VPNmanager Confi guration Guide
Copyright 2005, Avaya Inc All Rights Reserved
Declarations of Conformity
Page
Contents
Using VPNmanager
Setting up the network
Configuring IP Groups
Configuring user groups 129
Establishing security 163
Using advanced features 199
Contents
Monitoring your network 245
Glossary 313 Index 319
VPNmanager Overview
What Products are Covered
Network-wide Visibility and Control
Secure VPN Configuration
Intranet and Extranet Support
No Special Consoles Required
Related Documentation
Using VPNmanager Help
How This Book Is Organized
Complementary to Snmp Management Tools
Preface
Contacting Technical Support
Preface Avaya VPNmanager Configuration Guide Release
Security gateways
Components of the Avaya security solution
VPNmanager software
VPNremote Client software
Domain hierarchy
Overview of the VPN management hierarchy
Security gateway
Preparing to configure your network
Network zones Media type SG5 and SG5X SG200 SG203 SG208
IP groups
Remote users and user groups
Static Routes
Denial of Service
Security policies
Firewall policies
QoS
VoIP
NAT
Additional features
Syslog
Sequence to configure your VPN
Client IP address pooling
SSL for Directory Server
Sequence to configure your VPN
Page
Role Based Management
About VPNmanager administrators
To configure an administrator to be an SNMPv3 admin
To add an administrator
Add a policy server
Log into the VPNmanager console
Open Domain
Navigating the main window
VPNmanager console main window
File menu
File MenuNew Object list New object Objects Description
Edit menu
View menu
New object Objects Description
Toolbar
Tools menu
Help menu
Icons on toolbar
Toolbar commands Description Commands
VPN view pane
Network Diagram View
Tree View
Tiled View
Alarm monitoring pane
Configuration Console window
Configuration console window
Configuration Console Menu bar
NAT
Policy Services
Contents pane
Update Devices
Toolbar
Details pane
General tab
Preferences
Dyna Policy Defaults Global
Dyna Policy Defaults User
Preferences, Dyna-Policy Global Tab
Dyna Policy Authentication
Remote Client
Advanced
TEP Policy
Alarm/Monitoring
Tunnel End Point Policy
Page
To create a new domain
New VPN Domain
Select Level of security
Configuring a security gateway
Creating a new security gateway
To create a new security gateway
Setting up the network
Device tabs by release Tab All VPNos Releases Earlier Later
Using Device tabs to configure the security gateway
Snmp
Device General tab
To create a memo
Memo tab
DNS tab
DNS tab
To add a DNS Relay
DNS Relay Configuration area, click Add
To add a static DNS server
Configuring the DNS tab for VSU at VPNos 4.2 or earlier
To add a DNS server address
To edit an existing server address
To delete a DNS server address
Interfaces tab
Network zones Media SG5 SG200 SG203 SG208 Type
Interface tab
Ethernet2 Unused Public backup Private Semiprivate
Using Device tabs to configure the security gateway
Static addressing
Options for IP addressing for interface zones
Dhcp addressing
Manage-ment Address assigned
Local Dhcp Server
Point-to-Point Protocol Over Ethernet PPPoE Client
Wins
Dhcp Relay
To change the media interface configuration
Static
Changing network interfaces
To add an IP device to the security gateway
Media interface configuration dialog
To add an IP telephony device to the security gateway
