Pascal 4.0 User’s Guide
Trademarks
Contents
Pascal Compiler
Contents
Pic, -Kpicand -PIC, -KPIC
Contents Vii
Viii
Program Construction and Management
Separate Compilation
C++-Pascal Interface
Error Diagnostics
Xii
XView Toolkit
Math Libraries
Contents Xiii
Xiv
Figures
Pascal 4.0 User’s Guide
Fortran
Tables
Xviii
Preface
Installation
Operating Environment
Organization
Audience
AaBbCc123
Conventions Used in This Guide
Related Documentation
Shell Prompts in Command Examples
Manual
Hostname% imagetool floating-point.ps
Readme Files
Other Related Documentation
Documents in Hard Copy and in AnswerBook
CD-ROM
Standards
Introduction
Pascal Compiler
Features
Compatibility
Native Language Support
Text Editors
Debuggers
XView Toolkit
Internationalization
Locale
Licensing
Pascal 4.0 User’s Guide
Simple Pascal Program
Pascal Programs
Compiling the Program
Hostname% pc -o temp temp.p
Running the Program
Renaming the Executable File
Hostname% mv a.out temp
An Interactive Pascal Program
Goodbye, I must go now
Redirecting I/O
Hostname% pc -o copy copy.p
Hello, are you listening?
Using a File Name as a File Variable
Using Pascal Traceback
Where Did My Program Fail?
Hostname% pc -o copy2 copy2.p
Compiling and Running the Program
Using a Sample Program with Segmentation Violation
Hostname% more a.out.trace
Using the -gOption
Try compiling SegViol.p with -g
Pc Version Number
Pascal Compiler
Hostname% mcs -p a.out grep Pascal
Compile and Link Sequence
Optimizer
Language Preprocessor
Source
Compiler Preprocessor cpp or cppas
Suffix Description
File Name Extensions Accepted By pc
Hostname% pc -o rmc rmc.p
Option-Passing on the Command-Line
Option-Passing in the Program Text
Hostname% pc -l rmc.p
Option Description
Hostname% pc options.p
Options
Bbinding
Bsdmalloc
Cond
Calign
Cg89
Cg92
Dname=def
Config
Dryrun
Dalign
Fast
Fns
Fnonstd
Fround=r
Ftrap=t
Hname
Keeptmp
Help or -flags
Ipathname
Iname
Hostname% pc -l random.p
Ldirectory
Misalign
Libmieee
Libmil
Llib
Nolibmil
Native
Nocx
Nolib
Olevel
Notrace
Hostname% limit datasize 16M
Hostname% pc -o myprog myprog.p
Ofilename
Hostname% /usr/sbin/swap -s
Hostname% /usr/sbin/prtconf grep Memory
Pic,-Kpic and -PIC,-KPIC
Using the -pOption
Using the -pgOption
-pg
Qpathpathname
Qoption
Qproduce
Rpathdir
Pascal 4.0 User’s Guide
Examples
Hostname% pc -Rw recvar.p
Hostname% pc -Rw rr.p
Pascal main program, with.p with statement
Commands to compile and execute with.p
Hostname% pc -Rw with.p
Sbfast
Slevel
Hostname% pc -S rmc.p
Hostname% pc -temp=. hello.p
Temp=dir
Hostname% pc -time hello.p
Time
Xarch=a
Uname
Pascal 4.0 User’s Guide
Value Meaning
Limit the instruction set to V8 architecture
S1/l1/a1 S1/l1/a1s2/l2/a2 S1/l1/a1s2/l2/a2s3/l3/a3
Xcache=c
Example -xcache=16/32/41024/32/1specifies the following
Xchip=c
Xcg92
Xcg89
Xlibmil
Xildoff
Xildon
Xlibmieee
Xnolib
Xlibmopt
Xlicinfo
XMerge
Xprofile=p
Xpg
-xprofileValues
Example -xregs=appl,no%float
Xregs=r
Xsb
Xsafe=mem
Xsbfast
Xtarget=t
Xspace
XtargetExpansions
Pascal 4.0 User’s Guide
Pascal Compiler
Ztext
Units
Program Construction Management
Using Program Units and Module Units
Hostname% pc programunit.p moduleunit.p
