Page
Welcome
Student-Centered, Instructor-Facilitated
One Size Does Not Fit All
Hands-On, Skills-Based
Global Community
Guide Overview
Prerequisites
II. Course Overview
Target Audience
Course Description
Lab Requirements
Certification Alignment
Course Overview
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
III. Teaching Guide for Each TI
Nomenclature
Learning objective LO
Target indicator TI
Module
Lesson
Module 1 WANs and Routers
Overview
Module 1 Caution
WANs
Introduction to WANs
Introduction to routers in a WAN
Router LANs and WANs
ROM
Role of Routers in a WAN
Academy approach to hands-on labs
Router physical characteristics
Routers
Router external connections
Management port connections
Console Port Connections
Connecting Router LAN interfaces
Connecting WAN interfaces
Module 1 Summary
Module 2 Introduction to Routers
Module 2 Caution
Router user interface
Operating Cisco IOS Software
Purpose of Cisco IOS software
Router user interface modes
Cisco IOS software features
Operation of Cisco IOS software
Starting a Router
Router LED indicators
Initial router bootup
Initial startup of Cisco routers
Router login
Establish a console session
Keyboard help in the router CLI
Enhanced editing commands
Router command history
Troubleshooting command line errors
Show version command
Module 2 Summary
Module 3 Configuring a Router
Module 3 Caution
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Configure a Router
CLI command modes
Configuring a router name
Configuring router passwords
Examining the show commands
Configuring a serial interface
Making configuration changes
Configuring an Ethernet interface
Router#copy running-config startup-config
Finishing the Configuration
Importance of configuration standards
Configuring an interface description
Interface descriptions
Login banners
Configuring message-of-the-day Motd
Host name resolutions
Configuring host tables
Configuration backup and documentation
Backing up configuration files
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Module 3 Summary
Use the show cdp neighbors command
Module 4 Learning about Other Devices
Module 4 Caution
Discovering and Connecting to Neighbors
Introduction to CDP
Essential Labs Optional Labs
Information obtained with CDP
TLV
Implementation, monitoring, and maintenance of CDP
Creating a network map of the environment
Troubleshooting CDP
Disabling CDP
Command Purpose
Establishing and verifying a Telnet connection
Getting Information about Remote Devices
Telnet
Router131.108.100.152
Ctrl -Shift -6 then
Disconnecting and suspending Telnet sessions
Advanced Telnet operation
Resume
Alternative connectivity tests
StanlyLab#show sessions
LAB-A#trace lab-e
LAB-B#ping lab-c
