Building a Network Access Control Solution
Page
International Technical Support Organization
Second Edition January
Contents
Part 2. Customer environment
Part 3. Appendixes
Index
Copyright License
Vii
Trademarks
IBM
AIX
Preface
Team that wrote this redbook
Preface
IBM US
Become a published author
Comments welcome
Page
January 2007, Second Edition
New information
Changed information
Page
Part 1 Architecture and design
Page
Business context
Security compliance and remediation concept
Why we need this
Http//banking.senate.gov/conf
Does this concept help our mobile users
Business driver for corporate security compliance
Corporate security policy defined
Achievable benefits for being compliant
Policy Development and Assurance
Conclusion
Business context
Page
Architecting the solution
Architecture overview
Solution architectures, design, and methodologies
WAN
Network Admission Control
Page
Security Compliance Manager
Page
Architectural terminology
Tivoli Configuration Manager
Security policy
Compliance query
Compliance User Interface
Remediation handler
Network Admission Control process
TCM
ACS
Cisco NAC and Ieee
Using Cisco terminology
Authenticator
Supplicant
Network identity provisioning
Posture agent
Remediation process
Definition of a Network Admission Control project
Phased rollout approach
Internet
Security compliance management business process
Design process
Architecting the solution
Security policy life cycle management
Implementation
Creation
Solution objectives
Review and update
Enforcement
Network design discussion
Default network
Quarantine access
Trusted network
Performance controls
Scalability and high availability
Implementation flow
Page
Conclusion
Page
Component structure
Logical components
Solution logical block diagram
Network Admission Control
Network Admission Control Framework
Posture validation server
CSMon
CSlog
Admission control client
Policy enforcement device
Posture plug-in
Logging service
Clean Access Server CAS
Clean Access Manager CAM
Clean Access Agent CAA
Network Admission Control Appliance
Clean Access Policy Updates
Compliance
Compliance server
Compliance reporting
Administration
Compliance client
Compliance client logical component
Posture collector
Policy collector
Remediation
Default remediation handler
Remediation server
Posture cache
Physical components
Network client
Remediation handler component
Cisco Trust Agent
Security Compliance Manager client
Security Compliance Manager policy
IBM Integrated Security Solution for Cisco Networks servers
Network access infrastructure
Network access device
Cisco Secure Access Control Server
Tivoli Configuration Manager servers
Solution data and communication flow
Policy
Policy creation and deployment flow
Component structure
Posture collection process flow
Posture validation and policy enforcement flow
Page
Remediation flow
Secure communication between components
Secure communication
Security zones
Component placement
NAC communication
Security Compliance Manager communication
Less Secure
Network
Uncontrolled zone Internet, external networks
Controlled zone intranet
Controlled zone external network-facing DMZ
Restricted zone production network
Restricted zone management network
Policy enforcement points
Branch office compliance
Branch egress enforcement
Campus internal enforcement
Branch Office Compliance Campus Ingress Enforcement
Small Office Home Office compliance
Soho Compliance PAT access protection
Extranet Compliance
Extranet compliance
LAB Compliance
Lab compliance
Data Center Protection
Data Center protection
Remote Access Protection
Remote access protection
Part 2 Customer environment
Page
Armando Banking Brothers Corporation
Company profile
Network infrastructure
Current IT architecture
IBM Integrated Security Solution for Cisco Networks lab
Armando Banking Brothers Corporation
NAC Appliance
Armando Banking Brothers Corporation
Page
Application security infrastructure
DMZ
Middleware and application infrastructure
