Safety Considerations
Contents
General
Contents
Introduction
Unit Sizes and Modular Combinations 30GUN,R
Major System Components
Unit Sizes and Modular Combinations 30GTN,R
Unit Nominal Section a Section B 30GTN,R Tons Unit 30GTN,R
Carrier Comfort Network CCN Interface
Control Module Communication
Thermistor Designations
Status Switches
Output Relay
Page
24 V Control Schematic, Unit Sizes
24 V Control Schematic, Unit Sizes 080-110, 230B-315B
CCN LEN Data Communication Port
Main Base Board
Operating Data
040-110 130-210
Thermistor T3 and T4 Locations
Compressor Thermistor Locations T7 and T8
Belden 8205
Regular Wiring Plenum Wiring Alpha 1895 American
Manufacturer
Columbia D6451 Manhattan M13402 M64430 Quabik 6130
Compressor Protection Control System Module Sizes
Stepper Motor 12 VDC
CEPL130351
30GUN,R
Part Load Data Percent Displacement, Standard Units
Displacement Compressors
Approx
110, 290B
255A 60 Hz
390B 60 Hz
330A/B
360B 50 Hz
390B 50 Hz
B1†
A1,B1 A1†,A2,B1 A1*,B1†,B2
Unloaded compressor Two unloaders, both unloaded
170, 270A
190, 290A, 360A/B
A1*,B1*,B2
Required Hardware for Additional Unloaders
150-210
Head Pressure Control
Pumpout
Power
FAN Arrangement FAN Relay Normal Control
Service Test See Both main power
Scrolling Marquee Display
Modes
GEN.O Test
Strt
Run Status Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
SUB-MODE Keypad Range Item Expansion Comment Entry View
Vers
SUB-MODE Keypad Range Item Expansion Comment Entry Test
Service Test Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
Outs
Pressure Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
Temperature Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
Set Point Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
SUB-MODE Keypad Range Item Expansion Comment Entry GEN.I
Inputs Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
Reading and Changing Chilled Fluid Set Point
Crct
Configuration Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
Outputs Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
SUB-MODE Keypad Range Item Expansion Comment Entry GEN.O
CCN
OPT1
OPT2
EMM
240
Rset
Example of Temperature Reset Return Fluid Configuration
SUB-MODE Keypad Display Item Expansion Comment Entry Rset
Example of Configuring Dual Chiller Control Slave Chiller
Example of Configuring Dual Chiller Control Master Chiller
SUB-MODE Keypad Entry Display Item Expansion Comment Rset
SUB-MODE Keypad Display Item Expansion Comment Entry OPT2
Example of Compressor Lead/Lag Configuration
Time Clock Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
SUB-MODE Keypad Entry Item Expansion Comment Range Time
Setting an Occupied Time Schedule
Operating Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
Mode no Item Expansion Description
Operating Modes
Alarms Mode and Sub-Mode Directory
Example of Reading and Clearing Alarms
Configuration