LAB-D#ping lab-c
LAB-A#trace lab-d
Troubleshooting IP addressing issues
LAB-C#show ip route
Module 4 Summary
Module 5 Managing Cisco IOS Software
How a Cisco device locates and loads the Cisco IOS
Router Boot Sequence and Verification
Stages of the router power-on boot sequence
Essential Labs Optional Labs None Core TIs All Optional TIs
Using the boot system command
Configuration register
Troubleshooting IOS boot failure
Managing the Cisco File System
Additional Resources
IOS file system overview
IOS naming convention
Enter copy tftp running-config
Managing configuration files using Tftp
Managing configuration files using copy and paste
Select Transfer Capture Text
Show running-config
Managing IOS images using Tftp
Managing IOS images using XModem
Environment variables
File system verification
Discuss the following alternatives with the students
Module 5 Summary
Module 6 Routing and Routing Protocols
Module 6 Caution
Introduction to Static Routing
Introduction to routing
Static route operation
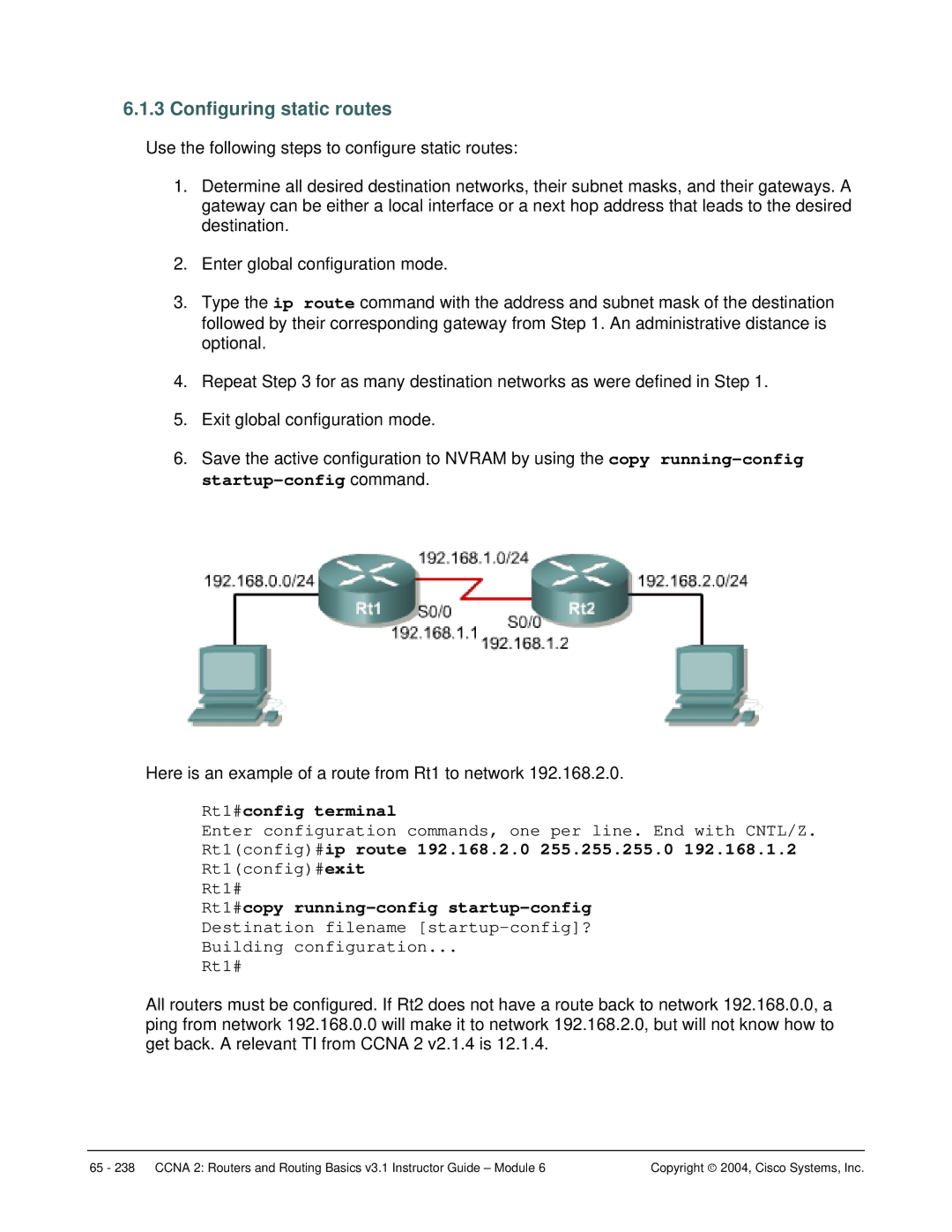
Rt1config#ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0
Rt1config#ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 s0
Rt1config#ip route 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.2
Configuring static routes
Rt1#config terminal
Configuring default route forwarding
Verifying static route configuration
Troubleshooting static route configuration
Show ip route output Rt1#show ip route
Rt1#show interfaces s0
Rt1#ping
Dynamic Routing Overview
Introduction to routing protocols
Autonomous systems
Distance vector routing protocol features
Purpose of a routing protocol and autonomous systems
Identifying the classes of routing protocols
Link-state routing protocol features
Routing Protocols Overview
Routing configuration
Path determination
Routing protocols
IGP versus EGP
Module 6 Summary
Module 7 Distance Vector Routing Protocols
Overview
Module 7 Caution
Distance vector routing updates
Distance vector routing loop issues
Distance Vector Routing
Problem Routing Loops
Defining a maximum count
Eliminating routing loops through split horizon
Routing Update
Avoiding routing loops with triggered updates
Route poisoning
Preventing routing loops with holddown timers
RIP
Configuring RIP
RIP routing process
Using the ip classless command
Common RIP configuration issues
Verifying RIP configuration
Troubleshooting RIP update issues
LAB-A#debug ip rip
Preventing routing updates through an interface
Load Balancing with RIP
Integrating static routes with RIP
Igrp
Load balancing across multiple paths
Essential Labs Optional Labs Core TIs
Igrp features
Igrp metrics
Igrp stability features
Igrp routes
Configuring Igrp