Corporate business vision and objectives
Project layout and implementation phases
Action Reference Part I Security compliance server
Project overview
NAC L3 IP
NAC L2 IP
Part III Remediation server
CCA OOB VG
Conclusion
Page
Solution design
Page
Business requirements
Network access control requirements
Functional requirements
Security compliance requirements
Remediation requirements
Solution functional requirements
Caused by worms and other hostile software
NAC solution conceptual functional requirements
Security compliance criteria
Remediation services
Attempt
Implementation architecture
Logical components
Component subsystems total solution
Establishing compliance criteria
Configuring the compliance server
Tivoli Security Compliance Manager client components
Establishing the policy collector parameters
Solution design
Setting the policy version
Maxdataagesecs conceptual flow
Setting the remediation handler URL attribute
Enforcing compliance criteria
11 Setting the remediation handler JAR classpath
ACS
Posture token
13 Posture validation policies
Page
14 Shared Radius Authorization Components
Assigning the System Posture Token
Performing remediation
Remediation handler Html pages
Physical components
IBM Security Compliance Manager server
Compliance subsystem
Access Control Server
Network Admission Control subsystem
IBM Tivoli Security Compliance Manager client
Solution design
Layer 2 devices
NAC-enabled network device
Layer 3 devices
LRE
Cisco Trust Agent
IBM Tivoli Configuration Manager server
Remediation subsystem
Software Package Web Server
Conclusion
Page
125
Compliance subsystem implementation
Installation of DB2 database server
Tivoli Security Compliance Manager setup
127
DB2 installation welcome window
DB2 version selection is presented similar to the one shown
129
Setup wizard welcome window
License agreement window
131
Installation type selection window
Installation action selection window
133
Installation folder selection window
User information dialog
135
Administration contact list dialog
10 DB2 Instance configuration window
11 DB2 Tools selection dialog
137
12 Administrator contact selection window
139
13 Installation options summary
14 Installation completion window
Installation of Tivoli Security Compliance Manager server
15 Language selection dialog
141
Administration Utilities
Database Configuration
Server
143
18 Setup type selection window
19 E-mail server configuration dialog
145
20 Server Communication Configuration window
Server Security Configuration window is displayed, as shown
22 Database Location selection window
147
23 Database configuration information
24 Database creation choice window
149
25 Administrator User ID Configuration window
151
26 Installation options summary window
27 Installation result window
Configuration of the compliance policies
Posture collectors
Posture items and posture elements
153
Posture collector parameters
Policy collector
Operational
Workflow
155
Installation of posture collectors
28 Tivoli Security Compliance Manager GUI login
157
30 Tivoli Security Compliance Manager Administration Console
32 Import file selection dialog
34 Collectors signature validation
159
35 Policy installation summary
161
Customization of compliance policies
37 Policies view
163
38 Collectors configuration view
Warnversions
Passversion
Versionwf
Faillastscanover
165
Warndefsolderthan
Defswf
Failminlenunder
Warnminlenunder
Minlenwf
Warnmaxageover
41 Editing collector parameters
167
Passwindowsnt
Warnwindowsnt
PASSWINDOWS2000
169
Warnhotfixes
Failhotfixes
Hotfixwf
KEY
171
Value
Nokeyrule
Novaluerule
Pass
173
Rule operators
Rules
Rule results
Checking for ZoneAlarm installation directory
Rule format
175
Checking for Windows XP firewall forced off
177
Reqservice
Reqdisabled
Servicerunningwf
Servicedisabledwf
Reqrunning
46 Copying an existing compliance query
179
47 Destination policy selection dialog
48 Renaming compliance query
181
49 Compliance query description modification
