The remote radiator may be mounted either vertically or horizontally. In general, the radiator will have an electric fan to provide cooling air and may be able to utilize the engine mounted coolant pump to provide coolant flow.
The piping system friction and head loss between engine and radiator must be calculated and not exceed the capacity of the engine pump. If the maximum coolant friction head loss external to the engine is exceeded, a hot well system must be used. Before designing the piping system using an auxiliary pump and hot well, the consultant should look very closely at increasing the system’s pipe size.
The electric fan and auxiliary pump, if used, must be connected to the emergency power system. Radiator and cooling fan must be sized to provide the cooling capacity required at an acceptable sound level.
Caution: In cold climates, the high volume of outside air drawn into the genset room can quickly reduce temperatures in the room to freezing. Any water piping or other equipment susceptible to freeze damage should be properly insulated or located elsewhere.
Heat Exchanger
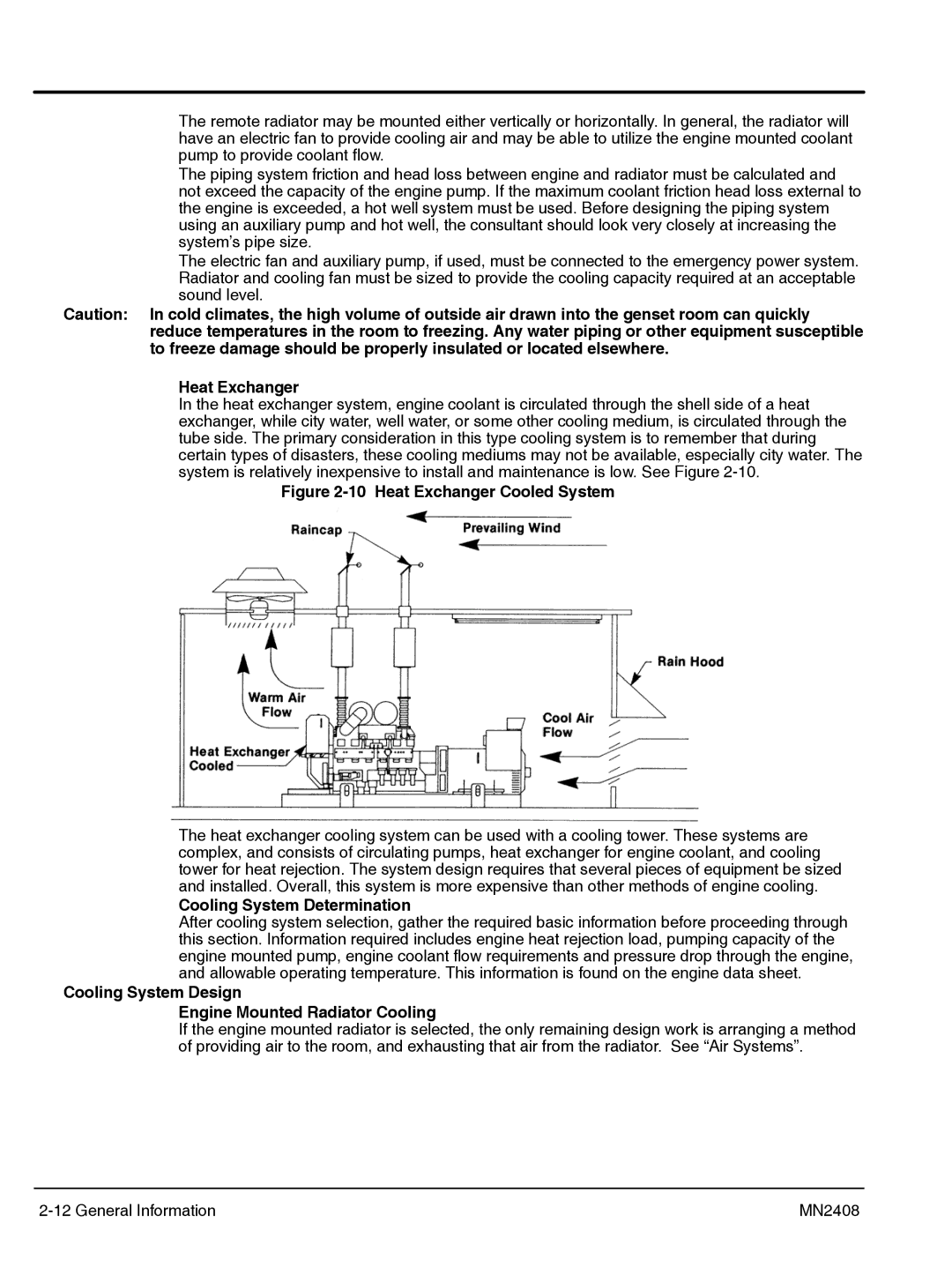
In the heat exchanger system, engine coolant is circulated through the shell side of a heat exchanger, while city water, well water, or some other cooling medium, is circulated through the tube side. The primary consideration in this type cooling system is to remember that during certain types of disasters, these cooling mediums may not be available, especially city water. The system is relatively inexpensive to install and maintenance is low. See Figure
Figure 2-10 Heat Exchanger Cooled System
The heat exchanger cooling system can be used with a cooling tower. These systems are complex, and consists of circulating pumps, heat exchanger for engine coolant, and cooling tower for heat rejection. The system design requires that several pieces of equipment be sized and installed. Overall, this system is more expensive than other methods of engine cooling.
Cooling System Determination
After cooling system selection, gather the required basic information before proceeding through this section. Information required includes engine heat rejection load, pumping capacity of the engine mounted pump, engine coolant flow requirements and pressure drop through the engine, and allowable operating temperature. This information is found on the engine data sheet.
Cooling System Design
Engine Mounted Radiator Cooling
If the engine mounted radiator is selected, the only remaining design work is arranging a method of providing air to the room, and exhausting that air from the radiator. See “Air Systems”.
MN2408 |