3Com Corporation
Restricted Rights Legend
Restricted Rights Notification for U.S. Government Users
Proprietary Material
Page
Overview
Solutions
Functionality
Multiple LANs
Bridging
Translational
No Local Bridging
Transparent
This Manual Topic
This Notice Topic
Switches
Bridging Features and Capabilities
Introduction
Bridging Primer
Ethernet LAN
Ethernet Bridge
Example
Operation
WAN application, but you can also bridge across an X.25 WAN
Mixed LAN Bridging
MAC Addressing
LLC2 Local
LLC2 Local Termination
Termination
LT Example
Autolearn for Local Termination
Filtering
NetBIOS Name
Mac Address
Filtering
Spanning Tree Protocol
What Is It? Automatic Manual Spanning Tree Support
Dual Ethernet LANs
WAN or Permanent Virtual Circuit PVC for Frame Relay
Basic Remote Bridging Examples
Across a WAN
Example of Bridges in an SVC Arrangement
Connections
Bridge
LAN Interface
Support
Bridging
Interface Connections Between WAN and LAN
Setting Up WAN Operation for Bridging
Setting Up WAN Operation for Bridging
Configure
Parameters
Bridge Parameters
These parameters make up the Bridge Parameter Record
Maximum Number of Bridge Links
Stpe Control
Bad Hello Timeout
AUTO, MAN
MAN
Bridge WAN Data Priority used for Ethernet only
Learn Only Period used for Ethernet only
Aging Period used for Ethernet only
Bridged Protocols
Bridge Link Parameters
Parameters control the characteristics of this connection
Bridge links as links to the networks attached to it
Bridge Link
Entry Number
These parameters make up the Bridge Link Record
BridgeType
SR, TB, Bothsrandtb
Largest Frame Size
Hop Count Limit
MAC Address Filter Action
NONE, PASS, Block
Stpe Link State
Netbios Name Filter Action
Protocol Filter Action
NORMAL,RFC1294, Trans
Link Mode
Normal
Virtual Ring Number
Over the WAN
LAN Connection Table
LAN Connection
Table Parameters
ROUT, BRID, Brout
LAN Forwarder Type
Rout
LAN Connection Type
Codex
Encapsulation Type
Autocall Mnemonic
Lcon Queue Limit
OFF, on
Billing Records
OFF
Traffic Priority
Limiting Bridge Frame Sizes
Where bridging is done remotely across a WAN
Overview
Transmission times for large frames become significant
Sizes
Standard Frame
Maximum frame size
Max Frame Size Line Speed Range kbps
Configuring Translational Bridging
Translational Bridging Example
Bridge Frame Handling
Configuring
Configuring Source Route Bridging Operation
Node for SRB
Individual Bridge
Bridging
Procedure
Connecting a Station to a Server in Source Route Bridging
LAN for a Source Route Bridging operation
Located on remote LAN CCC Figure
Server’s Destination MAC Address Not on LAN AAA
LAN Bridge Link
WAN Adapter Transmits Each are Frame Across the WAN
Server Responds with Specifically Routed Test Frame
Then
Step Action Result/Description
Forwarder
Transparent Bridging for Ethernet LANs
Learning
Forwarder Example
LAN link WAN link Link error
Statistics
Filtering
Hardware Accelerator Functions
Hardware
Accelerator LAN/WAN Handlers
Forwarder Functions Forwarder Initialization
Aging
Learn Only Period