50 Violation message modification
183
51 Disabling collector sharing
53 Saving changes made to the policy collectors
185
54 Save policy collectors warning
Assigning the policy to the clients
55 Create group action selection
187
57 Add policy menu selection
Deploying the client software
Tcmcli utility policy
189
Prerequisites
Cisco Trust Agent
61 Certs directory with CTA
191
62 Cisco Trust Agent installation wizard
Installation of Cisco Trust Agent on Windows
63 License agreement for Cisco Trust Agent
193
Accept the defaults -64and click Next
195
65 Cisco Trust Agent installation type
Click Next Figure
67 Confirmation of the certificate import
197
Click Finish to close the installation, as shown in Figure
199
IBM Tivoli Security Compliance Manager client
70 Language selection
Installation of the Security Compliance Manager client
71 The welcome window
201
72 Client Installation Utility window
203
74 Directory selection window
205
75 Setup type window
Pull
Accept the defaults and click Next
77 Client connection window
207
78 Server communication configuration window
209
79 Client Dhcp configuration window
Next
81 Successful completion window
211
82 Security Compliance Manager posture plug-in files
213
Network enforcement subsystem implementation
Configuring the Cisco Secure ACS for NAC L2
Configuring NAC Framework components
215
Installing Cisco Secure ACS
Configuring the administrative interface to Cisco Secure ACS
217
Interface configuration advanced options
Administration control
Allowing administrator access via Http optional
219
Cisco Secure ACS certificate setup
Using an ACS self-signed certificate
Generating self-signed certificate
221
Restart the Cisco Secure ACS Figure
223
Importing IBM Security Compliance Manager attributes
Example 7-1 Security Compliance Manager attributes
Example 7-2 Import Security Compliance Manager attribute
225
Click CSV Passed Authentications Figure
Configuring logging
227
Select CSV Failed Authentications Figure
11 Failed attempts logging
229
Configuring a network device group in Cisco Secure ACS
13 Interface Configuration screen for the creation of NDGs
14 Network Device Group check box
231
15 Network Configuration
16 AAA clients
233
17 AAA client setup
18 AAA Clients
235
19 Global Ietf Radius attributes
Configuring Radius attributes
237
Configuring groups
21 Group Setup
239
Configuring users
23 User-to-Group mappings
Global authentication setup
Click Submit + Restart
241
EAP-FAST configuration Condition
243
EAP-GTC
EAP-TLS
26 Posture Validation
Configuring posture validation
27 Posture Validation Policies
245
28 CTA Posture Validation Policy
29 Posture Validation for CTA
247
Click Add Condition Set Figure
31 Adding a condition set
249
32 Posture validation rule creation for CTA check
33 CTA rule defined
251
34 Quarantine condition applied as default action
35 Completed posture validation for CTA
253
Click Apply and Restart, as shown in Figure
37 Repeating the process for Security Compliance Manager
255
38 IBM Tscm policy creation
39 IBM Tscm policy creation
257
Click Add Rule to get to the screen shown in Figure
41 Tscm policy components
259
Page
261
Click Done Figure
45 Completed posture validation rules
263
Click Radius Authorization Components
Configuring Radius Authorization Components
Ietf
265
47 IOS RAC attribute
48 Ietf drop-down menu
267
49 Healthy Sales RAC
269
Tunnel-Medium-Type 802
Configuring Network Access Profiles
Click Add Profile
271
51 Newly created NAP
273
52 Authentication configuration for RAC
From the screen shown in -53,click Add Rule
275
54 Partial configuration of posture validation
55 Selecting CTA and Tscm policies
277
An example of the CTA Healthy pop-up is shown in Figure
58 CTA pop-up configuration
59 Completed posture validation for Naciisscn
279
60 Authorization rule creation
User group System posture token Shared RAC
281
RAC
62 Completed Authorization RAC configuration
External User Database
Configuring the Cisco Secure ACS for NAC L2/L3 IP
Unknown user policy
