APPLICATION EXAMPLES
Remote Connections with Fiber Cable
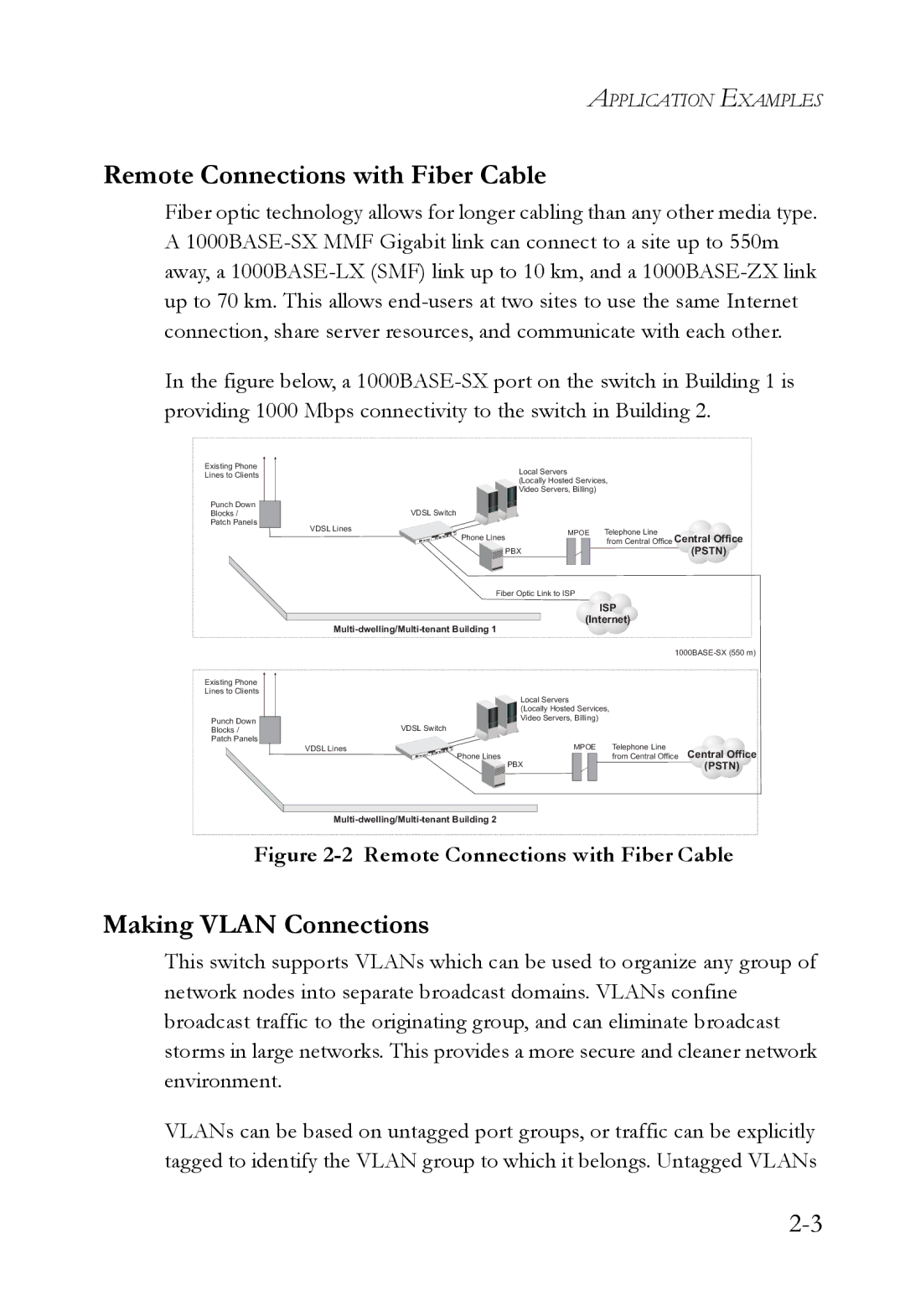
Fiber optic technology allows for longer cabling than any other media type. A
In the figure below, a 1000BASE-SX port on the switch in Building 1 is providing 1000 Mbps connectivity to the switch in Building 2.
Existing Phone Lines to Clients
Punch Down
Blocks /
Patch Panels
Existing Phone Lines to Clients
Punch Down
Blocks /
Patch Panels
Local Servers
(Locally Hosted Services,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Video Servers, Billing)
Video Servers, Billing)
| VDSL Switch |
|
|
VDSL Lines |
| MPOE | Telephone Line |
| Phone Lines |
| from Central Office Central Office |
|
|
| |
|
| PBX | (PSTN) |
| Fiber Optic Link to ISP |
| |
|
|
| ISP |
|
| (Internet) | |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| Local Servers |
|
|
| (Locally Hosted Services, | |
|
| Video Servers, Billing) |
|
| VDSL Switch |
|
|
VDSL Lines |
| MPOE | Telephone Line |
| Phone Lines |
| from Central Office Central Office |
|
| PBX | (PSTN) |
Figure 2-2 Remote Connections with Fiber Cable
Making VLAN Connections
This switch supports VLANs which can be used to organize any group of network nodes into separate broadcast domains. VLANs confine broadcast traffic to the originating group, and can eliminate broadcast storms in large networks. This provides a more secure and cleaner network environment.
VLANs can be based on untagged port groups, or traffic can be explicitly tagged to identify the VLAN group to which it belongs. Untagged VLANs