User’s Manual
Intel NetStructure ZT 8101 10/ 100 Ethernet Switch
Copyright 2002, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved
Contents
Gvrp
To save changes to NV-RAM
Using the Web Console
100
133
Date Revision Description
Tables
Revision History
Contents
Highlights
Ethernet Features
Layer 2 Switching Functions
Front Panel Features
Additional Features
Layer 3 Switching Functions
Warranty
Specifications
Management Functions
Electrical
Mechanical
Product Information and Sales Support
Environmental
Standards
Power on
Installing the Board
Identifying External Components
Uninstalling the Board
Front Panel
Status LEDs
Port LEDs
Link / Activity LED Mode
Health Status LED
Hot Swap LED
Link / Speed LED Mode
Accessing the Local Console
Switch contains the following components
Getting Started with Management
To configure the IP address
Setting the IP Address
To log in to the switch the first time
Parameter Default Description
To upgrade the firmware using Zmodem
Upgrading Firmware through Zmodem
Parameter Description
Installation and Initial Setup
Managing the Switch
Switch Management and Operating Concepts
Port Configurations
Switch IP and MAC Addresses
Flow Control
Ethernet Port Link Speed Duplex
Type Log Message
Port Type Duplex Mode Flow Control
Port Security and MAC Address Learning
Packet Forwarding
BOOTP/DHCP Relay
DNS Relay
Storm Control
MAC Address Aging Time
MAC Address Forwarding
IP Forwarding
Traffic Control
ARP Table
Router Ports
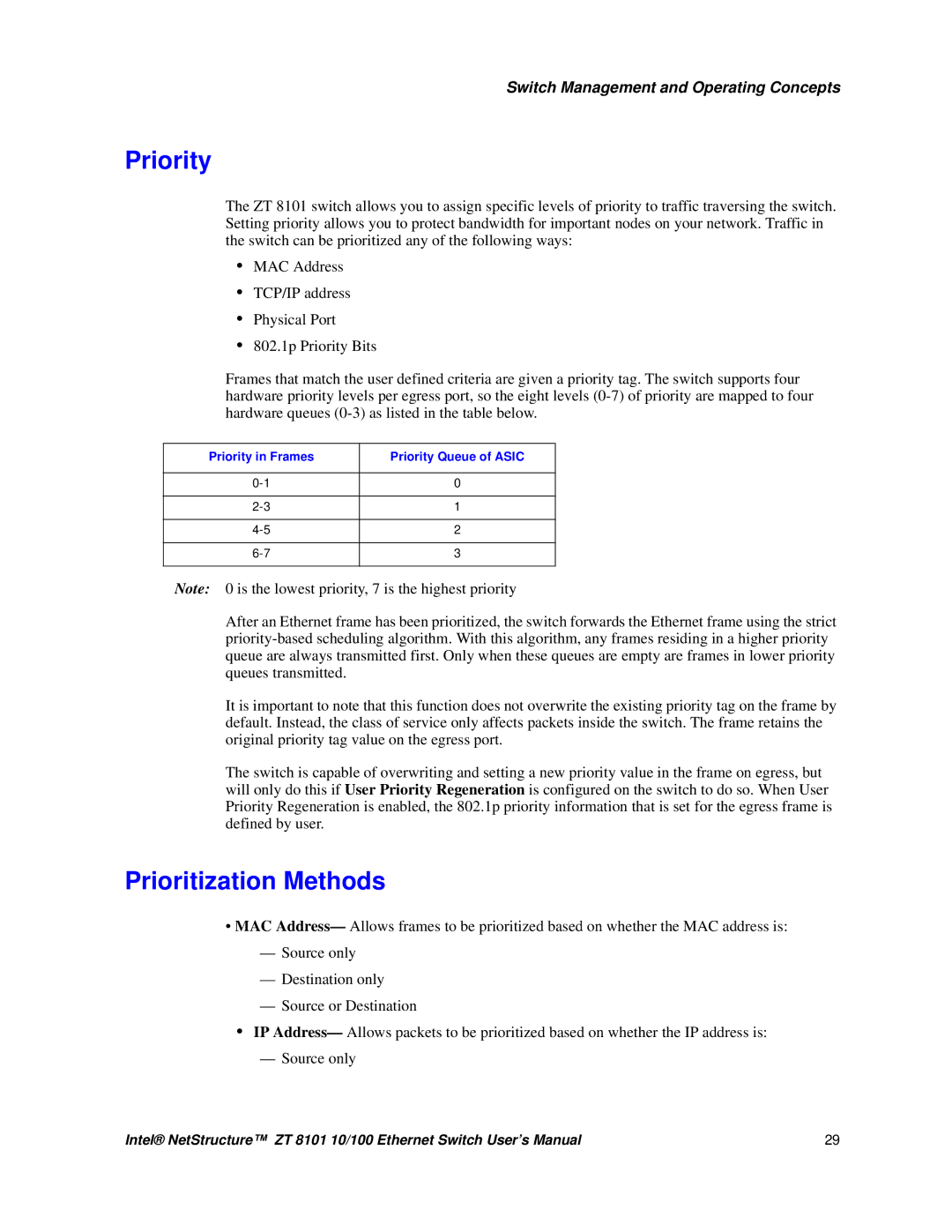
Priority in Frames Priority Queue of Asic
Priority
Prioritization Methods
IP Address Filtering
Filtering
MAC Address Filtering
STP Levels and Parameters
Port Mirroring
Spanning Tree Protocol
Parameter Description Default Value
STP Parameters for the Switch Level
STP Parameters for the Port Level
Variable Description Default Value
Link Aggregation
Switch Management and Operating Concepts
Port-Based VLANs
VLANs
Ingress Checking
Ieee 802.1Q VLANs
Ingress Checking
Broadcast Storm Control and VLANs
Layer 3-Based VLANs
IP Interfaces
IP Path MTU Discovery
Multi-Netting
System IP Interface
Additional IP Interfaces
Switch Ports
IP Addressing Scheme
Vlan Name
Address Description
Multicasting
Igmp Queriers
Internet Group Management Protocol Igmp
Igmp Snooping
Igmp Group Settings
Routing Protocols
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol Dvmrp
Protocol-Independent Multicast Dense Mode PIM-DM
Switch Management and Operating Concepts
General Deployment Strategy
Before You Start
Static Route Assessment
Vlan Layout
IP Addressing Scheme for VLANs
Getting Started
Connecting to the Switch
Console Usage Conventions
You use the following fields to enter or select items
Main Menu has these options
Main Menu
Advanced Setup
Basic Setup
To create a new user account
Creating User Accounts
Admin User Switch Configuration Management
Admin and User Privileges
Saving Changes
To log in once you have created a registered user
