |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Threshold | Redundancy is below |
| Actual power module redundancy |
| Option 1: If possible, install |
Alarm | alarm threshold. |
| has fallen below the |
| additional power modules. |
(continued) |
|
| redundancy alarm threshold. The |
| Option 2: Decrease the load. |
|
|
| power module(s) failed or the load |
| |
|
|
|
| Option 3: Use the PowerView | |
|
|
| has increased. |
| |
|
|
|
|
| to decrease the redundancy |
|
|
|
|
| alarm threshold. |
|
|
|
|
| (Startup>Setup>Alarms> |
|
|
|
|
| Redundancy) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Runtime is below alarm |
| The predicted runtime is lower |
| Option 1: Allow the battery |
| threshold. |
| than the |
| modules to recharge. |
|
|
| minimum runtime alarm threshold. |
| Option 2: If possible, increase |
|
|
| The battery capacity has |
| |
|
|
|
| the number of battery | |
|
|
| decreased or the load has |
| |
|
|
|
| modules. | |
|
|
| increased. |
| |
|
|
|
| Option 3: Decrease the load. | |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| Option 4: Use the PowerView |
|
|
|
|
| to decrease the minimum |
|
|
|
|
| runtime alarm threshold. |
|
|
|
|
| (Startup>Setup>Alarms> |
|
|
|
|
| Runtime) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bypass | Bypass is not in range |
| The frequency and/or voltage are |
| Option 1: Decrease the |
| (either freq or voltage). |
| out of acceptable range for |
| sensitivity to input frequency. |
|
|
| bypass. This message occurs |
| (Startup>Setup>OutputFreq) |
|
|
| when the UPS is online and the |
| Option 2: Correct input |
|
|
| bypass mode is unavailable. The |
| |
|
|
|
| voltage to provide acceptable | |
|
|
| system may start |
| |
|
|
|
| voltage and/or frequency. | |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Bypass contactor stuck in |
| The UPS is positioned in the |
| Call your contract service |
| bypass position. |
| bypass position and cannot go on- |
| provider or APC Technical |
|
|
| line. |
| Support. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Bypass contactor stuck in |
| The UPS is positioned in the on- |
|
|
|
| line position and cannot go to |
|
| |
|
|
| bypass. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| UPS in bypass due to |
| The UPS has transferred to |
|
|
| internal fault. |
| bypass mode because a fault has |
|
|
|
|
| occurred. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| UPS in bypass due to |
| The load exceeded the system |
| Option 1: Decrease the load. |
| overload. |
| power capacity. The UPS has |
| Option 2: If possible, add |
|
|
| switched to bypass mode. |
| |
|
|
|
| power modules to the system. | |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| System is in Maintenance |
| The UPS is in bypass because the |
| No corrective action |
| Bypass. |
| maintenance bypass switch is in |
| necessary. |
|
|
| the on position. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18