Compiling with Units
Program Construction and Management
Using Units and Header Files
Sharing Variables Between Units
Here is a program unit that declares a variable
Program Construction and Management
Libraries
Working with Units
Separate Compilation
Using Module Units
Using Program Units
Sharing Variables and Routines Across Multiple Units
Separate Compilation
Compiling without the -xlOption
Sharing Public Variables
Program unit
Using include Files to Share Variables and Routines
Using extern Option to Share Routines
Hostname% pc incprog.p incmod.p
Commands to compile and execute incprog.p and incmod.p
Program unit, incprog.p, which includes the file
Module unit, incmod.p, which also includes the file
Using public var Declarations
Using the -xlOption
Commands to compile and execute pubvarprog.p and pubvarmod.p
Using the define Variable Attribute
Commands to compile and execute defvarprog.p and defvarmod.p
Using the define Declaration
Module unit
Using include Files
Program unit, incprog2.p Module unit, incmod2.p
Commands to compile and execute incprog2.p and incmod2.p
Using extern
Program unit, extprog.p
Sharing Declarations in Multiple Units
Commands to compile and execute extprog.p and extmod.p
Module unit, extmod.p
Pascal 4.0 User’s Guide
Compilation of Mixed-Language Programs
C-Pascal Interface
Hostname% cc -c myc.c Hostname% pc -calign myc.o mypascal.p
Compatibility of Types for C and Pascal
Character Strings
Precautions with Compatible Types
C-Pascal Interface
Enumerated Types
Incompatibilities
Array Indexes
Aggregate Types
General Parameter Passing in C and Pascal
Procedure Calls C-Pascal
Pascal Set Types
Variable Parameters
Commands to compile and execute Samp.p
Simple Types without -xl
Pascal procedure, SimVar.p
Strings of Characters
Commands to compile and execute SimVar.p and SimVarMain.c
Pascal procedure
Simple Types with -xl
Fixed Arrays
Commands to compile and execute StrVar.p and StrVarMain.c
C main program
Commands to compile and execute FixVec.p and FixVecMain.c
Pascal procedure, FixVec.p
Day =
100
Univ Arrays
C-Pascal Interface 101
Conformant Arrays
102
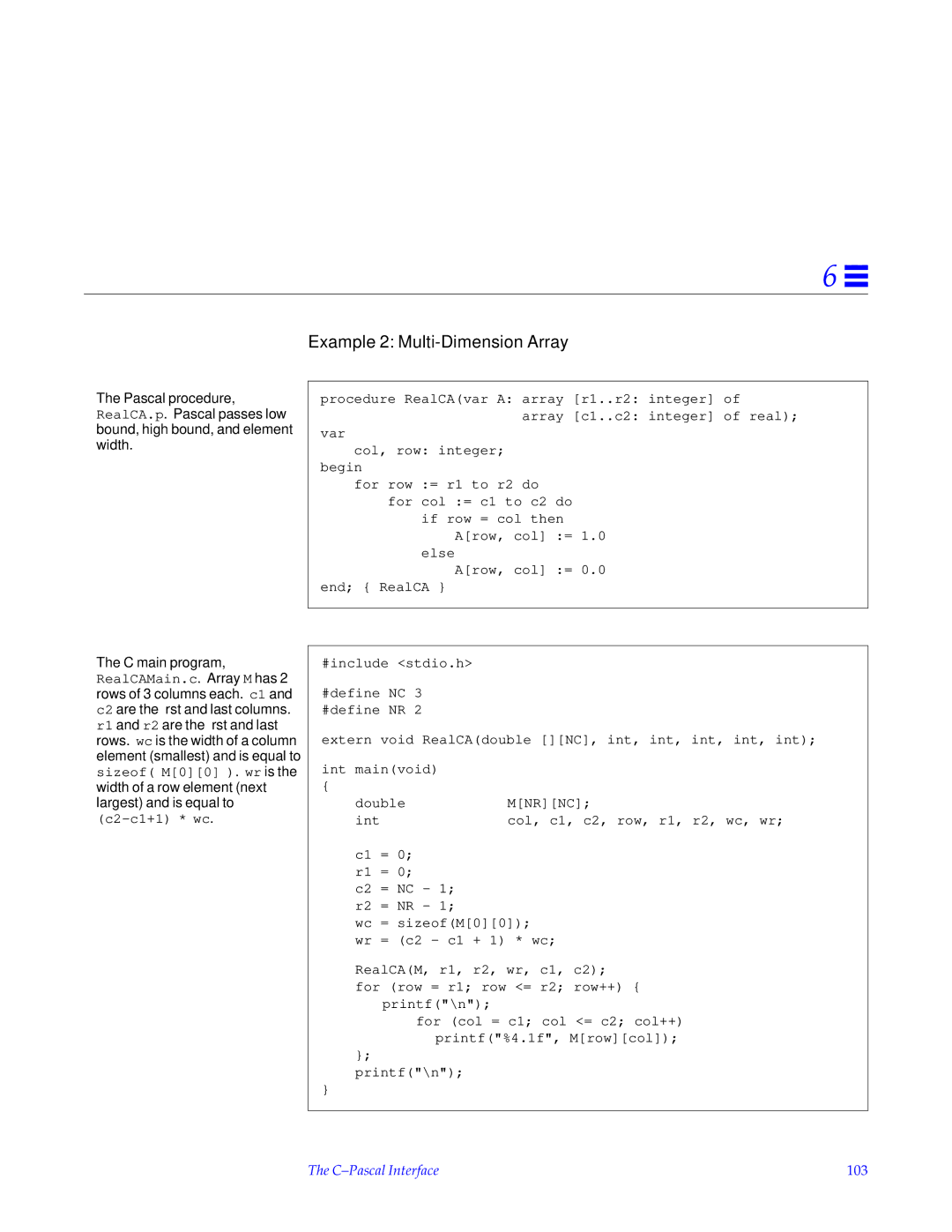
Example 1 Single-Dimension Array
C-Pascal Interface 103
Example 2 Multi-Dimension Array
104
Example 3 Array of Characters
C-Pascal Interface 105
Records and Structures
106
Commands to compile and execute StruChr.p and StruChrMain.c
C-Pascal Interface 107
Pascal routine
108
Variant Records
C-Pascal Interface 109
Commands to compile and execute VarRec.p and VarRecMain.c
110
Pascal Set Type
C-Pascal Interface 111
Pascal intset Type
112
Value Parameters
C-Pascal Interface 113
Commands to compile and execute SimVal.p and SimValMain.c
114
Arrays
C-Pascal Interface 115
Function Return Values
Simple Types
Pascal function
116
Commands to compile and execute RetReal.p and RetRealMain.c
Pascal procedure, IO.p C main program, IOMain.c
Input and Output
C-Pascal Interface 117
Procedure Calls Pascal-C
Hostname% cc IO.o IOMain.c -lpc
C function, SimRef.c
118
Pascal main program, StrVarMain.p
C function, StrVar.c
C-Pascal Interface 119
Incorrect use of string in static variable storage