Reboot
Basic Settings
To save changes to NV-RAM
Highlight Yes on the confirmation prompt and press Enter
Basic Switch Setup
Switch Information
For the Manual option
Highlight Apply and press Enter
To configure trap recipients
Network Management Setup
To configure Snmp
To configure the access list
Serial Port Settings
Port Configurations
Switch Utilities
To download a configuration file
To update firmware
To upload a configuration file
To upload a history log file
To enable the BOOTP/DHCP relay agent
BOOTP/DHCP Relay
To test connectivity with ping
To start the test, highlight Start and press Enter
DNS Relay
To configure DNS Relay services
To view port utilization
Network Monitoring
Port Statistics
Column Description
To view port error statistics
Port Utilization screen displays these statistics
To view the MAC address table
Address Tables
To view an analysis of packet sizes and types
Following information is displayed for each MAC address
To view the IP address table
To view the routing table
To view the ARP table
Status
To view Gvrp status
To view the router ports
To view the IP multicast forwarding table
To view the Igmp snooping status
To view the Igmp group table
You can view Igmp group information for each Vlan
To view the Dvmrp routing table
To view the switch’s history log
To configure global STP switch settings
Advanced Setup
Field Default Description
Spanning Tree
To define the port members of an STP group
Forwarding
To configure MAC address aging
To configure multicast MAC address forwarding
To configure unicast MAC address forwarding
Configure these fields for each port group
To configure storm control
To configure advanced traffic control
To configure static ARP
To configure static IP routes
IP Address Filtering
To specify an IP address for filtering
Select MAC Address Priority, and press Enter
Priority Settings
MAC Address Priority
Priority based on Port
IP Priority
User Priority Regeneration
Select and configure these fields
Select Priority Based on Port, and press Enter
Select User Priority Regeneration, and press Enter
To configure a port for mirroring
Mirroring Configurations
To configure Gmrp globally
To configure port Gmrp settings
Vlan Configuration
To configure VLANs supporting Gmrp
To configure Gvrp globally
To create or modify a port-based Vlan
Based Vlan
To create or modify an 802.1Q Vlan
To configure a link aggregation group
To configure the member ports of an 802.1Q Vlan
Switch
Link Aggregation
To configure link aggregation load sharing
RIP Configuration
Setting Up IP Interfaces
To set up IP Interfaces on the switch
Layer 3 IP Networking
To configure globally the multicast protocols
Multicast Global Configurations
To configure RIP
To configure Igmp snooping
Igmp Configuration
To configure Igmp for an IP interface
PIM-DM Interface Configurations
Dvmrp Interface Configuration
To configure Dvmrp for an IP interface