Private port tab with VPNos 4.2 or VPNos
Private port tab
IP Device Configuration with VPNos 4.2 or VPNos
Adding an IP Device Configuration
To add an IP Device
None
Device users tab
To add a device account user
Network Object tab
Device Network Objects tab
Routing
To build a routing table using the default gateway
Common Default Gateway for VPN Traffic topology
Default Gateway for VPN Traffic VPNos
To build a RIP table
About NAT types for VPNos
Policies tab, NAT services
Priority of NAT types
Configuring NAT VPNos
To add a NAT rule VPNos
To edit a NAT rule
To delete a NAT rule
NAT applications
About NAT types for VPNos
Access the Internet from private Networks
Accessing the Internet from private networks
Setting up VPN with overlapping private addresses
Setting Up a VPN with Overlapping private Addresses
Using NAT to support multiple gateway configurations
Interface for VPNos
Using NAT to Support Multiple Gateways
To configure a NAT rule
Add NAT Rule VPNos 4.2 or earlier
Original
Tunnel NAT rules
To add a tunnel NAT rule
About IP Groups
Creating a New IP Group
To create a new IP Group
IP Group General tab
New IP Group
IP Group General tab
Add IP Group member
Configuring an IP Group
To configure an IP Group that is associated with an extranet
Configuring an IP Group that connects to an extranet
Delete
Memo
Default client configuration
Configuring remote access users
User Dyna-Policy tab
Using dyna-policy
Dyna-Policy Defaults User tab
Configuring a global dyna-policy
Dyna-Policy Defaults Global tab
VPN configuration files on remote user’s computer
Disable split tunneling
Dyna-Policy Authentication tab
Radius authentication
Local authentication
Ldap authentication
Dynamic VPNs VPNos
Remote Client tab
Client DNS resolution redirection
Send Syslog messages
Remote Client inactivity connection time-out VPNos
Configure a default CCD with global dyna-policy
Creating new user object
About creating individual dynamic-policy
Default user
User General tab
To create a new user object
User General tab
Dyna-Policy tab
Actions tab
Reset User Directory Password. The user’s password is reset
User Advanced tab
Configuring a remote user object
Information for VPNremote Client users
Client IP address pool configuration
Using Policy Manager for user configuration
Using local authentication
Using Radius authentication VPNos 3.X and VPNos
Add Client DNS
Add Client IP address pool
To configure the Client IP configuration
Configuring client attributes
Add Client Wins
Creating a message
Policy Manager for client attributes
Enforce brand name
Enable RADIUS/ACE
RADIUS/ACE Services
Radius concepts
Settings
Radius protocol
Authenticating secret password
Add RADIUS/ACE server
Radius server data
RADIUS/ACE
To add a Radius server
Configuring remote access users
To create a user group
New user group
User Group Memo tab
User Group General tab
To configure a user group
Configuring a user group
Move to the Configuration Console window
User Group Actions tab
Configuring user groups
Skip VPNs
Types of VPN objects
VPN packet processing modes
IKE VPNs
Default VPN policy
To create a default VPN within a selected domain
Creating a default VPN
Creating a new VPN object
To create a new VPN object
Create a new VPN Object, see Creating a new VPN object on
Creating a designated VPN