Clientless user
63 Downloadable ACL creation
Downloadable Access Control Lists
64 Naming of ACL
285
Enter the name of the ACL and the ACL definition Figure
287
Select Radius Authorization Components
Vendor Attribute Value
289
Click Add Rule
68 L2IP Healthy Authorization rule
Deployment of the network infrastructure
Click Apply and Restart
291
Configuring Cisco 3750 switch for NAC L2
293
Page
295
Configuring Cisco 3750 switch for NAC L2 IP
Page
297
Has been applied to the switchport
No URL Redirect
Configuring Cisco IOS Router for NAC L3 IP
299
Page
301
Verifying Network Admission Control
Example 7-3 Output of show eou and show eou all command
303
Configuring NAC Appliance components
71 Installation wizard
Installing CCA Agent
305
72 Default install directory
CCA version Required ports
Configuring a CCA OOB VG server
307
75 CAM login
Clean Access Summary window will be displayed Figure
77 Device Management
309
78 Adding a new CAS
Click Add Clean Access Server
79 Successful CAS addition
311
80 CAS Status screen
81 Network IP screen
313
82 Managed subnets
Select Advanced → Vlan Mapping
Configure default login
Click Administration → User Pages → Login
315
Select Switch Management → Profiles → Group → New
Configuring a Switch Group
317
85 Switch Group creation
Verify your new switch group Figure
319
Configuring a switch profile
88 Switch profile
Configuring Port Profile
321
Select Switch Management → Profiles → Port → New Figure
90 Managed profile creation
Configuring Snmp receiver
Click Switch Management → Profiles → Snmp Receiver
323
Select Switch Management → Devices → Switches → New
Adding a managed switch
325
93 Manually adding a switch to be managed
As seen in -94,click the Ports icon
Defining user roles
Click User Management → User Roles → New Roles
327
Click Save Role when completed
Creating traffic policies
Click User Management → User Roles → Traffic Control → IP
329
98 Rules for trusted to untrusted
ActionAllow StateEnabled CategoryIP ProtocolTCP
Click Add Policy
331
Click User Management → Local Users → New Local User
Creating local users
333
Click Create User
102 List of local users
Configure Clean Access Agent
335
Click Add Check
104 CCA version compliance check
105 Rules check list check
337
Rule Description
Rule Name
Operating System
Rule Expression
107 CCA Compliance rule definition
339
Newly defined rules will be displayed Figure
Click Requirements → New Requirements Figure
Click Add Requirement
341
110 CCA Agent update
343
Click Requirement Rules
112 CCA Compliance Requirement rule
Click Role-Requirements
113 Role requirements
345
114 Viewing online users
Discovered clients
347
Logging on as a client
117 Web page pop-up informing user about non-compliance
Click Continue
349
118 Temporary access notification
120 Security Compliance Manager Compliance Report window
351
123 Successful login
Configuring Cisco 3750 switch for NAC Appliance
353
Example of interface configuration for CAM interface
Example of Snmp configuration
355
Remediation subsystem implementation
Page
357
Automated remediation enablement
Prerequisites
Remediation server software setup
Tivoli Configuration Manager
Tivoli Configuration Manager Web Gateway setup
359
Preparing for the installation
Installation of the DB2 database
Installation of Web infrastructure
WebSphere Application Server launchpad
361
WebSphere Installation Wizard window
Software License Agreement window
363
Installation type selection
Component selection dialog
365
Destination folder selection window
Node name selection window
367
Run as a service selection window
369
Installation options summary
10 Online registration dialog
371
Patching WebSphere Application Server installation
12 WebSphere product location
373
13 Installation option selection
14 Fix packs directory location
Creating the necessary user account
375
Installation of Tivoli Configuration Manager Web Gateway
Welcome window is presented -16. Click Next
17 License agreement window
377
