RAID Array Controller
RAID 5
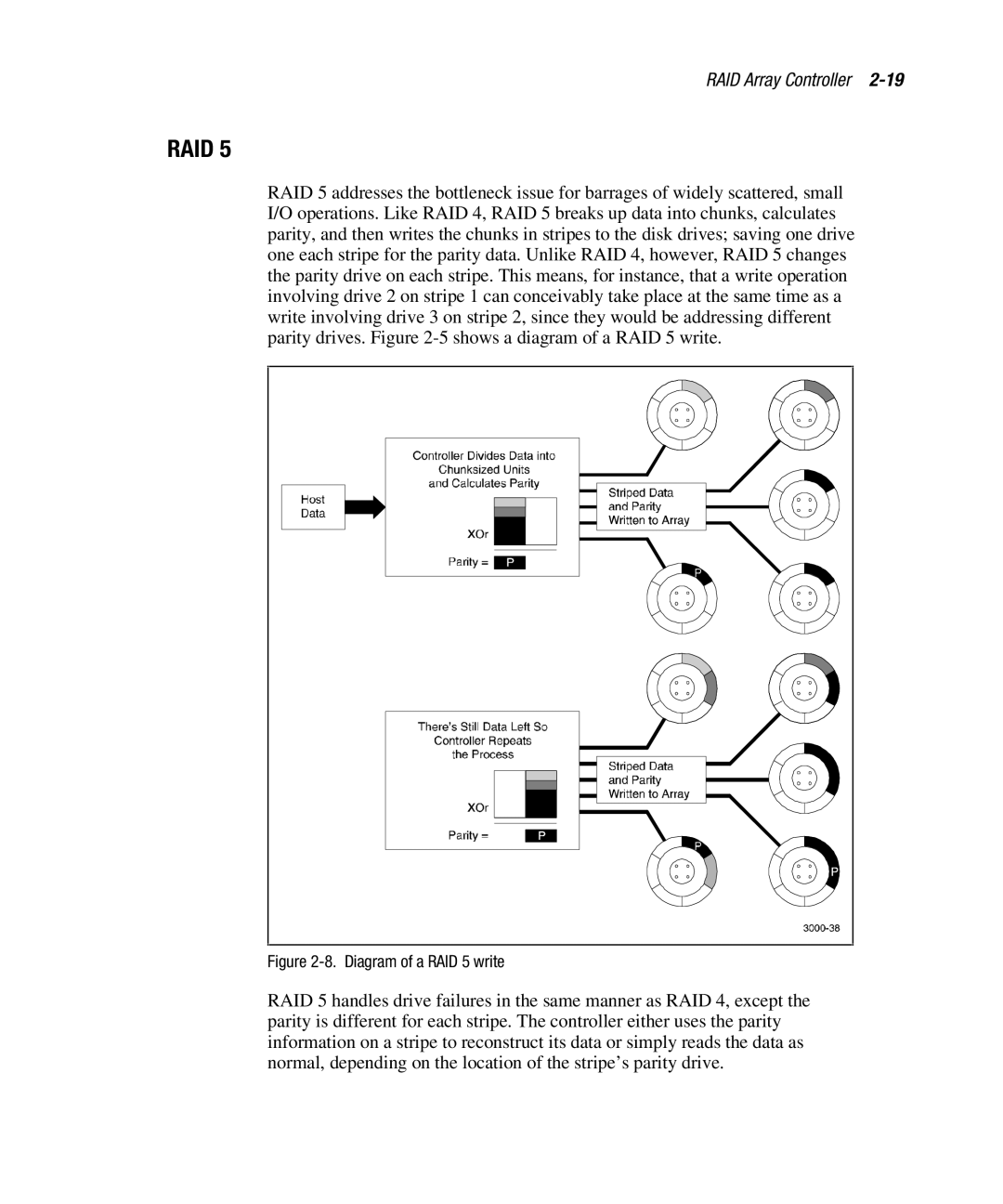
RAID 5 addresses the bottleneck issue for barrages of widely scattered, small I/O operations. Like RAID 4, RAID 5 breaks up data into chunks, calculates parity, and then writes the chunks in stripes to the disk drives; saving one drive one each stripe for the parity data. Unlike RAID 4, however, RAID 5 changes the parity drive on each stripe. This means, for instance, that a write operation involving drive 2 on stripe 1 can conceivably take place at the same time as a write involving drive 3 on stripe 2, since they would be addressing different parity drives. Figure
Figure 2-8. Diagram of a RAID 5 write
RAID 5 handles drive failures in the same manner as RAID 4, except the parity is different for each stripe. The controller either uses the parity information on a stripe to reconstruct its data or simply reads the data as normal, depending on the location of the stripe’s parity drive.