Verifying Igrp Configuration
Migrating from RIP to Igrp
Troubleshooting Igrp
Ip classless command
Module 7 Summary
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Module 8 TCP/IP Suite Error and Control Messages
Module 8 Caution
Icmp
Overview of TCP/IP Error Message
Error reporting and error correction
Icmp message delivery
Using ping to test destination reachability
Unreachable networks
Detecting excessively long routes
Miscellaneous error reporting
Echo messages
Destination unreachable message
TCP/IP Suite Control Messages
Introduction to control messages
Icmp redirect/change requests
Address mask requests
Clock synchronization and transit time estimation
Information requests and reply message formats
Router discovery message
Router solicitation message
Congestion and flow control messages
Module 8 Summary
Module 9 Basic Router Troubleshooting
Module 9 Caution
Show ip route command
Examining the Routing Table
Determining the gateway of last resort
Determining route administrative distance
Determining route source and destination
Determining L2 and L3 addresses
Determining the last routing update
Determining the route metric
Determining the route next hop
Using a structured approach to troubleshooting
Network Testing
Introduction to network testing
Observing multiple paths to destination
Layer 3 troubleshooting using ping
Testing by OSI layers
Layer 1 troubleshooting using indicators
Layer 7 troubleshooting using Telnet
Troubleshooting Layer 2 using the show interfaces
Troubleshooting Router Issues Overview
Troubleshooting Layer 1 using show interfaces
Troubleshooting using show cdp
Troubleshooting using traceroute
Troubleshooting routing issues
Troubleshooting using show controllers
Introduction to debug
Module 9 Summary
Show cdp Traceroute Show controllers serial Debug
Module 10 Intermediate TCP/IP
Module 10 Caution
TCP Operation
TCP operation
Synchronization or three-way handshake
Denial of service attacks
Windowing and window size
Sequencing numbers
Positive acknowledgements
UDP operation
Overview of Transport Layer Ports
Multiple conversations between hosts
Ports for services
Ports for clients
Port numbering and well known port numbers
Example of multiple sessions between hosts
Comparison of MAC addresses, IP addresses, and port numbers
Module 10 Summary
Module 11 Access Control List ACLs
Access Control List Fundamentals
Introduction to ACLs
How ACLs work
Rt1config#access-list 1 permit 192.168.0.1 ?
Rt1config#access-list ?
Rt1config#access-list 1 permit ?
Creating ACLs
C.D Wildcard bits Log
Function of a wildcard mask
Verifying ACLs
Access Control Lists ACLs
Standard ACLs
Rt1config#access-list 101 ?
Rt1config#access-list 101 permit ?