General tab with IKE
Using the VPN tabs
General tab with Skip
Members-IP Groups tab
Members-Users tab
VPN, Members IP Groups Tab
Security IKE tab
SHA1
Field Description
Pre-Shared Secret
Security IPSec
IPSec Proposals
Authentication
Add IPSec proposal
Field Description Encryption
Field Description Lifetime
Export
VPN configuration
Advanced VPN tab
Rekey site-to-site VPN
Rekey
To configure a new Skip VPN object
Configuring a Skip VPN
Configuring a Skip VPN
To configure a new IKE VPN Object
Configuring an IKE VPN
Configuring an IKE VPN
Configuring VPN objects
Configuring an IKE VPN
Enabling CRL checking
Enabling CRL checking
Click Update Devices
Exporting a VPN object to an extranet
To remove the CRL from the VSU
VPN Object Export Checklist Task
VPN Object export checklist
To export a VPN Object
Export procedure
Open the Configuration Console window
Importing a VPN object from an extranet
To import a VPN Object data file
To rekey a Skip VPN Object
Rekeying a VPN object
Levels of firewall policy management
Firewall rules set up
Domain level firewall rules
Firewall rules
To create domain level firewall rules
To create device level firewall rules
Device level firewall rules
Priority of Firewall rules versus NAT rules
Security Gateways and FTP
Firewall templates
To add a new firewall rule for FTP-control or passive FTP
To add a new firewall rule for active FTP
Predefined templates
User defined templates
To create a user-defined firewall template
Select Template, Device, or None Parameter Description
Services property
Services
Denial of Service
Device Group
To create a device group object
Denial of Service
Using the IP Trunking Call Model
Voice Over IP
To select or deselect DOS categories
To enable VoIP and add IP Trunking
Voice Over IP
Voice over IP tab
Using the Gatekeeper Routed Call Model
To enable VoIP and add gatekeeper settings
Add gatekeeper settings
QoS Policy
QoS policy and QoS mapping
QoS policy and QoS mapping
QoS policy
To add a QoS policy
Modify QoS bandwidth. burst and Dscp value screen
Packet Filtering
QoS mapping
Mapping QoS policies
What can be filtered
Packet Filtering and NAT
Traffic types that can be filtered
Policy Manager, Packet Filtering/QoS
Permit/Deny non-VPN traffic Radio Buttons
Add Packet Filtering Policy
From/Where
Filtering Policy in progress
To Where
Locating this filtering policy
Running the packet filtering policy wizard
To start or stop filtering services
Starting and stopping filtering services
Running the Policy Manager for packet filtering
Managing the ACL
To configure advanced filtering options
Configuring advanced filtering options
ACL commands Command Description
To edit, change the sequence, or delete a filtering policy
Packet Filter rule-advanced options Option Description
Marking packets for differentiated services QoS
How a VSU marks packets
About Differentiated Services
Types of marking rules
How to create a packet marking rule
To create a packet marking rule
IP packet marking information Description
Parameters used in a Packet Marking Rule Description
Policy Manager for firewalls
Packet filtering firewall
To use the firewall policy management
Add firewall policy
To add a firewall policy
Parameter Description
Establishing security
Device Advanced
Using advanced features
ARP
You would then want to
Path MTU Discovery