To configure PIM-DM for an IP interface
Static Router Port
To configure a static router port
Using the Web Console
Using the Web Console
Logging
Configuration Options
Web Console has the following configuration options
Left panel has these options
Web Console
Advanced Setup
Left panel, click Save Changes
To retain any configuration changes permanently
Click Save Configuration
Restart
Factory Reset
To reset the switch to factory default values
Switch Information
Click Apply
Gigabit ports, the choices are Auto,1000/Full, or 100/Full
Network Management
To configure Snmp community strings
Configure the following fields
To configure management station IP addresses
Top panel, click Management Station IP Addresses
To start the download, click Download
To download a configuration file
To configure the BOOTP/DHCP relay agent
BOOTP/DHCP Relay Agent
Click New and configure these fields
To configure the static Bootp relay setup
To configure the static DNS table
To configure DNS Relay
Port Statistics
Tx-Transmitted packets ExDefer
Self, and Static. Self is used to identify the switch
Click Find Following ARP information is displayed
To view Igmp snooping status
To view router ports
110
Click Find Table displays this information
Spanning Tree Protocol
To configure STP switch settings
Click Apply Following information is displayed about STP
Both have the same priority
To configure multicast MAC address forwarding
Field Description IP Address
Configure these following fields for each port group
IP Address Filtering
To set up a MAC address priority
Priority Settings
MAC Address Priority
Field
Priority based on Port
IP Priority
Top panel, click User Priority Regeneration
User Priority Regeneration
Click Apply To change an entry, repeat steps
Vlan Configurations
To configure an 802.1Q Vlan
To configure a port-based Vlan
To configure Gmrp globally
To configure member ports of an 802.1Q Vlan
To configure port Gmrp settings
To configure VLANs supporting Gmrp
To configure a link aggregation group
To configure link aggregation load sharing
To configure RIP interface settings
To globally enable or disable RIP
Rx Mode
Igmp Configurations
Select the interface and click Edit Configure these fields
Dvmrp Interface Configurations
Top panel, click Dvmrp Interface Configurations
Top panel, click PIM-DIM Interface Configurations
PIM-DM Setup
Static Router Port Settings
Top panel, click Static Router Port Settings
132
CE Certification
Safety
Emissions Test Regulations
EN 50081-1 Emissions
Safety Precautions
Product Safety Information
Regulatory Information
FCC-Federal Communications Commission USA
AC and/or DC Power Safety Warning AC and/or DC Powered Units
Safety Information
Rack Mount Enclosure Safety
Warranty Information
For the Americas
Returning a Defective Product RMA
For Emea
For Apac
Mail address sugiyamakx@intel.co.jp
For Ijkk
DB-9 Pin
Pin Assignments
RJ-45 Pin
Building the Cable
Serial Cable Diagram