Configuring Temperature Reset
Mode Keypad SUB-MODE
Entry Expansion
RED LED Entry Expansion Configuration
Configuring Demand Limit
DLS2
Troubleshooting
To 20 mA Demand Limiting
Page
Alarm and Alert Codes
T051
FSM
By Control Method Cause Code Alert GENERATED?
EWT
LCW
T170
T153
T155
T173
T205
T203
T204
T206
Oil Charge
Service
Electronic Components
Compressor OIL Required
Cooler Thermistor Locations
Plugs
Components for Part Number Plugging
Condenser Coils
Cooler Head Bolt Tightening Sequence Typical Tube Sheet
Condenser Fan Adjustment Hz Low Noise Fan Option Units
Dimension FAN Type
Printed Circuit Board Connector
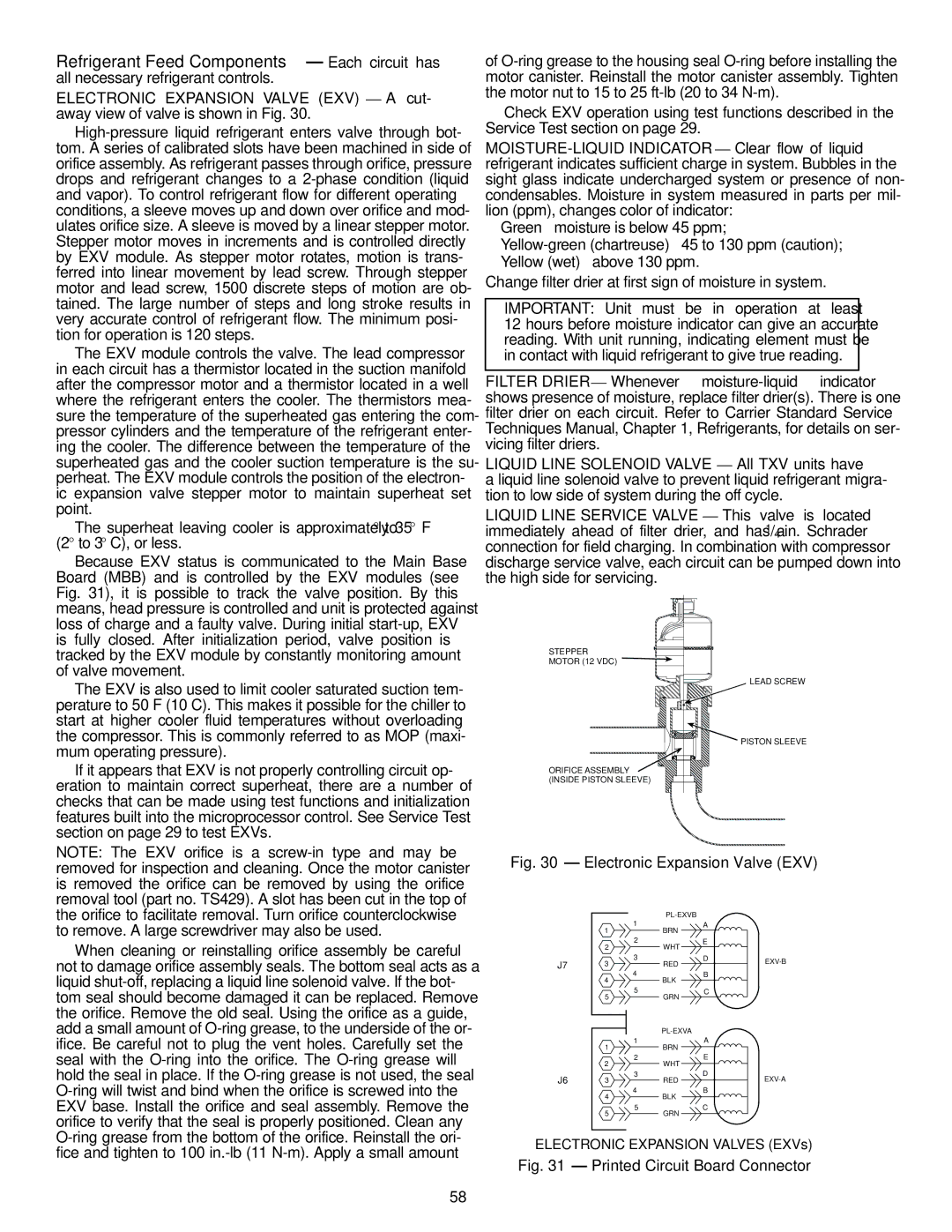
Refrigerant Feed Components Each circuit has
Thermistors Temperature Sensors
Drop B
5K Thermistor Temperature F vs Resistance/Voltage
Drop a
5K Thermistor Temperature C vs Resistance/Voltage
Temp Voltage Resistance Drop
200,510
30GTN,R Units
Pressure Switch Settings Psig kPa
Switch Cutout CUT-IN
30GUN,R Units
PRE-START-UP
System Check
Maximum Ambient Temperature 125
Temperature Limits for Standard Units
Temperature
START-UP and Operation
Refrigerant Circuit
Field Wiring
Nominal and Minimum Cooler Fluid Flow Rates
CWP
ALM
Hgbps
Energy Management Module EMM Wiring
Compressor Expansion Board CXB Accessory Wiring
Description Status Default Units Point
Unit Configuration Settings
OPTIONS1 Options Configuration
Description Status Default Point
Alarmdef Alarm Definition Table
OPTIONS2 Options Configuration
Appendix a CCN Tables
Resetcon Temperature Reset and Demand Limit
Brodefs Broadcast POC Definition Table
Circadio Circuit a Discrete Parameters
Aunit General Unit Parameters
Circaan Circuit a Analog Parameters
Description Status Units Point Forceable
Circban Circuit B Analog Parameters
Circbdio Circuit B Discrete Parameters
Options Unit Parameters
Strthour
Description Status Units Point
Description Status Units Point Defaults
Currmods
Line Description Point
CSM/FSM Equipment Table Type 621H, Block
Description Status Point
Appendix B Fluid Drop Pressure Curves
Cooler Fluid Pressure Drop Curves 30GUN,GUR040-110
Cooler Fluid Pressure Drop Curves 30GUN,GUR130-210
Appendix B Fluid Drop Pressure Curves
Cooler Pressure Drop KEY
Appendix B Fluid Drop Pressure Curves
Cooler Fluid Pressure Drop Curves 30GUN,GUR230B-315B
Cooler Fluid Pressure Drop Curves 30GTN,GTR040-110
Cooler Fluid Pressure Drop Curves 30GTN,GTR130-210
Appendix B Fluid Drop Pressure Curves
Module B 30GTN,GTR230,245 Module B 30GTN,GTR255,290,315
Service Training
Call for Free Catalog
Remove and use for job file Preliminary Information
START-UP Checklist for Comfortlink Chiller Systems
Equipment Chiller Model no
Preliminary Equipment Check Check box if complete
System Fluid Volume in Loop Type System
UnitStart-Up
Unit Start-Up
Ccnb
Description Status Units Value Ctrl
Ccna
Baud
Slct Heating Cooling Setpoint Select
CND.P RMT.A
All Units