Commands to compile and execute StrVar.c
120
C-Pascal Interface 121
Commands to compile and execute FixVec.c
C function, FixVec.c
Pascal main program
122
C function, UniVec.c
C-Pascal Interface 123
C function, IntCA.c
C function, StruChr.c
Commands to compile and execute IntCA.c and IntCAMain.p
124
Out
Commands to compile and execute StruChr.c and StruChrMain.p
StruChr.c
Calign StruChr.o StruChrMain.p
126
C function, VarRec.c
Commands to compile and execute VarRec.c
Non-Pascal Procedures
C-Pascal Interface 127
128
C-Pascal Interface 129
C function, SimVal.c
130
Commands to compile and execute SimVal.c
C function, ProcPar.c
Parameters That Are Pointers to Procedures
Commands to compile and execute RetReal.c and RetRealMain.p
C function, RetReal.c
132
Procedures and Functions as Parameters
Global Variables in C and Pascal
Pascal procedure, GloVar.p
C-Pascal Interface 133
File-Passing Between Pascal and C
C procedure, UseFilePtr.c
134
C-Pascal Interface 135
136
Sample Interface
C++-Pascal Interface
++ Name Encoding
Procedure Calls C++-Pascal
Pascal procedure, Samp, in the file, Samp.p
Compatibility of Types for C++ and Pascal
C++-Pascal Interface 139
Arguments Passed by Reference
C++ main program, SampMain.cc
Hostname% pc -c Samp.p
Simple Types without the -xlOption
Pascal procedure, SampRef, in the file, Samp.p
140
Hostname% pc -c SamRef.p
Commands to compile and execute SamRef.p and SamRefMain.cc
Simple Types with the -xlOption
C++ main program
142
Hostname% pc -c StrRef.p
Commands to compile and execute StrRef.p and StrRefMain.cc
C++-Pascal Interface 143
144
Hostname% pc -c FixVec.p
C++-Pascal Interface 145
Hostname% pc -c DaysOfWeek.p
-calignoption
146
Hostname% pc -c StruChr.p
Commands to compile and execute StruChr.p
C++-Pascal Interface 147
148
C++-Pascal Interface 149
150
Arguments Passed by Value
Hostname% pc -c DayWeather.p
Hostname% pc -calign -c DayWeather.p
C++-Pascal Interface 151
152
Commands to compile and execute SimVal.p
Hostname% pc -c RetReal.p
Commands to compile and execute RetReal.p
C++-Pascal Interface 153
154
Input and Output
Hostname% pc -c RetShortReal.p
Pascal function, IO.p
C++-Pascal Interface 155
Procedure Calls Pascal-C++
C++ main program, IOMain.cc
Hostname% CC IO.o IOMain.cc -lpc hostname% a.out
C++ function, SimRef.cc
Simple Types Passed by Reference
156
C++-Pascal Interface 157
158
C++ function, SimVal.cc
C++-Pascal Interface 159
Commands to compile and execute SimVal.cc
160
C++ function, RetReal.cc
C++-Pascal Interface 161
Pascal procedure, GloVar.p C++ main program, GloVarMain.cc
Commands to compile and execute GloVar.p and GloVarMain.cc
Global Variables in C++ and Pascal
Pascal File Pointers to C++
C++ procedure
162
Compiler Mixed-Language Programs
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface
164
Compatibility of Types for Fortran and Pascal
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 165
Real Integer Integer*2
166
General Parameter-Passing in Fortran and Pascal
Multidimensional Arrays
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 167
168
Procedure Calls FORTRAN-Pascal
Fortran main program
