36 of 66 | Calibrations - 3654 Portable H2/N2 Analyzer |
|
|
4.2 Sensor Calibration
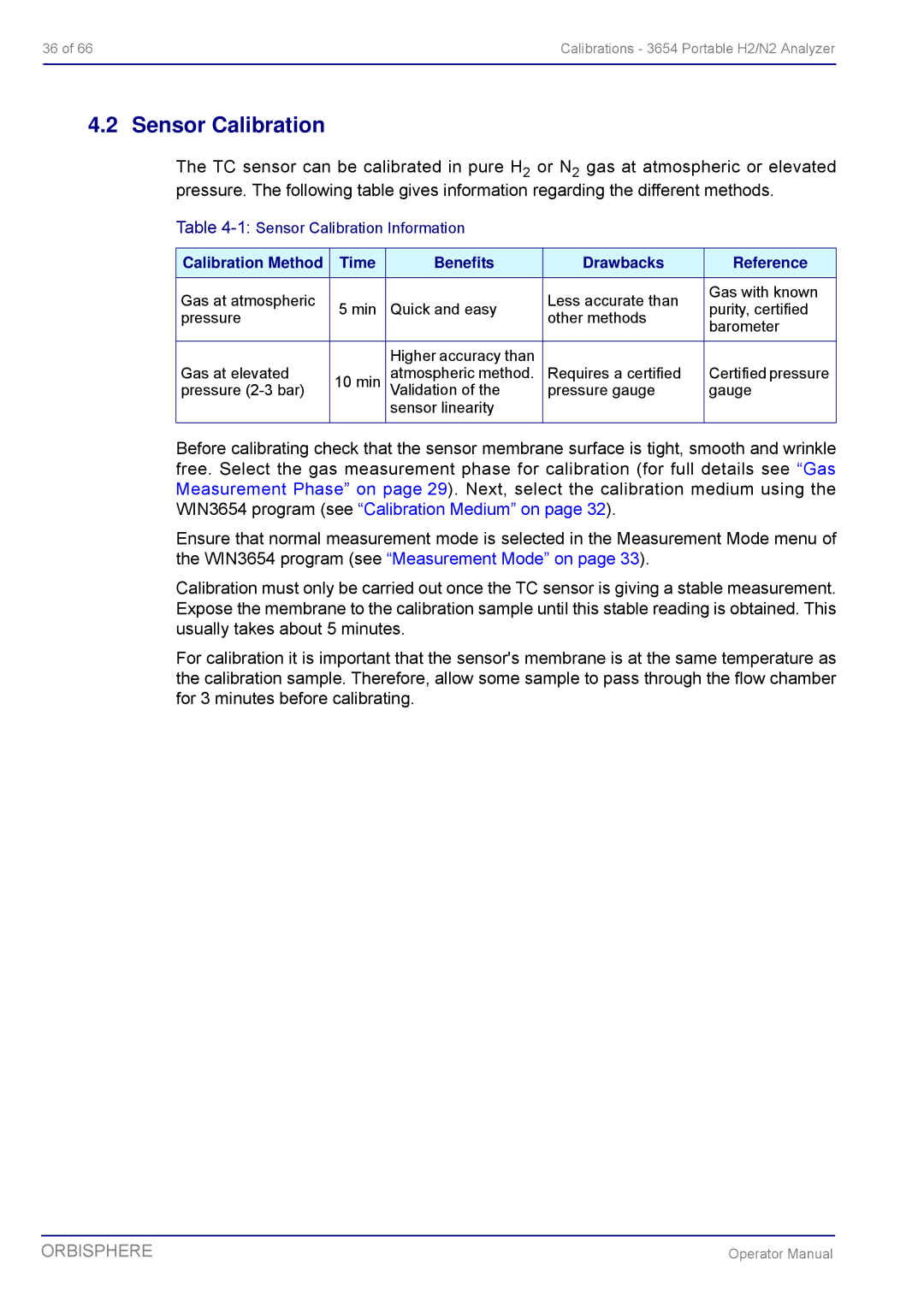
The TC sensor can be calibrated in pure H2 or N2 gas at atmospheric or elevated pressure. The following table gives information regarding the different methods.
Table
Calibration Method | Time | Benefits | Drawbacks | Reference | |
Gas at atmospheric |
|
| Less accurate than | Gas with known | |
5 min | Quick and easy | purity, certified | |||
pressure | other methods | ||||
|
| barometer | |||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| Higher accuracy than |
|
| |
Gas at elevated | 10 min | atmospheric method. | Requires a certified | Certified pressure | |
pressure | Validation of the | pressure gauge | gauge | ||
|
| sensor linearity |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Before calibrating check that the sensor membrane surface is tight, smooth and wrinkle free. Select the gas measurement phase for calibration (for full details see “Gas Measurement Phase” on page 29). Next, select the calibration medium using the WIN3654 program (see “Calibration Medium” on page 32).
Ensure that normal measurement mode is selected in the Measurement Mode menu of the WIN3654 program (see “Measurement Mode” on page 33).
Calibration must only be carried out once the TC sensor is giving a stable measurement. Expose the membrane to the calibration sample until this stable reading is obtained. This usually takes about 5 minutes.
For calibration it is important that the sensor's membrane is at the same temperature as the calibration sample. Therefore, allow some sample to pass through the flow chamber for 3 minutes before calibrating.
ORBISPHERE | Operator Manual |