18 Component selection
379
19 Installation directory selection window
20 Database configuration window
381
21 Web infrastructure configuration window
22 Endpoint configuration window
383
23 Secure access configuration
24 Summary of installation options
385
Configuration of the remediation server
Installation of Software Package Web Server
387
26 WebSphere administrative console login
27 Install new application
389
28 Preparing for the application installation
29 Installation option summary dialog
391
30 Installation status window
31 Saving the configuration changes
393
Configuration of the Software Package Web Server
Installation of the Software Package Utilities
395
Cd %BINDIR% Cd tcmremed\cfg Sputilinitialsetup.bat
397
Creating remediation instructions for the users
Locating Html
33 Directory structure for Html pages
399
Defaultlang
Base Html
Posture item Html
401
Html pages example
Posture element Html
Variables and variable tags
Wfattribute tag
Field Tag
403
Fail
Remattribute tag
\PROGRA~1\IBM\SC
405
Logging available attributes
Debug attributes
407
Logging posture items
Logging the Html search path
409
Creating Html pages for Abbc policy
Example 8-4shows the Html source code for this
411
Example 8-5 Content of style definition file
Page
413
Example 8-6 Html source for password length policy details
Wfattributecurrentvalues.brbWARNING fieldmsg/bbr
415
Example 8-7shows the Html source for
Page
417
Building the remediation workflows
TCRNavScan workflow
419
Example 8-8 Content of NavScanMessageen.wsf
Example 8-9 Content of Sample.properties file for TCRNavScan
421
38 Remediation handler interface with the warning
423
TCRNavVirusDefUpdate
Page
425
TCRNavSoftwareInstalled
TCRMSPatchesInstallWinXP
427
HotfixId=KB896423 TmfWebUIEndpoint=tcmweb
429
TCRMSServicePackInstallWinXpSp2
Page
AddRegistryValueBeforeExecData.arrayLength=2
431
TCRZLSoftwareInstalled
433
Noreboot
TCRZLSoftwareRunning
435
TCRMessengerDisabled
Modification of the remediation packages
437
Page
439
Part 3 Appendixes
Page
441
Appendix A. Hints and tips
Deployment overview
Appendix A. Hints and tips
443
Top-level sequence of events
Figure A-2 Isscn top-level sequence diagram
Cisco Trust Agent
Security Compliance Manager and NAC compliance subsystem
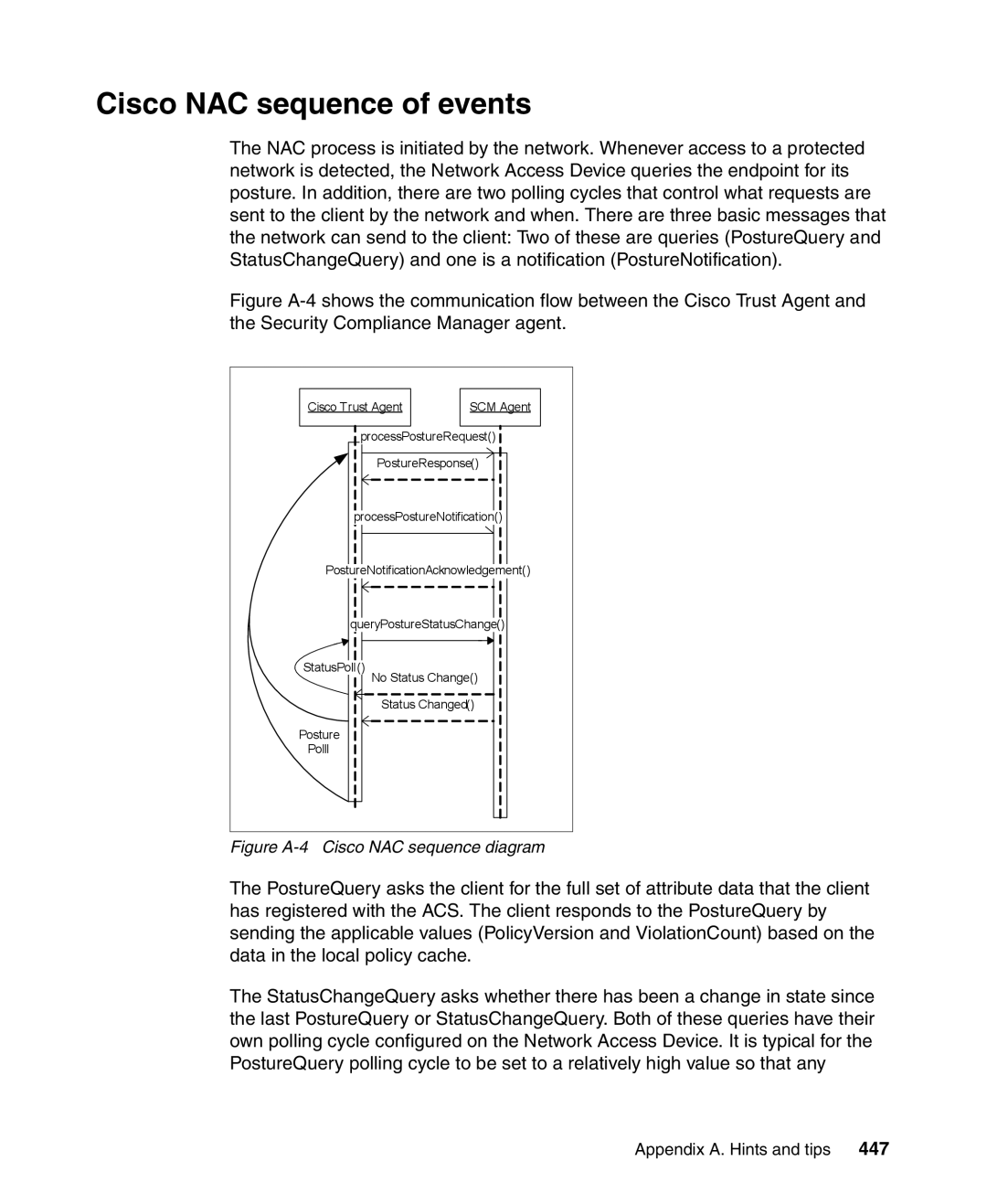
Cisco NAC sequence of events
Figure A-4 Cisco NAC sequence diagram
Fault isolation
Appendix A. Hints and tips
Tivoli Security Compliance Manager Server
Security Compliance Manager server and client
Tools and tricks
Summary of default port usage
Communication port usage
Cisco NAC
Cisco IOS Software router
Cisco IOS Software switch
Cisco Secure ACS server
Tools and tricks for the client
40500
Cisco NAC Appliance components
NAC Appliance details
In-band versus out-of-band
NAC Appliance integration
Integration design
NAC Appliance Agent
Integration components
NACApplianceCompliance.entry
TSCMAgent.bat
Kickrich.html
Scheduler
Installing and configuring prototype integration components
Scheduler.bat
System path
NAC Appliance Manager
Considerations for designing a production solution
State mapping and scenarios
Page
Appendix A. Hints and tips
Page
43 Sequence of Events for Scenarios #5 and #6
Conclusion
471
Appendix B. Network Admission Control
Benefit of NAC
Executive summary
473
Dramatically improve network security
NAC implementation options
475
NAC Appliance
Investment protection
NAC Framework solution
477
Planning, designing, and deploying an effective NAC solution
Next steps
NAC technology
NAC Appliance components
479
NAC Framework components
Page
481
Locating the Web material
How to use the Web material
Using the Web material
IBM Redbooks
Other publications
483
Online resources
How to get IBM Redbooks
Help from IBM
IBM Support and downloads IBM Global Services
Page
487
Numerics
SCM client communication
Html
Glba
NAD
NAC
Creation Deployment
PPP
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
UDP
URL
Vlan
Page
Page
Page
Building a Network Access Control Solution