HARmonica Software Manual
USA
Elmo Motion Control Inc
HARSFEN0602ElmoHARmonicaSoftwareManual
HARSFEN0602ElmoHARmonicaSoftwareManual
Program execution
Preliminary
115
HARSFEN0602ElmoHARmonicaSoftwareManual
Language
100
HARSFEN0602ElmoHARmonicaSoftwareManual
Scope
About This Manual
Relevant documentation
Glossary
Harmonica
Units
Related Software
Position units
Can EDS
Speed and acceleration units
Current and torque
Internal Units and Conversions
Speed
Power DC voltage
Electrical angle
Peripherals
A/D converter
Digital inputs
Digital output
General RS232 Communications
Communication With the Host
1 RS232 Basics
Description
Echo
Errors and exceptions in RS232
Background Transmission
CANopen Communication
Interpreter Language
ElmoHARSFEN0602HARmonicaSoftwareManual Preliminarydraft
Expressions And Operators
Command line
Numbers
Mathematical And Logical Operators
XOR
Operator details
Subtraction
Addition
Multiplication
Division
Bitwise or
Bitwise not
Bitwise
Logical Equality
Logical Less than
Logical Greater than or equal
Logical
Logical or
Unary Minus
Logical not
Bitwise Left Shift and Right Shift operators
Mathematical functions
Expressions
Simple Expressions
Assignment Expressions
Built-in Function Calls
User variables
Time functions
Example ca1 =
Comments
User Function Calls
User Program Organization
Harmonica User Programming Language
Common
Line and Expression Termination
Line Continuation
Limitations
Expressions And Operators Numbers
General rules for operators
Syntax
Expressions Simple Expressions
System Commands
Built-in Function Calls
Program Flow Commands
For iteration
Labels Entry points
#@LABELNAME
XQ ##LOOP2
Infiniteloop
While iteration
While expression
Until iteration
If condition
Wait iteration
OFF
Switch selection
Break
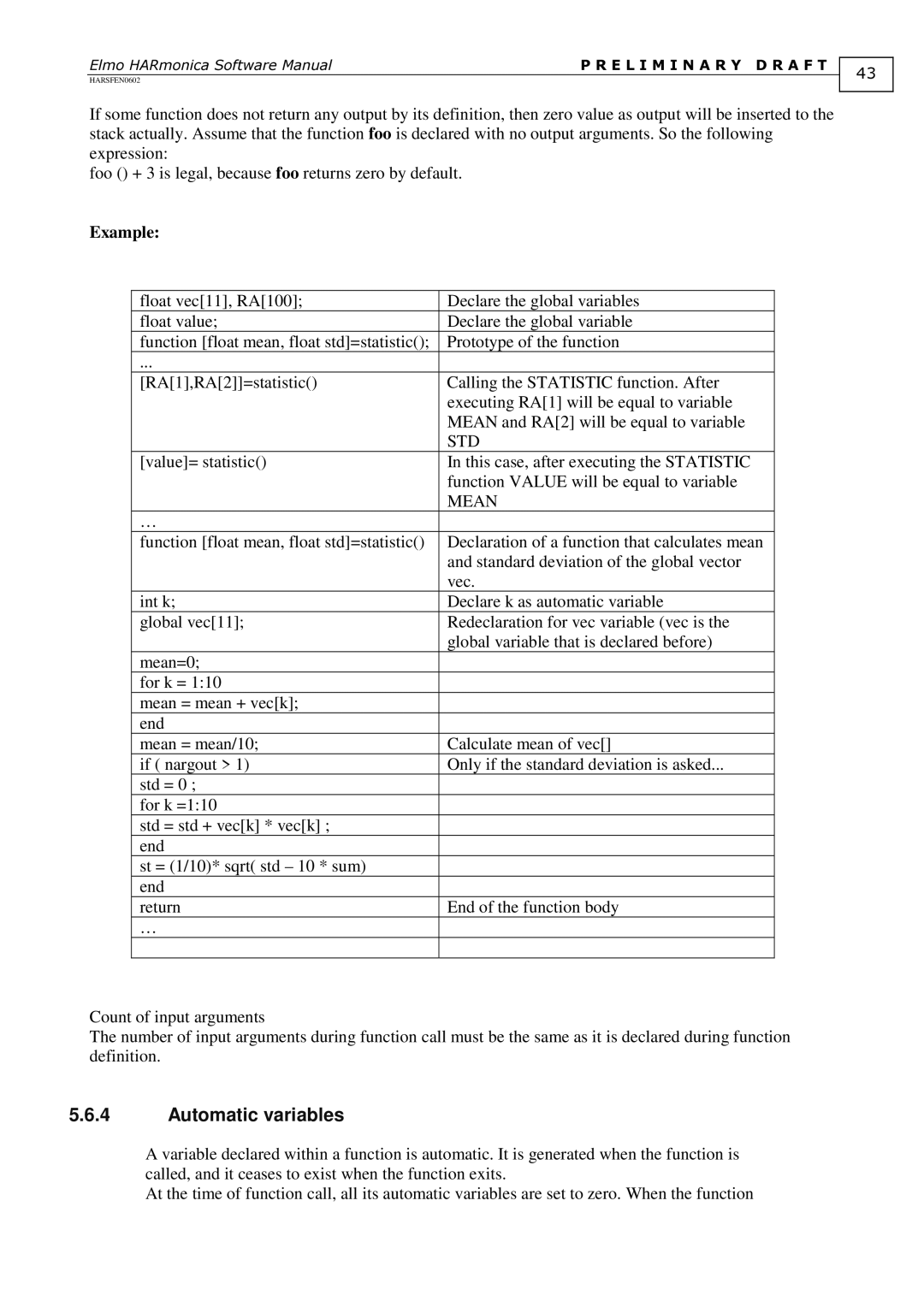
Functions Function definition
Syntax break
Function is absent
Count of output variables
Dummy variables
Automatic variables
STD
Mean
Jumps
Global variables
Functions and The Call Stack
##LABEL1
##LABEL2
Return
Automatic subroutines List Of Automatic Routines
Killing The Call Stack
##STARTNEW
#@AUTOI1
Autoer
Autoexec
Autostop
Autobg
Automatic Subroutine Mask
Automatic Routines Arbitration
##LOOP
#@AUTOI3
MI=MI8
#@TESTPARS
Program Development and Execution
Compilation Error List
Editing a Program
Compilation
HARSFEN0602ElmoHARmonicaSoftwareManual
Asusid@elmo.co.il
Preliminarydraft
Preliminarydraft
Preliminarydraft
Preliminarydraft
Asusid@elmo.co.il
#@AUTOEXEC
Downloading and Uploading a Program
Assisting Commands For Down/Upload LPN command
Binary data
Examples
CC command
CP command
Downloading a Program DL command
Program downloading process
Program execution
Uploading a Program LS command
Initiating a Program
Halting and resuming a program
XQ##TASK1
DB command
Automatic program running with power up
Save to Flash
Clear user program from Flash
Program status
Machine status
DB##MS
DB##PSN
Continuation of the program
Setting and clearing break points
Single step
Run to Cursor
Step Over
Step
Step Out
Setting stack
Getting stack entries
Getting call stack
View of local variables
View of global variables
HARSFEN0602ElmoHARmonicaSoftwareManual
Virtual Machines
Virtual Machine registers