Forwarder Database and Spanning Tree
Using Filters
Frame is dropped
Multicast Link
List, the frame is dropped
Control menu located in the Main menu
TB Forwarding
Transparent Bridge Configuration Parameters
Local MAC Address
Bridge Link Number
Bridge Filtering
What is It? How Filtering is Used
Parameter Action
MAC Address Filtering
Parameter Action Value
Parameter
Process
MAC Filtering
Example of a Frame Passing on a Bridge Link
Mac Filtering Process Incoming and Outgoing Frames
Configuring the Bridge Link Record
How To Configure Example
MAC Address Filtering Examples
First Example
Configuring the MAC Address Filter Table
Address Links
Why it is Important
Identifying Address Links for MAC Addressing
Filtering works
Series Switch Support
MAC Wildcard Filtering
Categories
Configuring the MAC Address Filter Table
Broadcast frames in the LAN network
Incoming Source Address Link Action
These parameters make up the MAC Address Filter Table
PASS, BLOCK, PASSLIST, Blocklist
Pass
Incoming Destination Address Link Action
Outgoing Source Address Link Action
List of Links
Outgoing Destination Address Link Action
Protocol Filtering
These parameters make up the Protocol Filter Table Record
Protocol Filter
Protocol SAP hex value
Protocol Type
Protocol OUI/IP hex value
Protocol Value
Outgoing Protocol Link Action
Incoming Protocol Link Action
Dsap Values
Parameter Actions
Transparent Bridging
NetBIOS Name Filtering
Broadcasts to and from the SVR* name pattern
Forcing a Local
Checking NetBIOS
Domain With
Filters
How to Configure
Configuring NetBIOS Name Filtering
NetBIOS Name Filtering
Step Action
Step Action Result
Select Configure Configure
Entry Number 1 appears
Bridge Bridge Link
NetBIOS Name Filter Table
Configure NetBIOS
Bridge -NetBIOS Name Filter
Name Filter Table
Ascii
Typical Filtering
String Type
Incoming NetBIOS Name List of Links
Incoming NetBIOS Name Link Action
Outgoing NetBIOS Name List of LInks
Outgoing NetBIOS Name Link Action
NetBIOS broadcasts filtered on the link
NetBIOS Name Filtering Statistics
Each bridge link
Check Detailed
IBM NetBIOS Formats When to Use NetBIOS Name Filtering
NetBIOS Packet Formats
All of the following are true
Either one of the following is true
Spanning Tree Protocol Entity Stpe
Configuration Stpe Control= Auto Stpe Control = Manual Menu
Spanning Tree
Tree
Bridge Links
Spanning Tree Protocol Entity Stpe
Bridge Network
Stpe Parameter Setting Considerations
Example of a
Determining Root Links Designated Links
Setting the Root Bridge Spanning Tree
Bridge ID equals Bridge Priority Value in hex + MAC Address
Type of Network Speed Stpe Path Cost
Nature
Consider
Expected Number
SVCs
Two Bridge Links Between B3 and B4
Spanning Tree Protocol Entity Stpe
Timer Parameters
Spanning Tree Timers
Hello Timer
Max Age
Considerations
Other
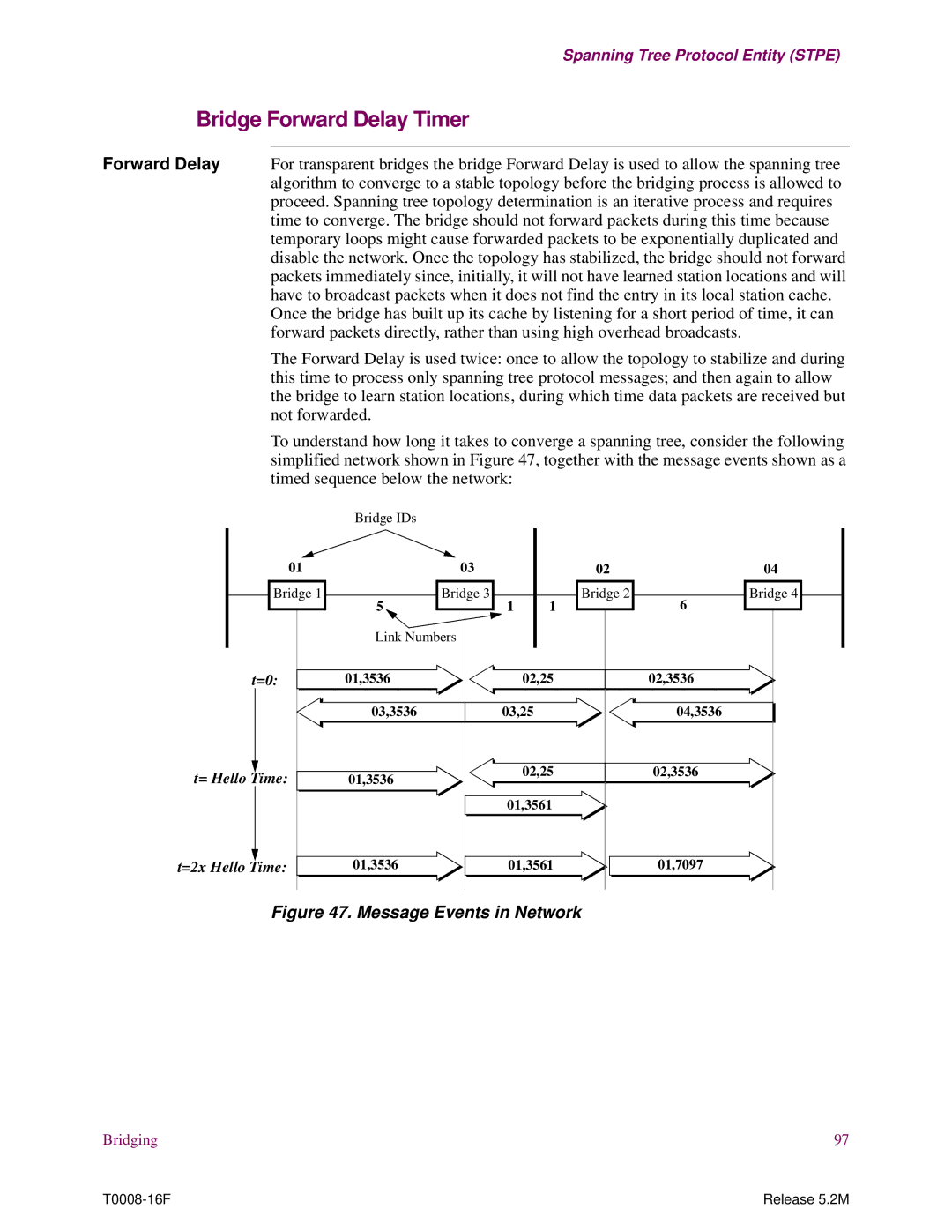
Message Events in Network
Bridge Forward Delay Timer
Spanning Tree Protocol Entity Stpe
Location and forwards packets to it properly
Aging Timer
Bridges can adjust to the change
LLC2 Local Termination
