| R |
|
|
|
|
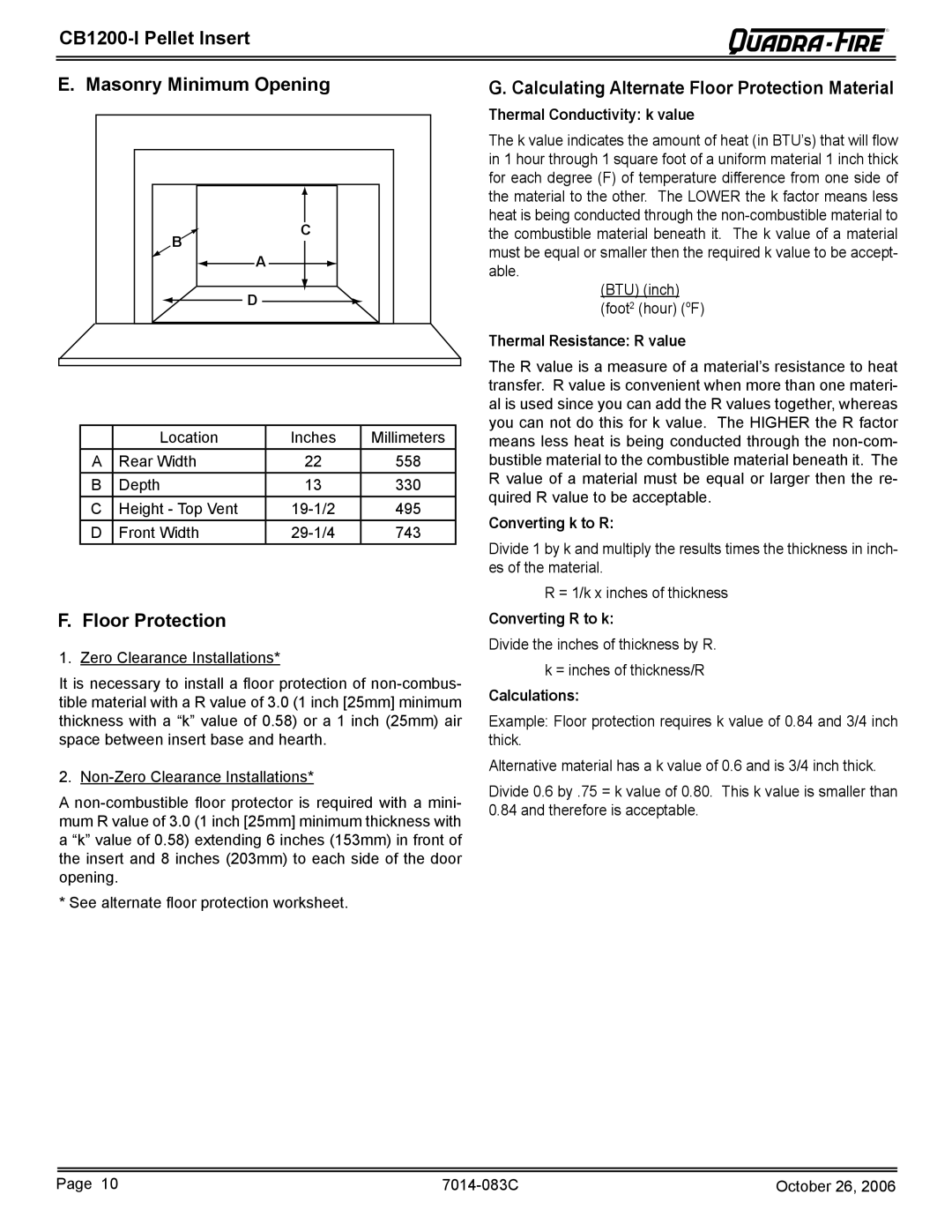
E. Masonry Minimum Opening | G. Calculating Alternate Floor Protection Material |
B | C | |
A | ||
| ||
| D |
| Location | Inches | Millimeters |
A | Rear Width | 22 | 558 |
B | Depth | 13 | 330 |
C | Height - Top Vent | 495 | |
D | Front Width | 743 |
F. Floor Protection
1.Zero Clearance Installations*
It is necessary to install a floor protection of
2.
A
* See alternate floor protection worksheet.
Thermal Conductivity: k value
The k value indicates the amount of heat (in BTU’s) that will flow in 1 hour through 1 square foot of a uniform material 1 inch thick for each degree (F) of temperature difference from one side of the material to the other. The LOWER the k factor means less heat is being conducted through the
(BTU) (inch) (foot2 (hour) (oF)
Thermal Resistance: R value
The R value is a measure of a material’s resistance to heat transfer. R value is convenient when more than one materi- al is used since you can add the R values together, whereas you can not do this for k value. The HIGHER the R factor means less heat is being conducted through the
Converting k to R:
Divide 1 by k and multiply the results times the thickness in inch- es of the material.
R = 1/k x inches of thickness
Converting R to k:
Divide the inches of thickness by R. k = inches of thickness/R
Calculations:
Example: Floor protection requires k value of 0.84 and 3/4 inch thick.
Alternative material has a k value of 0.6 and is 3/4 inch thick.
Divide 0.6 by .75 = k value of 0.80. This k value is smaller than 0.84 and therefore is acceptable.
Page 10 | October 26, 2006 |