Series II Modem Series II Modem 336+
Series II Modems
Series II Intelligent DATA/FAX Modems
Contents
Manual Dial and Automatic Answer
Command Mode
Registers
Callback Security and Remote Configuration
Modem Testing
Other Appendixes
DIP-Switch Settings
Appendix a Troubleshooting
Introduction and Description
Introduction How To Use This Manual
Software Configuration
Installation and Connection
AT Command Mode Operation
Manual Dial and Automatic Answer
DIP-Switches
Callback and Remote Configuration
Testing Your Modem
Modem Features
What is in Your Modem Package?
Fax Features
Technical Specifications
Intelligent Features
Mode of Operation
Command Buffer
Modulation
Frequencies
Fax Carrier
Lease Line Restoral
Carrier Frequencies
Diagnostics
Connectors
Indicators
Operating Temperature
Modem LED Indicators
Power
Introduction and Description
Controls on PC Board
Safety Warnings
Installation and Connection
Installation
Series II Modem 336 MD1641A Connections
Series II Intelligent DATA/FAX Modems
Is Your Series II Modem Ready for Use?
Operating Your Series II Modem
Simple Operations
Answer/Originate Voice/Data Toggle Switch
Serial Port Limitations
Introduction
How Can You Identify Your Uart Type?
Software Configuration
COMnFIFO=1
16550 Uart and Windows
Configuring Software for Your Modem
Configuring Your Software
PC Initialization Strings
Changing Default Parameters
AT &F X4 S0=0 M
AT &F X4 S0= 2 M
Macintosh Initialization
Other Parameters
AT &F X4 M
AT &F X4 &E5 &E13 &D0 M
Configuring Software for the Remote System
Configuring Software for Your Computer
Software Configuration
AT &F9 &W0 CR
Terminal Emulation
When to Disable Data Compression
File Transfer Protocols
User Guide for Series II Modems
AT &F S0=0 X4 &E0 M
Disabling Error Correction
AT &F S0=0 X4 &E14 M
Dialing/On-Line/Answering
Manual Dial and Automatic Answer
Series II Intelligent DATA/FAX Modems
Automatic Leased Line Restoral Operation 336+ Only
Manual Dial Backup Call Termination 336+ Only
Dial Backup and Leased Line Restoral 336+ Only
Series II Intelligent DATA/FAX Modems