Commands to compile and execute SimVar.p
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 169
Fortran main program, StrVarmain.f
Pascal procedure, StrVar.p
170
Fortran main program, FixVecmain.f
Commands to compile and execute StrVar.p and StrVarmain.f
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 171
172
Commands to compile and execute FixVec.p
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 173
Commands to compile and execute UniVec.p and UniVecmain.f
174
Commands to compile and execute IntCA.p
Fortran main program, ChrCAmain.f
Commands to compile and execute ChrCA.p
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 175
176
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 177
178
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 179
180
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 181
182
Commands to compile and execute SimVal.p and SimValmain.f
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 183
Pascal procedure, ChrCAx.p
Commands to compile and execute ChrCAx.p
Pointers
184
Commands to compile and execute PastPtr.p
Fortran main program, RetRealmain.f
Procedure Calls Pascal-FORTRAN
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 185
186
Fortran subroutine
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 187
188
Fortran subroutine, StrVar.f
Hostname% pc StrVar.o StrVarmain.p -lpfc -lF77
Commands to compile and execute StrVar.f and StrVarmain.p
Character Dummy Arguments
Hostname% f77 -c StrVar.f
190
Following example illustrates this method
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 191
Commands to compile and execute FixVec.f
Pascal main program, UniVecmain.p
Fortran subroutine, UniVec.f
192
Hostname% f77 -c UniVec.f
Commands to compile and execute UniVec.f and UniVecmain.p
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 193
194
Fortran subroutine, StruChr.f
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 195
Commands to compile and execute StruChr.f and StruChrmain.p
Hostname% f77 -c StruChr.f
Hostname% pc StruChr.o StruChrmain.p -lpfc -lF77
196
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 197
198
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 199
200
Fortran function, RetReal.f
Commands to compile and execute PassPtr.f and PassPtrmain.p
Hostname% f77 -c PassPtr.f
Hostname% pc PassPtr.o PassPtrmain.p -lpfc -lF77
Routines as Parameters
Commands to compile and execute RetReal.f and RetRealmain.p
202
FORTRAN-Pascal Interface 203
204
Compiler Syntax Errors
Error Diagnostics
Illegal Characters
Digits in Real Numbers
String Errors
206
Error Diagnostics 207
Replacements, Insertions, and Deletions
Hostname% pc synerr.p
Undefined or Improper Identifiers
Expected Symbols and Malformed Constructs
208
Pascal program, mism.p
Error Diagnostics 209
Expected and Unexpected End-of-file
Hostname% pc synerr2.p
210
Compiler Semantic Errors
Format of the Error Diagnostics
Incompatible Types
Error Diagnostics 211
Procedure and Function Type Errors
Scalar Class
Expression Diagnostics
Scalar Error Messages
212
Error Diagnostics 213
This program generates the following error messages
214
Type Equivalence
