Note: mode 1 is for
2. Configure Phonebook, using “pbook” command.
Users can refer to chapter 5.11 [pbook] command for more information.
usr/config$ pbook –add name TEST1 ip 10.1.1.1 e164 10
Note:
The command is to add a record onto Phonebook. After the command completed, you can type “pbook
3.3 Behind IP-Sharing
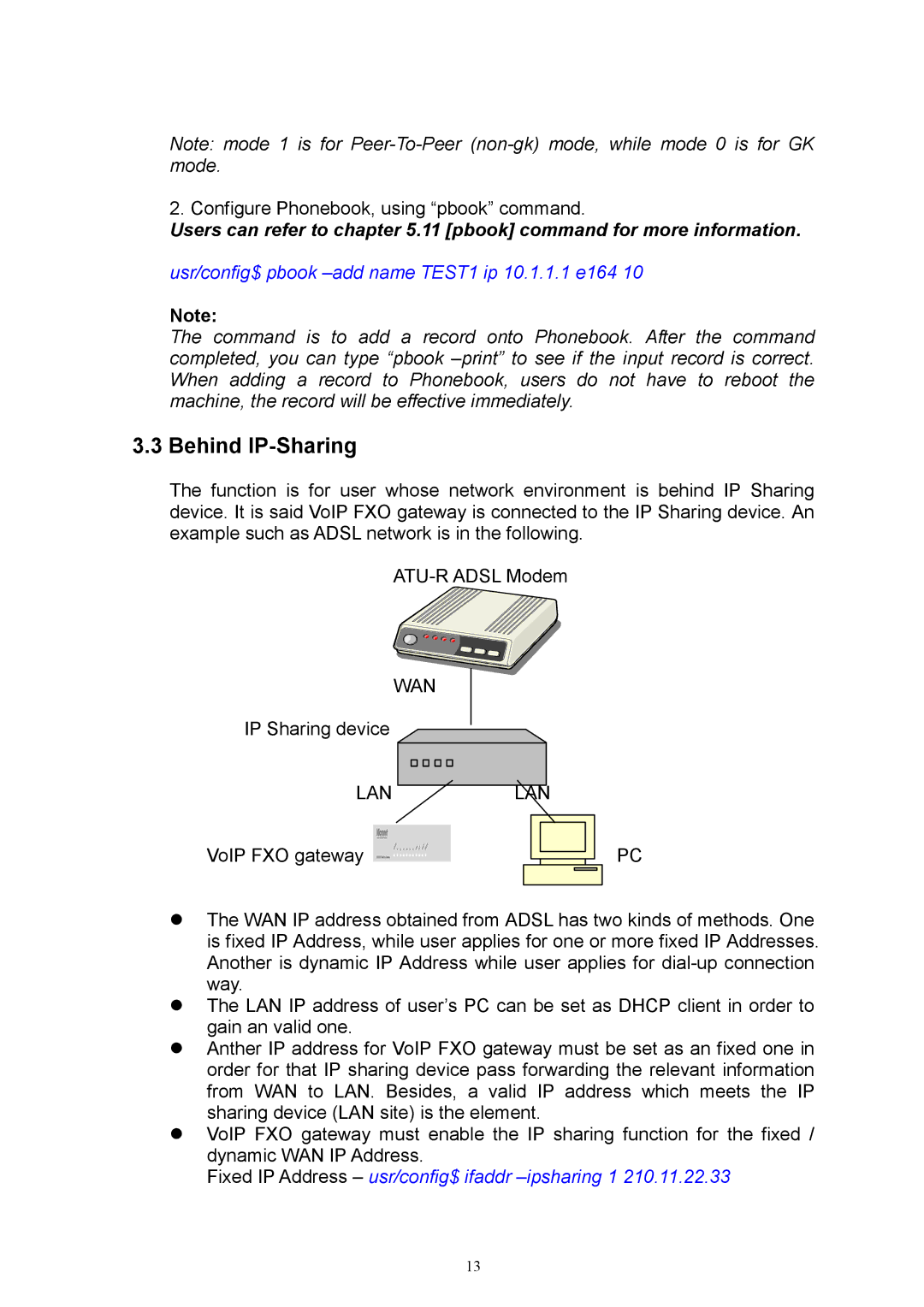
The function is for user whose network environment is behind IP Sharing device. It is said VoIP FXO gateway is connected to the IP Sharing device. An example such as ADSL network is in the following.
WAN
IP Sharing device
LAN | LAN | ||
VoIP FXO gateway |
|
| PC |
|
| ||
zThe WAN IP address obtained from ADSL has two kinds of methods. One is fixed IP Address, while user applies for one or more fixed IP Addresses. Another is dynamic IP Address while user applies for
zThe LAN IP address of user’s PC can be set as DHCP client in order to gain an valid one.
zAnther IP address for VoIP FXO gateway must be set as an fixed one in order for that IP sharing device pass forwarding the relevant information from WAN to LAN. Besides, a valid IP address which meets the IP sharing device (LAN site) is the element.
zVoIP FXO gateway must enable the IP sharing function for the fixed / dynamic WAN IP Address.
Fixed IP Address – usr/config$ ifaddr –ipsharing 1 210.11.22.33
13