Enter the Path MTU Timeout value
To configure the Path MTU Discovery
NAT Traversal
Port for dyna-policy download
Port for Secure Authentication
Private IP Address VPNos
To change the port number
Send Device Names
Select the Enable Private IP Address check box
To add a private IP address
To select a VSU name distribution method
SuperUser Password VPNos
Tunnel Persistence
VSU Tunnel Persistence
TEP Policy
Add servers
Servers
To edit, change the sequence, or delete a backup server
To create a backup server
Add Directory Server Commands Description
Managing the server list
Resilient Tunnel
Servers list commands Command Description
Primary and Resilient Tunnels
Tunnel Switching
Resilient Tunnel tab for a security gateway Object
Creating a resilient tunnel
Add resilient tunnel
Prerequisites
To create a resilient tunnel
Managing the resilient tunnel list
Primary end-point service
Stopping and starting resilient tunnel services
Secondary end-point service
Move to the Configuration Console window. Select Devices
Failover TEP tab for a security gateway object
Failover TEP
Configuring failover TEP
To configure failover TEP
Advanced Action
Switch Flash
Reset password
Disable Fips
High Availability
High Availability
Virtual addresses
Advanced parameters
Select the Deny all non VPN traffic radio button
Members
Creating a High Availability Group
Configuring high availability
Updating a high availability group using Update Device
To update HA VSUs
Deleting a high availability group
Failover Tab
Failover
Configuration is as follows
To configure failover
Failover connectivity checks in 10-second intervals
Set consecutive no responses
Failover reconnect
To set up failover reconnect
Converged Network Analyzer Test Plug
Enter the test request port value
Select the CNA Test Plug Services interface
Keep Alive
Keep alive tab
To configure keep alive
About VSU certificates
Policy Manager My Certificates
Installing a Signed Certificate into a VSU
Creating and Installing a Signed Certificate
Policy Manager for My Certificates
To install a signed certificate into a VSU
To switch certificates
Switching certificates used by VPNmanager Console
About Issuer Certificates
Issuer certificates
To install an Issuer Certificate into a VSU target
Installing an issuer certificate
IKE Certificate Usage
An Example of an Issuer Certificate
Assigning a Target for a Certificate
About Certificate Usage Exchange
Click Add to open the Add IKE Certificate Policy
To assign a target for a certificate
Policy Manager My Certificates
Page
Monitoring your network
Using Snmp to monitor the device
Snmp Tab for a security gateway Object
To add Snmp trap targets
Configuring Snmp for a security gateway
Adding Admin Users for SNMPv3
VPN active sessions
To delete Snmp trap targets
Policy Manager for Syslog Services
Syslog Services
Add Syslog Policy
To run Syslog services
Using Monitor
Enterprise MIB
Monitoring wizard
Using Monitor
System Group Parameters
Log Group Parameters Description
ActiveSessions Parameters Description
IpRouteTable Parameters
Address Table Parameters Description
IpRouteTable Parameters Description
IpRouteTable Parameters Description
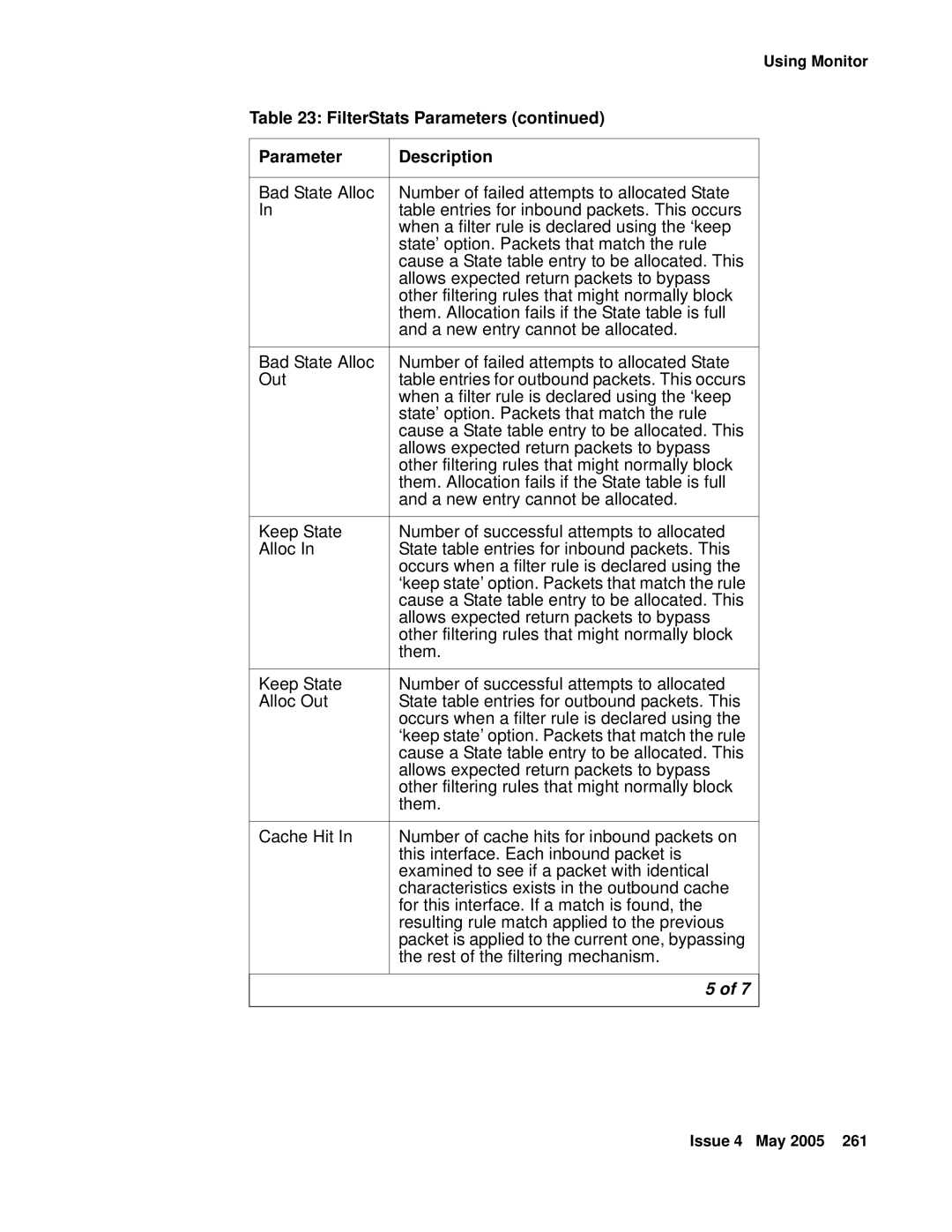
FilterStats Parameters
FilterStats Parameters Description
FilterStats Parameters Description
FilterStats Parameters Description