Unreachable Statements
Error Diagnostics 215
Pascal program, unreached.p
Hostname% pc unreached.p
Goto Statement
Uninitialized Variables
Unused Variables, Constants, Types, Labels, and Routines
Runtime Errors
Compiler Panics, I/O Errors
Error Diagnostics 217
218
Error Diagnostics 219
220
Overview
XView Toolkit
222
Tools
Objects
Object-Oriented Programming
Drawable Object Window Icon
Pascal Interface
XView Toolkit 223
Names
Attribute Procedures
Compiling with Libraries
Header Files
XView Toolkit 225
Attribute Lists
226
Handles
Data Types
Here, mymenu is an object of type XVobject
XView Toolkit 227
Conversion of C to Pascal
Coding Fragment
An Example
228
Pascal
XView Toolkit 229
Sample Translation of an XView Function to Pascal
230
Sample Program
XView Toolkit 231
Menu Demo Program
232
Panelbutton
Math Libraries
Contents of the Math Libraries
Math Libraries 235
Libm Functions
236
Ieee Support Functions
Ieeevalues
Ieeefunctions
Math Libraries 237
Ieeeretrospective
Sparc Libraries
238
Math Libraries 239
Arithmetic Exceptions
240
Math Library Exception-Handling Function matherr
Math Libraries 241
242
Libsunmath Support for Ieee Modes and Exceptions
Math Libraries 243
244
Conditional Variables
Pascal Preprocessor
246
Compiler Directives
Pascal Preprocessor 247
%config Directive
248
Hostname% pc -xl config.p hostname% a.out
Pascal Preprocessor 249
Output when you define two
Output when you define foo
%debug Directive
Hostname% pc -xl -cond debug.p hostname% a.out
%else Directive
250
Pascal Preprocessor 251
Hostname% pc -xl -config red ifthenelse.p hostname% a.out
%elseif Directive
Pascal program, ifthenelse.p
252
Hostname% pc -xl -config blue elseif.p hostname% a.out
%elseifdef Directive
Pascal program
Pascal Preprocessor 253
Hostname% pc -xl -config bird2 ifdef.p hostname% a.out
%enable Directive
254
Pascal Preprocessor 255
%error Directive
Hostname% pc -xl enable.p hostname% a.out
%endif Directive
%exit Directive
Error.p
256
Hostname% pc -xl exitdirective.p hostname% a.out
%if Directive
Pascal Preprocessor 257
258
%ifdef Directive
Pascal Preprocessor 259
%include Directive
Module unit, includemod.p
%list Directive
260
Pascal Preprocessor 261
Pascal program, list.p
List.p
%nolist Directive
262
Pascal Preprocessor 263
%slibrary Directive
%var Directive
%warning Directive
Pc -xl warning.p
Output when you compile warning.p without the -configoption
264
Error Messages
266
Fourth argument to function must be of type type, not type
Error Messages 267
268
Error Messages 269
270
Function requires a to be an unpacked array, not type
Error Messages 271
272
Error Messages 273
274
Identifier
Error Messages 275
276
Unknown option for procedure pointer ignored option
Error Messages 277
278
Error Messages 279
280
Error Messages 281
282
Cannot mix sets with integers and reals as operands of type
Error Messages 283
284
Error Messages 285
286
Error Messages 287
288
Multiply defined label in case, lines number and number
Error Messages 289
290
Error Messages 291
292
Error Messages 293
294
OUT
Error Messages 295
296
297
Index
298
Index 299
300
Index 301
302
Index 303
304
Index 305
306
Index 307
Marques

![]()