Manual Call Origination
Dial-Up Operation 336+ Only
Automatic Answering
Handshaking Details
Manual Answering
Call Termination
Abort Timer
AT Command Editing
Command Mode
Functional Modes
Command Mode
Functional Modes
Summary of AT Commands
Memorize Phone Numbers
#L1
#L0
#L2
#L3
E15
E14
$BA1
+++ATCR
Sr?
Result Codes
Sr=
#RCBNxx
Q1 Standard AT Result Codes
Q0 Series II Result Codes
Continuous Redial a or
Dialing Commands Dialing Action Commands
Dial Command D
DTR Dialing $D
Dialing a Stored Number N
Pulse or Tone Dial P or T
Dial Modifier Commands
Voice/Data Dialing $VD
Long Space Disconnect Y
Set Pulse Dial Ratios &P
Automatic Pauses in Dialing
Wait for New Dial-Tone W
Return to Command Mode after Dial Command Execution
Reverse the Mode of Operation R
Calling Card Detect Tones $
Flash On Hook
Quiet Answer @
ATDT101099907247465500$0123 4567 8910
Storing Phone Numbers D...N
Phone Number Memory Commands
Number Linking NN
ATX4&E1&E5&E13&E15DT17247465500N3
Listing Numbers Stored in Memory L
Loading Factory Defaults &F
Configuration and Default Storage Commands
Unix Uucp Spoofing $SP
Modem Reset Z
32terbo Enable/Disable #V 336 Only
Synchronous Transmit Clock Select &X
Async/Sync Mode Switching &M
Echo Command Mode Characters E
Command Response Result Code Commands
Result Codes Enable/Disable and No Response Answer Q
Chap 5 Command Modeter
Result Codes Basic and Extended and Call Progress Selection
Result Codes Verbose/Terse
Command Mode
Enable/Disable Trelis Coded Modulation #T
Phone Line Conditioning Commands
Guard Tones &G
Phone Line Monitoring Speaker M
Cleardown at Disconnect &CD
Fallback Modes When On-Line #F
Enable/Disable Lowspeed Fast Connect $FC 336+ Only
Carrier Detect Control &C
7 RS232C Interface Control Commands
Auto Speed Detect #A
Clear to Send Control &R
Data Terminal Ready Control &D
Data Set Ready Control &S
Error Correction Commands
CTS/RTS Interaction Control &RF
DSR/CD Interaction Control &SF
Auto-Reliable Mode &E1
Normal Mode &E0
Mode Select #L
Reliable Mode &E2
Originate Mode