FilterStats Parameters Description
FilterStats Parameters Description
Filter Rules Parameters
Traffic Rate Table Parameters
Active Ports Parameters Description Group
Overview Statistics Table Parameters
Traffic Rate Table Parameters Description
Ethernet Statistics Table Parameters
Overview Statistics Table Parameters Description
Ethernet Statistics Table Parameters Description
Define Custom
Monitoring alarms
Monitoring wizard Presentation
Presentation
Alarm Descriptions Alarm Type
Alarm Types
Report Wizard
To create a report using the report wizard
Report Sample
Generating the report
Diagnostic Reports Report Type Description
Device diagnostics
Diagnostic Reports Report Type Description
Setting Up SSH and Telnet
Using the Management tab
To set up SSH or Telnet
Changing device administrator’s passwords
To reset the passwords
Using the Connectivity tab
Connectivity tab for a security gateway Object
Check connectivity by ping
Check Connectivity by Proxy Ping
Using the Device Actions tab
To directly ping a specific security gateway
To proxy ping a specific security gateway
Update Configuration
Reset Device Time
Reboot Device
Import Device Configuration
Re-setup Device
Ethernet Speed
To import configuration data for a device
Network Interface Status
Redundancy
Importing and exporting VPN configurations to a device
Switching
Export VPN
Exporting Radius
Device management
Centralized firmware management
Upgrading firmware and licenses
Device Upgrade tab
To upgrade a security gateway’s firmware
Upgrading a security gateway’s firmware
Select Save this file to disk. Click OK
License
Remote Access VSU-100 Only
Encryption Strength
Open
Page
Installing Certificates for Running SSL
When to Configure your VPNmanager for SSL
To view all the installed issuer’s certificates
To install a certificate in VPNmanager Console
To delete an installed issuer’s certificates
Windows NT and Windows 2000 Computers
Installing the Issuer’s Certificate into a security gateway
To install the issuer’s certificate into a security gateway
Solaris OS Computers
Using SSL with Directory Server
General
Appendix B Firewall rules template
Public zone firewall templates
Public high and medium security firewall rules
Telnet
Ikein
Public VPN-only firewall rules
Public low security firewall rules
Private zone firewall templates
Private medium security firewall rules
Private high security firewall rules
Private low security firewall rules
Semi-private zone firewall templates
Ping
Semi-private high security firewall rules
Semi-private medium security firewall rules
Semi-private VPN-only security firewall rules
Semi-private low security firewall rules
DMZ high and medium security firewall rules
DMZ zone firewall templates
DMZ low security firewall rules
Management zone security
Converged Network Anaylyzer template
Management high, medium, and low security firewall rules
CNA-RT
Converged network analyzer firewall rules
Alarms
Aggressive mode
Certificate Authority
Service DNS
Certificates
Certificate
Dyna Policy
Dynamic VPNs
Encapsulation
Extranet security
Mask Pairs
Lifetime, Key
MIB Enterprise
Non-Enterprise
Packet Filter
Oakley
Perfect Forward
Secrecy
Split Tunneling
Smart Card
Triple DES
User Groups
Index
DOS
254
55, 97, 115, 129
PAP
Radius
ToS, marking 193
Zone, public zone, public-backup