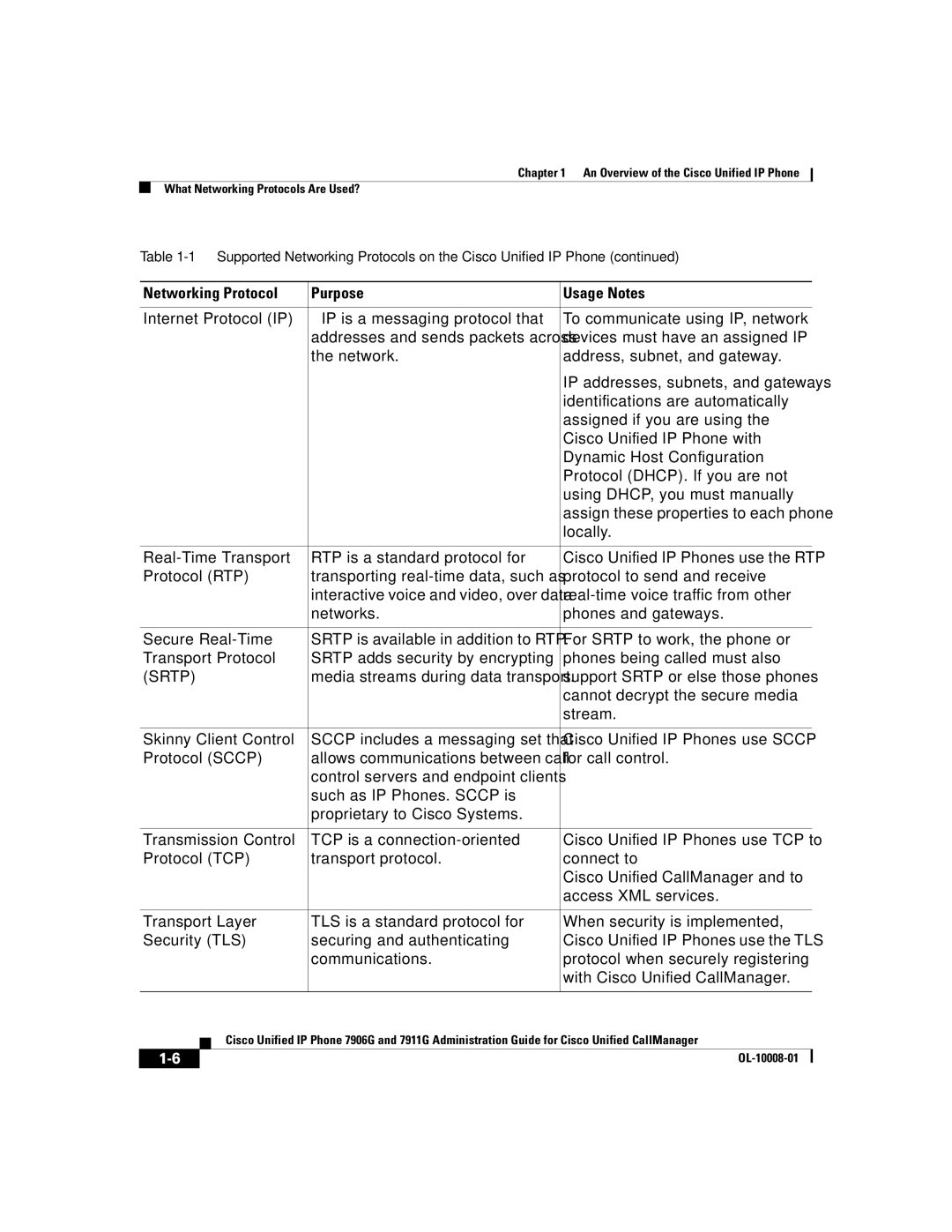
7906G, 7911G specifications
The Cisco Systems 7911G is a versatile IP phone designed to enhance communication in enterprise environments. Targeting workers in various organizational settings, this model is known for its reliability, ease of use, and robust features that cater to both basic and advanced telephony requirements.One of the key features of the Cisco 7911G is its support for Voice over IP (VoIP) technology. Using this technology allows for the transmission of voice signals over the internet rather than through traditional telephone lines. This not only reduces telephony costs but also offers enhanced functionality that integrates seamlessly with existing communication systems.
The phone is equipped with a monochrome graphical display that provides users with clear visibility of their call status, directory information, and menu options. With a resolution of 128x64 pixels, the screen is large enough to offer important information without overwhelming the user. This simplicity makes it an ideal choice for users who require straightforward functionality without the complexity of advanced features.
Ergonomically designed, the Cisco 7911G features a comfortable keypad with dedicated buttons for frequently used functions such as mute, hold, and transfer. It supports multiple lines, providing users with the ability to manage multiple calls simultaneously. Additionally, it offers programmable line keys that can be customized for speed dial or as soft keys for quick access to features.
The device supports Power over Ethernet (PoE), which allows the phone to receive power through the network cable rather than needing a separate power source. This feature not only simplifies installation but also enhances mobility within the workspace, as it reduces cable clutter.
Another significant characteristic of the Cisco 7911G is its compatibility with Cisco Unified Communications Manager, which ensures centralized management of telephony systems. It also supports a range of audio codecs that help in delivering high-quality audio during calls, reducing latency and improving overall communication quality.
Security is also a focus with the Cisco 7911G, as it features a secure access feature that includes Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP) for encrypted voice communications. This ensures that sensitive conversations are protected from eavesdropping.
Overall, the Cisco Systems 7911G is a reliable, feature-rich IP phone that provides an excellent solution for organizations looking to upgrade their communication systems. Its combination of user-friendly design, powerful integrations, and security features makes it a cornerstone in the suite of Cisco telecommunications solutions.