RAID Array 3000 Controller Shelf
From the storage shelf’s perspective, the controller receives the I/O requests from the host and directs them to the devices. Since the controller processes all the I/O requests, it eliminates the
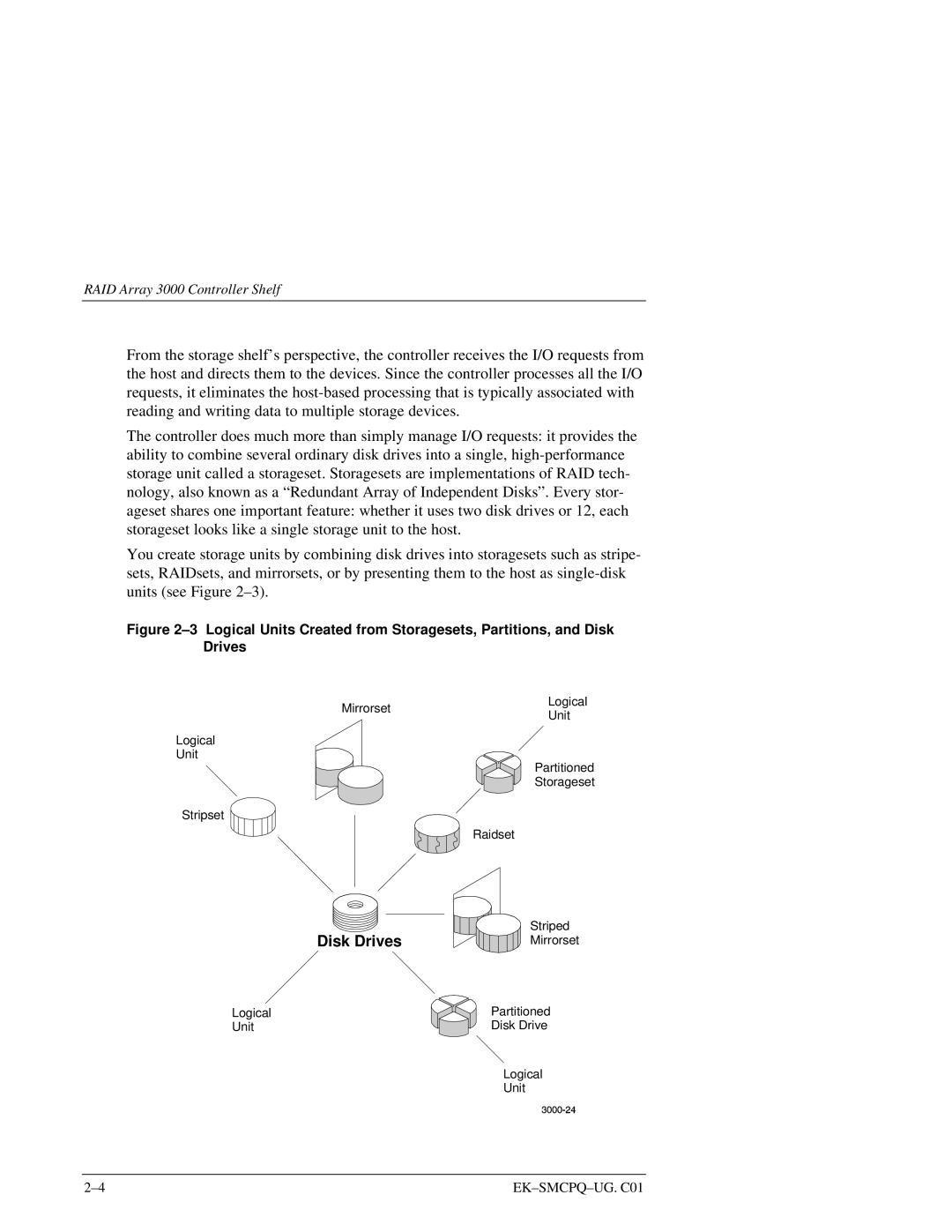
The controller does much more than simply manage I/O requests: it provides the ability to combine several ordinary disk drives into a single,
You create storage units by combining disk drives into storagesets such as stripe- sets, RAIDsets, and mirrorsets, or by presenting them to the host as
Figure 2–3 Logical Units Created from Storagesets, Partitions, and Disk Drives
Logical
Mirrorset
Logical
Unit
Unit
Partitioned
Storageset
Stripset
Raidset
Disk Drives | Striped |
Mirrorset | |
Logical | Partitioned |
Unit | Disk Drive |
| Logical |
| Unit |