VIVOTEK
Network > Streaming protocols
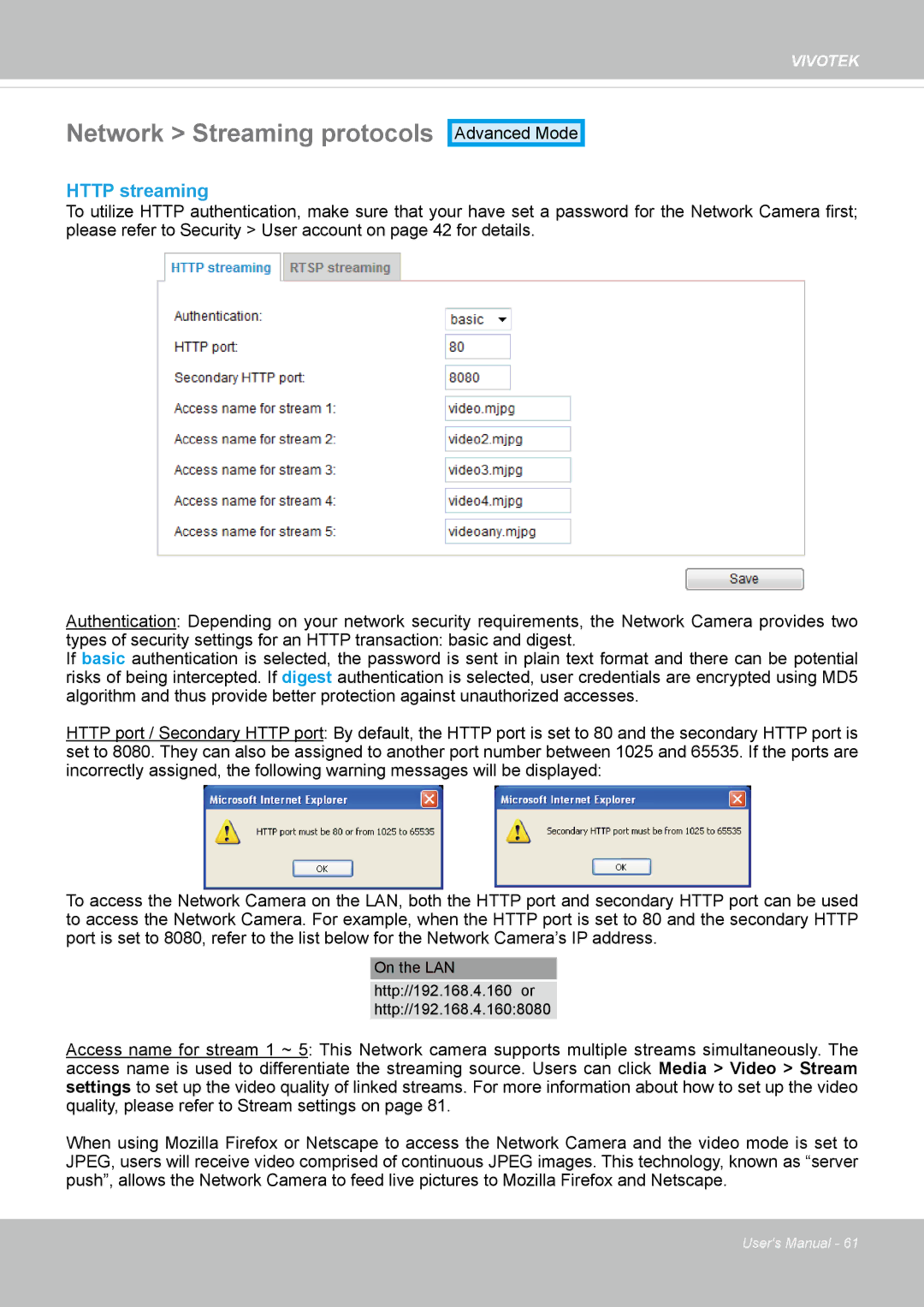
HTTP streaming
Advanced Mode
To utilize HTTP authentication, make sure that your have set a password for the Network Camera first; please refer to Security > User account on page 42 for details�
Authentication: Depending on your network security requirements, the Network Camera provides two
types of security settings for an HTTP transaction: basic and digest�
If basic authentication is selected, the password is sent in plain text format and there can be potential risks of being intercepted� If digest authentication is selected, user credentials are encrypted using MD5 algorithm and thus provide better protection against unauthorized accesses.
HTTP port / Secondary HTTP port: By default, the HTTP port is set to 80 and the secondary HTTP port is set to 8080� They can also be assigned to another port number between 1025 and 65535� If the ports are incorrectly assigned, the following warning messages will be displayed:
To access the Network Camera on the LAN, both the HTTP port and secondary HTTP port can be used to access the Network Camera� For example, when the HTTP port is set to 80 and the secondary HTTP port is set to 8080, refer to the list below for the Network Camera’s IP address�
On the LAN
http://192.168.4.160 or
http://192.168.4.160:8080
Access name for stream 1 ~ 5: This Network camera supports multiple streams simultaneously� The access name is used to differentiate the streaming source� Users can click Media > Video > Stream settings to set up the video quality of linked streams� For more information about how to set up the video quality, please refer to Stream settings on page 81�
When using Mozilla Firefox or Netscape to access the Network Camera and the video mode is set to
JPEG, users will receive video comprised of continuous JPEG images� This technology, known as “server
push”, allows the Network Camera to feed live pictures to Mozilla Firefox and Netscape.
User's Manual - 61