Call Stack During Function Call
Usrsubj
Data types
Short reference
Op code structure and addressing modes
Rsltand
REM
Rsltor
Not
Bitwise and Operator
Alphabetic reference
Purpose
Algorithm
DIV Divide
CMP Compare
EOL End Of Line
Foritr for Loop Iteration
Algorithm itr iterator
For Bitwise or Operator
Freevac Free Virtual Machine
JMP Jump
Getcomm Get Command
Jmplabel Jump to the label
Jmpeol Jump
Jnzeol Jump Not Zero
JNZ Jump Not Zero
JZ Jump If Zero
Jzeol Jump If Zero
Link
MOV Assignment Operator =
MLT Multiply
REM Reminder
Not Bitwise not Operator
Rsltae Relational Operator =
Rslta Relational Operator
Rsltb Relational Operator
Rsltand Logical and Operator
Rsltbe Relational Operator =
SP SP
Rsltne Relational Operator !=
Rslte Relational Operator ==
Rsltor Logical or Operator
Setcomm Set Command
SHL Shift Left
SHR Shift Right
Spadd
Unarynot Logical not Operator
Syssubj Jump To System Subroutine
Usrsubj jump To User Subroutine
Usrsubrt Return from user subroutine
OP2
XOR Bitwise XOR Operator
BG,BT
Recorder
ILN
RPN
Signal Signal Name Command Length Description Type
Signal mapping
Defining the set of recorded signals
Programming the length and the resolution
Example The commands RV1=5RV2=1RC=3
Trigger events and timing
Slope and window trigger types
Trigger delay
Definition
Preliminary
100
Launching the recorder
Uploading recorded data
101
Byte Number Value Type
Preliminary Draft
Commutation
103
General
Brush DC motors
104
Bldc commutation policy
Mechanical and electrical motion Figures are missing
Rotor Magnetic field sensors
Commutation sensors
Shaft Angle Sensors
106
Detecting commutation errors loss of feedback
107
Hall sensors parameterization
Encoder parameterization
108
109
Commutation search General
Selecting the parameters
110
Method limitation
Protections
Continuous Vs. Six-Steps commutation
111
Continuous commutation
112
Winding shapes
113
Loading the commutation table
114
Current controller
115
ID = I hθ + 90 + Ib hθ + 210 + Ic hθ +
116
Peak/Continuous current limit selection
117
118
Torque command filter
32768
119
PI current controller
120
Current amplifier protections
121
122
Torque control Unit mode
123
Unit Modes
Speed mode Unit mode
11.2.1The software speed command
124
125
Speed Profiling using JV, AC and DC
126
11.2.2The auxiliary speed command
127
Stop management
RLS,FLS
128
Stepper mode Unit mode
129
Dual feedback mode UM=4
130
Dual feedback mode UM=4
131
Single feedback mode UM=5
132
12.1.1Switching Between Motion Modes
Position reference generator
Software reference generator
12.1.3The Idle Mode and Motion Status
133
12.1.2Comparison of the PT and the PVT interpolated modes
12.1.4Point-To-Point PTP Basic Point-To-Point
134
Example
135
More Complicated PTP Motions
136
Example On-The-Fly Change of The Position Target
137
Jogging
138
Example On the fly mode switching
139
Example Simple jogging
140
Vt = 3at − t0 2 + 2bt − t0 + c
141
Ifference Counts Msec 500 1000 1500 2000 2500
142
143
QP… QV… QT…
144
Motion Management
145
146
PVT Decisions Flow Chart
Mode Termination
PVT Motion Using can
147
PVT Motion Programming Message
148
Underflow
149
Programming Sequence for The Auto Increment PVT Mode
Parameters of The PVT Motion Mode
