RAID Array 3000 Controller Shelf
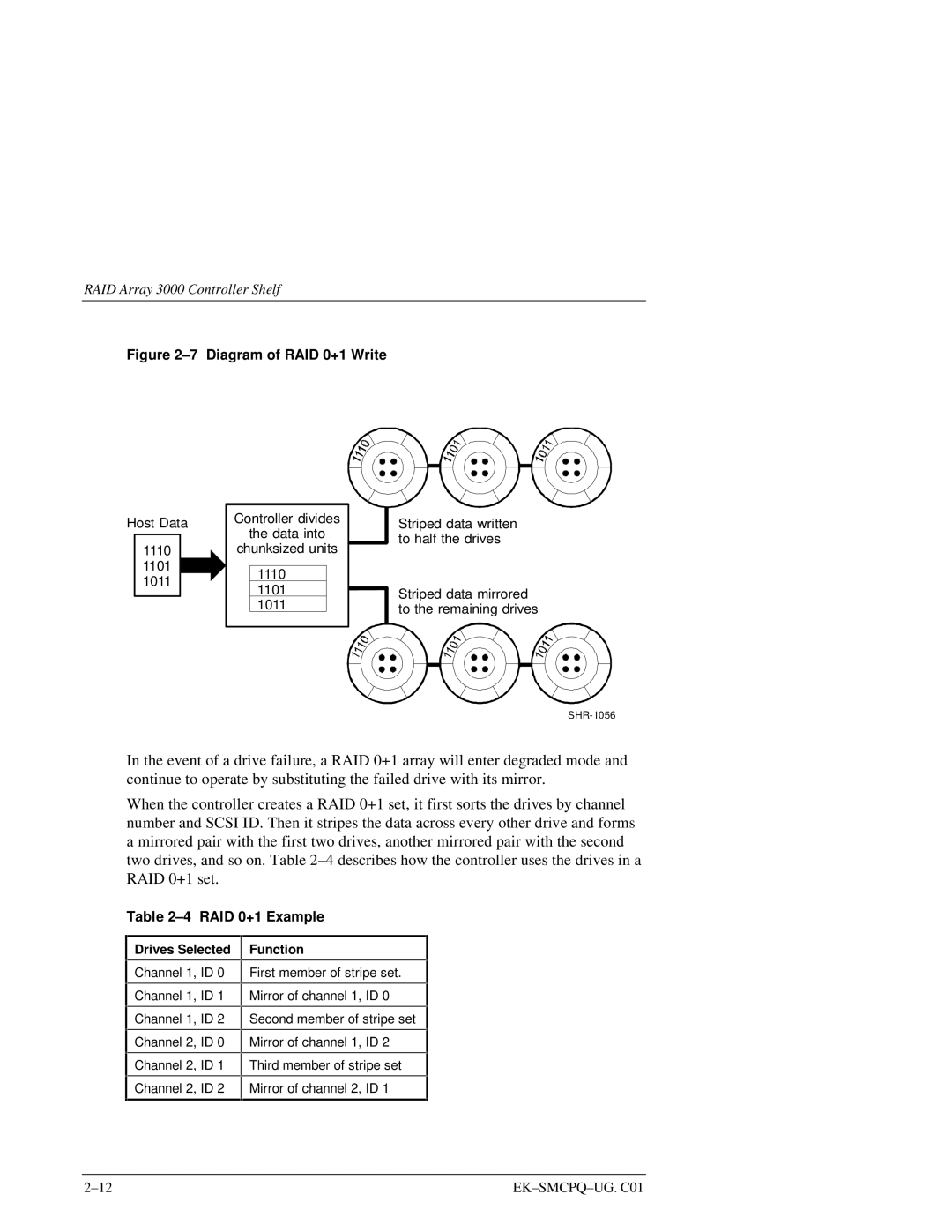
Figure 2–7 Diagram of RAID 0+1 Write
Host Data | Controller divides | Striped data written | |||
the data into | |||||
| to half the drives | ||||
1110 | chunksized units | ||||
| |||||
1101 |
|
|
|
| |
| 1110 |
|
| ||
1011 |
|
|
| ||
| 1101 |
| Striped data mirrored | ||
|
|
| |||
|
| 1011 |
| ||
|
|
| to the remaining drives | ||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
| |
In the event of a drive failure, a RAID 0+1 array will enter degraded mode and continue to operate by substituting the failed drive with its mirror.
When the controller creates a RAID 0+1 set, it first sorts the drives by channel number and SCSI ID. Then it stripes the data across every other drive and forms a mirrored pair with the first two drives, another mirrored pair with the second two drives, and so on. Table
Table 2–4 RAID 0+1 Example
Drives Selected
Channel 1, ID 0
Channel 1, ID 1
Channel 1, ID 2
Channel 2, ID 0
Channel 2, ID 1
Channel 2, ID 2
Function
First member of stripe set.
Mirror of channel 1, ID 0
Second member of stripe set
Mirror of channel 1, ID 2
Third member of stripe set
Mirror of channel 2, ID 1