Answer Mode
Auto-Reliable Buffering $A
Enable/Disable Auto Reliable Fallback Character $F
Retransmit Count $R
Error Correction/300bps $E
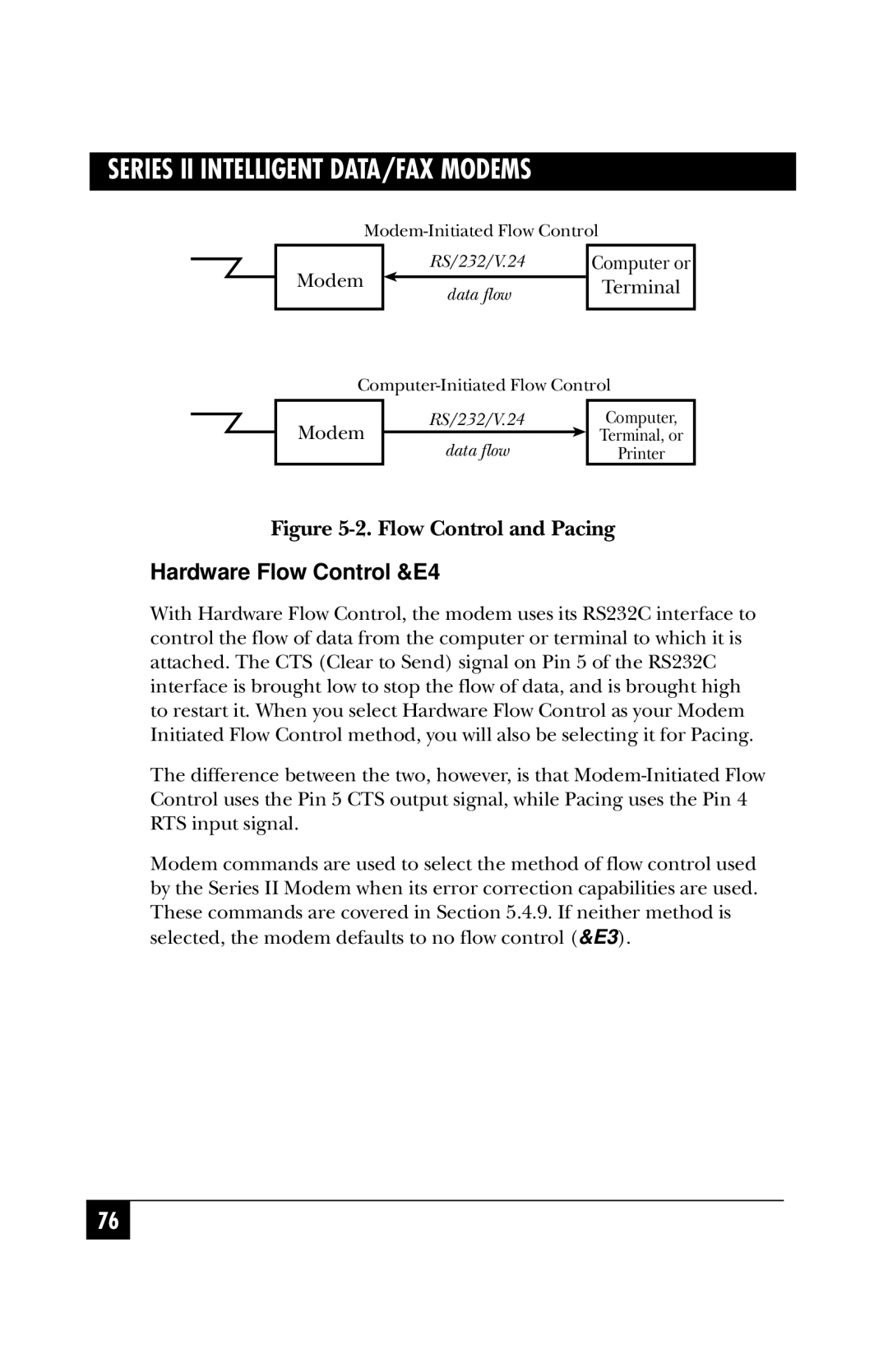
Flow Control Commands
Modem Terminal
Hardware Flow Control &E4
Xon/Xoff Pass-Through &E7
Xon/Xoff Flow Control &E5
Hewlett-Packard ENQ/ACK Pacing &E9
Normal Mode Modem Flow Control On &E11
Send Xon/Xoff Characters #X
Maximum Block Size &BS
Terminal/Computer Initiated Pacing &E13
Parity Selection #P
Asynchronous Word Length Selection $EB 336 Only
#X1 =
#X0 =
Normal Mode Modem Flow Control Commands
Speed Conversion Commands
Enq/Ack Pacing Commands
Modem Baud Rate $MB
Speed Conversion $BA
Serial Port Baud Rate $SB
Help Screens $H
Immediate Action Commands
Windows 95 Autodetect Inquiry
Inquiry for Product Code
Listing S-Register Values L6
Listing On-Line Diagnostics L8
Listing Current Operating Parameters L5 L7
On-line diagnostics information On or Off Hook H
Break Atcr
Exiting Command Mode, Going Back On-Line O
Line Probe Commands
Force Answer Mode a
Immediate Action Line Probe Commands
Format of Line Probe Graph or Table Commands DF0
DP1
DF1
Rings Which Have Occurred
Number of Rings Until Modem Answers
Line Feed Character
Escape Code Character
Return Character
Backspace Character
Time for Carrier Abort Timer
Wait Time for Dial Tone
Pause Time for Comma
Carrier Detect Response Time
S10 Carrier Loss Disconnect Delay Time
S11 Tone Dialing Tone Spacing and Duration
S13 Remote Configuration Escape Character
S15 Callback Time Delay
S18 Automatic Leased Line Restoral 336+ Only
S16 Callback Attempts
S17 Changing Break Time
S25 DTR Dropout Time
S19 Dial-Back Timer 336+ Only
S24 PBX/CBX Disconnect Drop Time for DSR/CTS/CD
S29 Local Inactivity Timer
S26 Failed Password Attempts
S32 Time Elapse for Escape Sequence
S30 Inactivity Timer
S48 Program V.34bis Connect Speeds
S36 Time Between DTR Inactive and Modem Off-Hook
S37 Time Between DTR Active and Modem On-Hook
Examples of Assigning Values
Reading and Assigning S-Register Values
ATS0=30S3?, and ATS7=55S7?