150
151
152
PT Motion What Is PT
153
Interpolation Mathematics
154
PT Motion Programming The Basic Mode
155
Flow chart of the basic PT mode is depicted below
PT Motion Using can
156
PT Motion Programming Message
157
Programming Sequence for The Auto Increment PT Mode
158
Parameters of The PT Motion Mode
External Position Reference Generator
159
External position reference generator
160
Xt = 10000 ⋅ cos2πt + ct
161
Ecam
162
163
164
Dividing Ecam table into several logical portions
165
166
On the fly Ecam programming using can
167
Initializing the external reference parameters
Jump-Free Motor Starting Policy
Stop management 12.3.1General description
168
Stop Manager Internals
169
VHN,VLN
XM,YM
Forward Limit Switch Marked as 4 in the Figure
Right Limit Switch Marked as 3 in the Figure
170
Rate and Acceleration Marked as 5 in the Figure
Position output of the stop manager
171
172
Sensors, I/O, and Events
Modulo counting Modulo Counting
Digital Outputs
173
Events, and response methods
174
Manual inquiry
Periodical Inquiry
175
Homing and Capture What Is Homing?
Automatic routines
Real time Motion management, Homing, Capture, and Flag
176
Homing Programming
Homing the auxiliary encoder
On the fly position counter updates
13.5.5A homing with home switch and index example
177
178
Switches location
Example Double homing corrects backlash offsets
179
Capturing
180
181
Limits, Protections, Faults, and Diagnosis
182
Current limiting
VLN
Speed Protection
183
Position Protection
184
185
Enable switch
Limit switches
Connecting an external brake
186
When the motor fails to start
Motion faults
187
188
14.9.2Inconsistent setup data
Diagnosis Monitoring motion faults
189
Polling the amplifier status
Sensor faults Motor cannot move
190
14.9.3Device failures, and the CPU dump
191
Commutation error is static i.e. Does not change in time
Commutation is lost General
Reasons and effect of incorrect commutation
192
Detection of Commutation Feedback Fault
Commutation is drifting i.e Changes in time
Double sensor systems
193
Controller
KPN
Speed Control 15.2.1Block diagram
194
Not found
Parameters of the Speed Controller
195
196
Position Controller 15.3.1Block Diagram
Parameters of the Position Controller
197
High Order Filter Block Types
198
Double lead block Block type=12
Fist order block Block type=14
199
Second order block Block Type=15
Scheduled Double lead block Block type=22
200
User Interface
An Example
Gain-Scheduling Algorithm
201
Automatic Controller Gain-Scheduling
202
KP = SpeedKpTable k KI = SpeedKiTable k
203
204
Table of Contents TOC
Appendix a The Harmonica Flash Memory Organization
Main partitions
Contents of Text1
Contents of Text2
Contents of Text3
206
Contents of Text4-Text7
Contents of Text8
Contents of Text9
207
Autostop Autobg Autorls
208
Autoena AUTOI1
AUTOI5
209
210
TOC
Compilation Done Flag
Function Symbol Table
Text Backup & Compiler data segment
211
Virtual Machine Code Segment
Variable Symbol Table
212
Automatic Routines Table
Appendix B Harmonica Internals
213
Software Structure
17.1.1The Initialization block
Idle Loop
214
Idle loop
215
Converter
216
Converter Call
Algorithm
18.5 Examples
217
JP##LABEL
JS##LABEL Label
218