Internet/Print Server User’s Guide
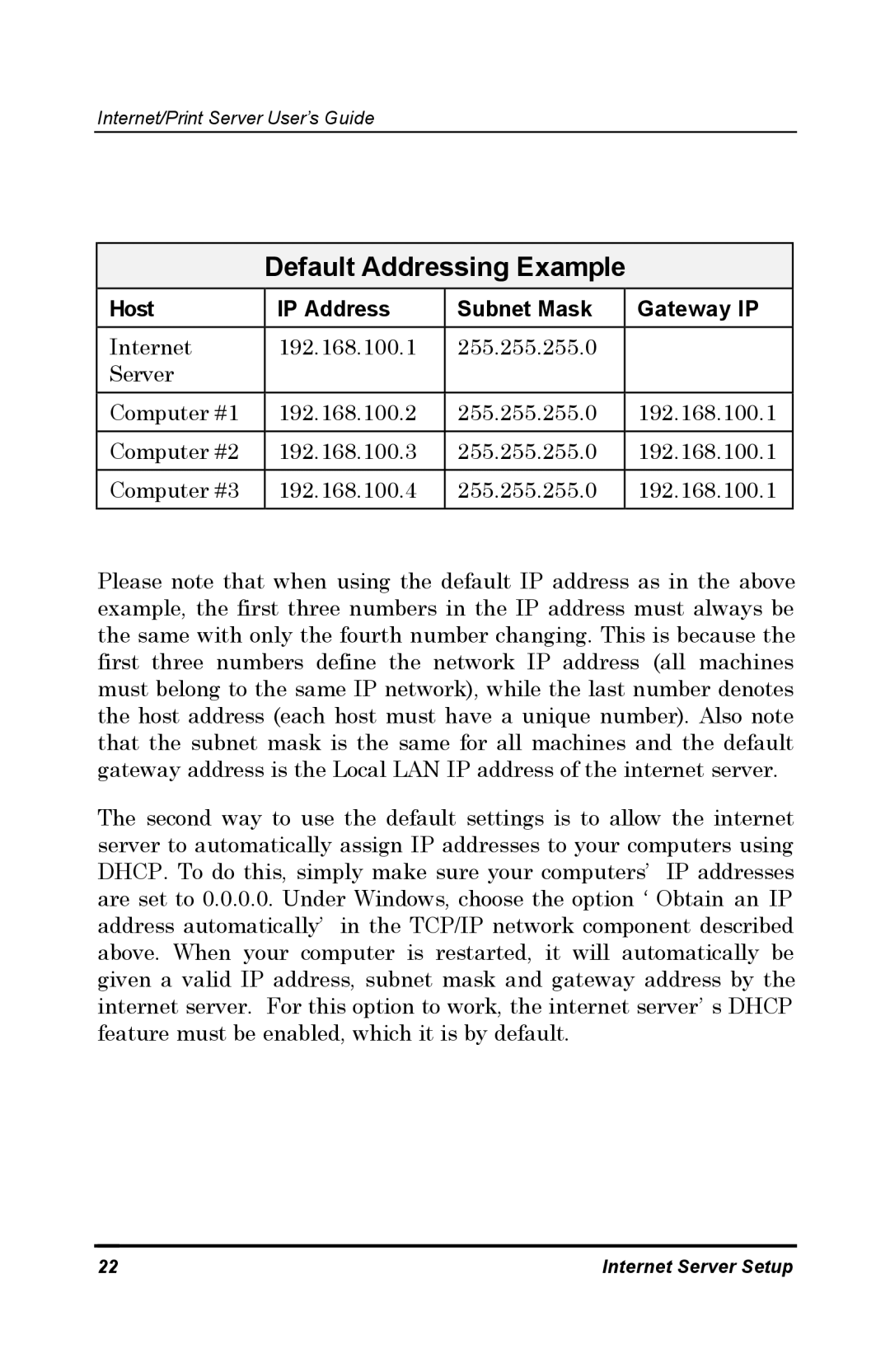
Default Addressing Example
Host | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Gateway IP |
|
|
|
|
Internet | 192.168.100.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
|
Server |
|
|
|
Computer #1 | 192.168.100.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.100.1 |
|
|
|
|
Computer #2 | 192.168.100.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.100.1 |
|
|
|
|
Computer #3 | 192.168.100.4 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.100.1 |
|
|
|
|
Please note that when using the default IP address as in the above example, the first three numbers in the IP address must always be the same with only the fourth number changing. This is because the first three numbers define the network IP address (all machines must belong to the same IP network), while the last number denotes the host address (each host must have a unique number). Also note that the subnet mask is the same for all machines and the default gateway address is the Local LAN IP address of the internet server.
The second way to use the default settings is to allow the internet server to automatically assign IP addresses to your computers using DHCP. To do this, simply make sure your computers’ IP addresses are set to 0.0.0.0. Under Windows, choose the option ‘Obtain an IP address automatically’ in the TCP/IP network component described above. When your computer is restarted, it will automatically be given a valid IP address, subnet mask and gateway address by the internet server. For this option to work, the internet server’s DHCP feature must be enabled, which it is by default.
22 | Internet Server Setup |