AT Command and S-Register Summary
Examples of Reading Values
Callback Feature Description
Callback Security Remote Configuration
Remote Configuration Description
Callback Security and Remote Configuration
To change your Remote Configuration feature status
Error
To set parity of the password/message prompt
To turn your modems Callback Security feature on and off
AT#DB2CRÊorÊAT#DB1CR
AT#IxxxxxxxxxxCR xxxxxxxxxx from Table
AT#CBN0xxxxxxxxxxCR
AT#CBN1xxxxxxxxxxCR
AT#SyyyyyyyyyyCR yyyyyyyyyy from Table
Password
Callback Operational Sequence Procedures
Remote Configuration Operation Procedures StepProcedure
Remote Configuration Procedures
Callback Security Enable/Disable #DB
Remote Configuration and Callback Security AT Commands
Assign Passwords for Callback Phone Numbers #CBN
Change Setup Password #S
Change Login Password #I
Erase Callback Password #RCBNxx
Erase Callback Phone Number #RDNxx
Remote Configuration Character S13
Remote Configuration/Callback Security S-Registers
Callback Time Delay S15
Callback Attempts S16
Local Inactivity Timer S29
Failed Password Attempts S26
Modem Testing
Local Analog Loopback Test/V.54 Loop
Modem Testing
Digital Loopback Test local/manual
Digital Loopback Test/V.54 Loop 2 Local/Manual
119
Digital Loopback Test remote/automatic
Digital Loopback Test/V.54 Loop 2 Remote/Automatic
Back-to-Back Test
122
Local Analog Loopback Test Synchronous Mode
Synchronous Mode Testing
Digital Loopback Test Local/Manual Synchronous Mode
Digital Loopback Test Remote/Automatic Synchronous Mode
126
DIP-Switch Settings
Series II Modem 336+ MD1640A PC Board
DIP-Switch Option Settings
129
130
Switch #4 AS/400 Mode Synchronous Mode/Leased Line/Dial-Up
131
132
133
134
135
Speaker Volume Control
Function Position Effect
Recording Option Configurations
AT vs. Series II Result Codes
DIP Switches #13-16
None of the LEDs Light When the Modem Is On
Possible Causes and Solutions
Modem Does Not Respond to Commands
141
Modem Dials But Cannot Make a Connection
143
Modem Disconnects While On-line
Modem Cannot Connect When Answering
Am Losing Data
File Transfer Is Slower Than It Should Be
Am Getting Garbage Characters on the Monitor
Modem Model No
Contacting Black Box Recording Modem Information
Shipping and Packaging
Making the Call
Upgrading the Series II Modem’s Firmware
Tone Dial Frequencies 697 770 852 941 1209 Digits 1336 1633
Appendix B Dial Pulse and Tone-Dial Frequencies
Dial Pulses
Command
Appendix C Command Summary
Description
$An
$BAn
BSn
CDn
DsNd
$Dn
DFn
DPn
$EBn
$En
#Fn
$FCn
$Hn
Command Values Description
NdNe
#Ln
$MBn
RFn
#Pn
$Rn
$SBn
Sr=n
SFn
$SPn
$VDn
#Tn
#Xn
160
Command Description #DBn
Callback Security/Remote Configuration Command Summary
#CBNyyxxxxxx
+ Dxxxxxx???Nxx
Password Command Summary
25bis Commands
DIP-Switch Condition Effect
Appendix D DIP-Switch Summary
Asynchronous Mode
Synchronous Mode
166
Appendix E S-Register Summary
Appendix E S-Register Summary
S15
S13
S24
S36
Digit Words
Appendix F Result Code Summary
Effect
172
Appendix F Result Code Summary
Appendix G V.25bis Operation
Delayed and Forbidden Numbers
25bis Operation
Appendix G V.25bis Operation
25bis Set-Up and Initialization
25bis DIP-Switches
25bis Mode AT Commands
25bis Responses Result Codes
25bis AT Commands
Change Serial Baud Rate CSP Command
Enable/Disable V.25bis Mode $V Command
Dial Phone Number Provided CRN Command
Disregard or Connect to Incoming Calls DIC or CIC Command
Listing Delayed Phone Numbers RLD Command
Listing Forbidden Phone Number RLF Command
DTR Dialing $D Command
Italy
ITU V.25bis Country Specific Information
Austria
Belgium
France
Singapore
Appendix H Series II Modem Cables
Appendix H Series II modem cables
188
Appendix I RS232C Interface Specifications
Appendix I RS232C Interface Specifications
Request To Send Pin 4, RTS CA
Received Data Pin 3, RD BB
Direction to modem
Direction from modem
Clear To Send Pin 5, CTS CB
Signal Ground Pin 7, SG AB
Data Set Ready Pin 6, DSR CC
Data Carrier Detect Pin 8, CD CF
Data Terminal Ready Pin 20, TR or DTR CD
Transmit Clock Pin 15, TC DB
Receive Clock Pin 17, RC DD
External Transmit Clock Pin 24, XTC
Ring Indicator Pin 22, RI CE
Terminal Busy Out of Service Pin 25, OOS
FCC and IC EMI/RFI Statements
Appendix J Regulatory Information
FCC Part 68 Regulations for Telephone-Line Interconnection
Appendix J Regulatory Information
196
197
Canadian Limitations Notice
Copyright 2000. Black Box Corporation. All rights reserved