Preventing session timeouts in a Bridging application
Terminal session, causing
Well as network delays
Before Local
After Local
Improper LT
Supported
Topologies
Type Name Description
Proper LT configuration
LLC Protocol LLC Frame Description LLC2 Frame Description
Local Termination does not spoof
Local Termination spoofs
Bridging 105
Local Termination
Configuring Local Termination
Station Table Entry Number
Boot Type LLC LT Station
Step
T2 Rx Ack Timer
WAN Parameters T1Reply Timer
Local SAP
LLC Profile Name
Ti Inactivity Timer
Boot Type LLC LT WAN Parameters
N3 ACK Delay Count
N2 Retry Count
Tx Window Size
Configuration Entry Number
LCC LT WAN Data Priority
HIGH, MEDIUM, LOW
T1 Reply Timer
112 Bridging
Deleting LT Configuration Records
Mixed LAN Environment Limitations
27x switch, as shown in Figure
Mixed LAN Operation
Bridge Link Parameters menu
Select Configure Bridge
Bridge Link Parameters from
CTP Main menu, to activate Bridge link
Bothsrandtb
Dual LAN Ethernet
System powerup
Supported
Routing
Dual Ethernet LAN
Cmem
Parameters
For Details on
LAN Server Subsystem
Alarms
Example of LCC
Configuring the LSS Record
Record
Virtual Port’s MAC Address
Disable
ENABLE, Disable
Virtual Bridge ID
Path Trace Control
Statistics Menu screen
Bridge Statistics
Stpe Status
Spanning Tree Statistics
Status report
Term Description
State
Disabled The Stpe is disabled. If Stpe Control
Are
Parameter is MAN
Detailed Bridge Link Statistics First
Detailed Bridge Link Statistics
Screen Terms
RIF
Link Filter
Bridge Link Filter Summary
Summary
Description
Bridging 131
Stats Example
Transparent Bridge Forwarding Table Statistics
Stats Descriptions
Shown in Figure
Bridging 133
Terms-Transparent Bridge Second
Transparent Bridge Detailed Bridge Link Statistics
Received/transmitted of all types on this link
FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
Frame Totals This is a count of the number of frames
Detailed LAN Connection Statistics
LAN Connection Statistics
Statistics Menu
Detailed LAN Connection Statistics Second
Last clear diagnostic code This is the diagnostic code
Explains why the last call was cleared
Connection and explains why the call was cleared
SVCs. The possible states are Blank for PVCs blank
Bridging 139
Connection Summary Statistics
Example of LAN shows the LAN Connection Summary Statistics
Heading Description
LLC2 LT Session Summary Statistics
SAP
Remote MAC Addr
Heading
Session Statistics
LLC2 LT Detailed Session Statistics
Field, ring number, and bridge number information
Last Statistics Last time statistics were reset Reset
Routing information field used in all frames transmitted
Heading Description Local Station Session Summary
Heading Description Remote Spoofer Session Summary
Reset Statistics
148 Bridging
Technical Support
3ComFacts Automated Fax Service
Access by Analog Modem
Access by Digital Modem
Country Data Rate Telephone Number
Country Telephone Number
Support from
3Com
Country Telephone Number Fax Number
Numerics
Index
LAN
OUI
URL A-1
Index-5