Extended ACLs
Named ACLs
Placing ACLs
Firewalls
Restricting virtual terminal access
Module 11 Summary
IV. Case Study
Overview and Objectives
Scenario and Phase 1 Project Description
Phase 2 IP Addressing
Network Diagram IP Addressing
Phase 3 Basic Router and Workstation Configuration
Boaz Center
Instructor approval Date
Phase 4 Access Control Lists
Ping from Router Boaz to Workstation
Eva Security management documentation Boaz
Phase 5 Documenting the Network
Configuration management documentation Boaz
Eva
Case Study Deliverables
General Documentation
Technical Documentation
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Phase 1 Project Description
Case Study Instructor Notes
Class Range
Optional
Phase 5 Documenting the Network Sample outputs Boaz
Case Study Instructor Sample Outputs
Boaz#show ip interface brief
Boaz#show startup-config Using 1090 out of 32762 bytes
Security Management documentation Boaz
Boaz#show ip interface
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Phase 5 Documenting the Network Sample outputs Centre
Configuration Management documentation
Centre#show version
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Security Management documentation Centre
Centre#show ip interface
Centre#show ip access-lists
Phase 5 Documenting the Network Sample outputs Eva
Configuration Management documentation Eva
Eva#show hosts
Eva#show startup-config Using 1156 out of 32762 bytes
Security Management documentation Eva
Eva#show ip interface
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Appendices
Appendix a Cisco Online Tools and Utilities
Output Interpreter
Error Message Decoder
Software Bug Toolkit
IP Subnet Calculator
Password Recovery Procedures
TAC Case Collection
Software Advisor
Feature Navigator
TAC Advanced Search
What is meant by best practices?
Best Practices
Nets
Nets Standards
Literacy, math, and science standards
Web Links
Timss report
Timss Report Participating Countries
Student-centered learning
Learner Model Academy Student
Multiple intelligences
Multiple Intelligences
Web Links
Inquiry-based learning
Inquiry Based Learning
Special needs
Special Needs
Web Links
Learning disabilities
Learning Disabilities
Strategies for Teaching Students with Learning Disabilities
Lab-Centric Instruction
Ccna labs
PPP Isdn
Ccnp labs
Ccnp Labs
Web Links
Netlab
Web Links
Simulations
Simulations
Sponsored curriculum labs
Sponsored Curriculum Labs
Sponsored Curriculum Labs
IT Essentials PC Hardware and Software IT Essentials
IT Essentials Network Operating Systems
Fundamentals of Voice and Data Cabling
Fundamentals of Unix
Fundamentals of Java Programming
Fundamentals of Web Design
Http//cisco.netacad.net/cnacs/prot-doc/newcourses.html
Emerging technologies
PIX Firewall PhotoZoom
Wireless solutions
Troubleshooting
Steps in the Problem-Solving Model
Teaching Methods Web Resources
Project-based Instruction
Challenges and projects
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Dartmouth Problem-Solving Cycle
Design activities
Web Links
Cluster Diagram
Brainstorming
Gifted Education a Resource Guide for Teachers
Case studies
Case Studies
Case Study Teaching in Science a Bibliography
Web research
Cisco.com
Instructional Strategies
Instructor-led classrooms
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Self-paced instruction
Cooperative/collaborative work
Pairs or partners
Small groups
Large groups
Teams
Competitive teams
Whole class
Student-led discussions Demonstrations Presentations
Jigsaws
Jigsaw Puzzle
Ask the right questions
Ask the Right Questions
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
6 PMI
PMI
Problem-Solving Matrix
Graphic organizers
Flowchart
Extended Star Topology in a Multi-Building Campus
Digital Signal
Data Encapsulation
Local Area Networks and Devices
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
RFI EMI
Setting goals
Kinesthetic activities
Kinesthetic Activities
Web Links
Assessment Strategies
Review strategies
Journals and reflection
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Web Links
Rubrics
Grading Rubric Sample
Rubistar http//rubistar.4teachers.org
Portfolio
Guidelines for Portfolio Assessment in Teaching English
Oral exams
Oral Exams
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc
Lab exams
Lab Exams
Web Links
Six lenses
Six Lenses
Copyright 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc