Chapter 5 | Configuration Using the |
Usage Type This is the RADIUS server authentication type. The possible values are:
•Login (Default value) Indicates that the RADIUS server is used for authenticating user name and passwords.
•802.1X Indicates that the RADIUS server is used for 802.1X authentication.
•All Indicates that the RADIUS server is used for authenticating user name and passwords, and 802.1X port authentication.
Click Add to List to add the RADIUS configuration to the RADIUS table at the bottom of the screen.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel Changes to cancel the changes.
QoS
Network traffic is usually unpredictable, and the only basic assurance that can be offered is best effort traffic delivery. To overcome this challenge, Quality of Service (QoS) is applied throughout the network. This ensures that network traffic is prioritized according to specified criteria, and that specific traffic receives preferential treatment. QoS in the network optimizes network performance and entails two basic facilities:
Classifying incoming traffic into handling classes, based on an attribute, including:
•The ingress interface
•Packet content
•A combination of these attributes
Providing various mechanisms for determining the allocation of network resources to different handling classes, including:
•The assignment of network traffic to a particular hardware queue
•The assignment of internal resources
•Traffic shaping
The terms Class of Service (CoS) and QoS are used in the following context:
•CoS provides varying Layer 2 traffic services. CoS refers to classifying traffic into traffic classes, where each class is handled as an aggregate whole, with no
•QoS refers to Layer 2 traffic and above. QoS handles
The QoS configuration options are CoS Settings, Queue Settings, DSCP Settings, and Basic Mode.
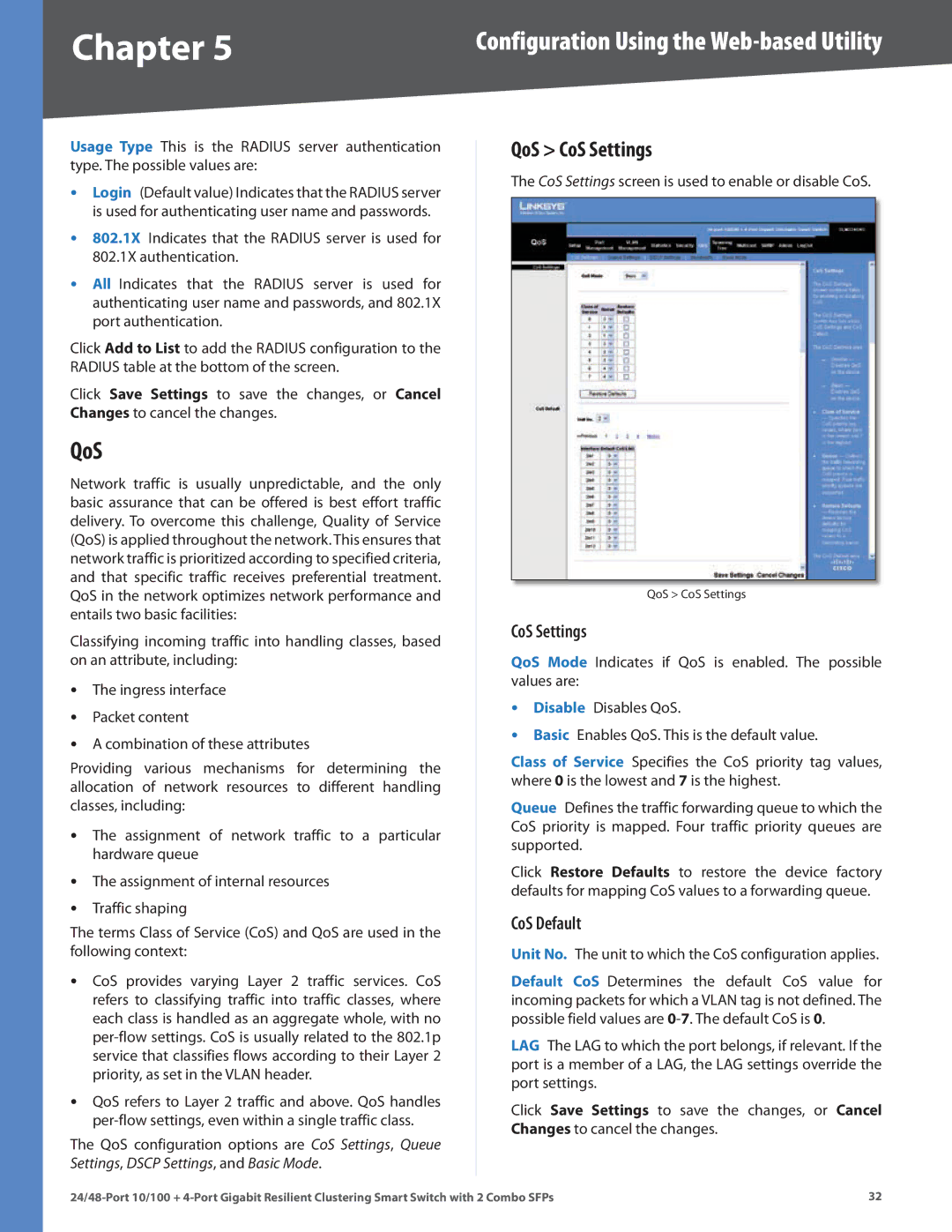
QoS > CoS Settings
The CoS Settings screen is used to enable or disable CoS.
QoS > CoS Settings
CoS Settings
QoS Mode Indicates if QoS is enabled. The possible values are:
•Disable Disables QoS.
•Basic Enables QoS. This is the default value.
Class of Service Specifies the CoS priority tag values, where 0 is the lowest and 7 is the highest.
Queue Defines the traffic forwarding queue to which the CoS priority is mapped. Four traffic priority queues are supported.
Click Restore Defaults to restore the device factory defaults for mapping CoS values to a forwarding queue.
CoS Default
Unit No. The unit to which the CoS configuration applies.
Default CoS Determines the default CoS value for incoming packets for which a VLAN tag is not defined. The possible field values are
LAG The LAG to which the port belongs, if relevant. If the port is a member of a LAG, the LAG settings override the port settings.
Click Save Settings to save the changes, or Cancel Changes to cancel the changes.
32 |