4.7Servo Control
The actuator motor and the spindle motor are submitted to servo control. The actuator motor is controlled for moving and positioning the head to the track containing the desired data. To turn the disk at a constant velocity, the actuator motor is controlled according to the servo data that is written on the data side beforehand.
4.7.1Servo control circuit
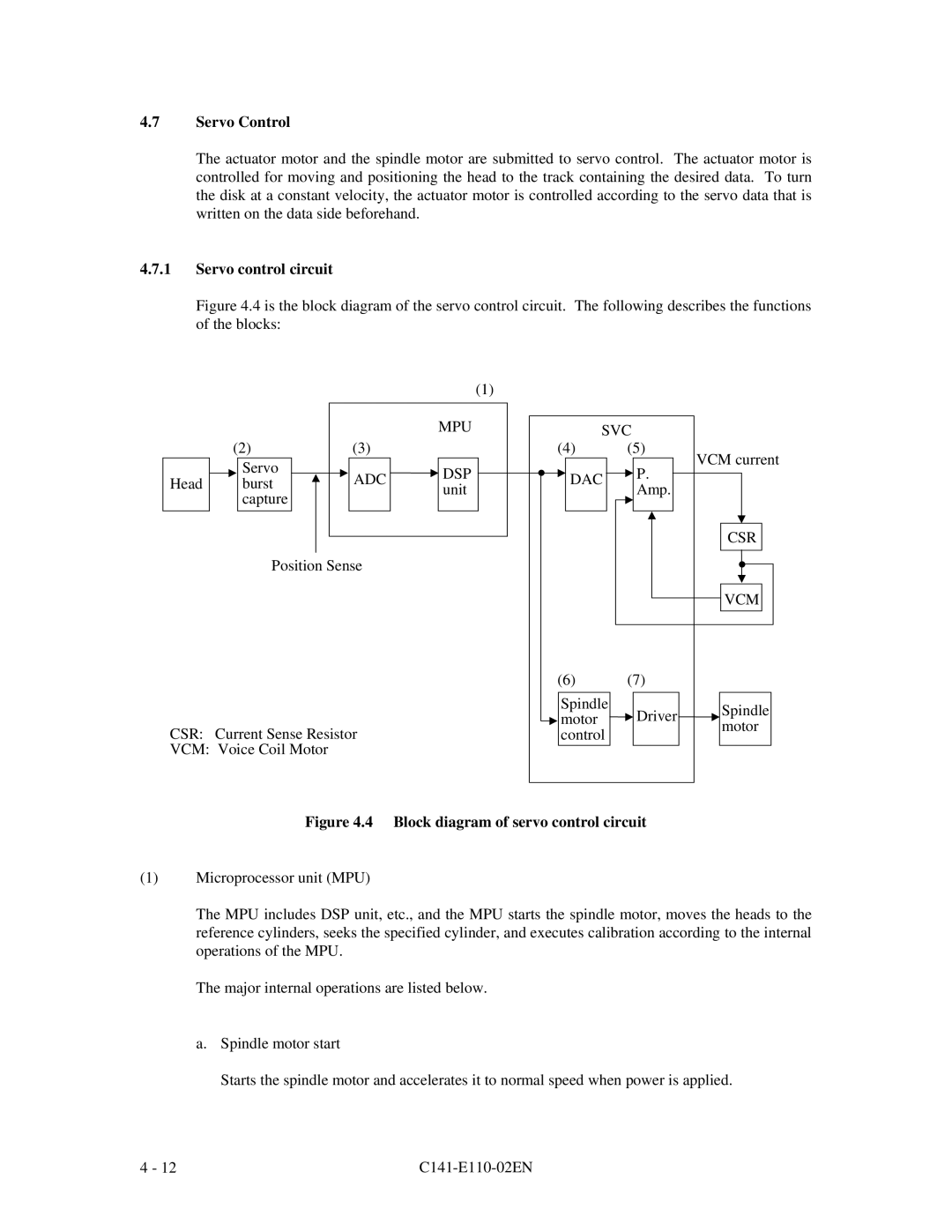
Figure 4.4 is the block diagram of the servo control circuit. The following describes the functions of the blocks:
Head
(2)
Servo burst capture
(1)
MPU
(3)
![]() ADC
ADC ![]() DSP unit
DSP unit
| SVC | ||
(4) |
| (5) | |
|
| VCM current | |
DAC | P. | ||
Amp. | |||
|
| ||
|
| CSR | |
Position Sense
CSR: Current Sense Resistor
VCM: Voice Coil Motor
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| VCM |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(6) |
| (7) |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Spindle |
|
| Driver |
| Spindle | |||
motor |
|
|
| |||||
|
|
| motor | |||||
control |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 4.4 Block diagram of servo control circuit
(1)Microprocessor unit (MPU)
The MPU includes DSP unit, etc., and the MPU starts the spindle motor, moves the heads to the reference cylinders, seeks the specified cylinder, and executes calibration according to the internal operations of the MPU.
The major internal operations are listed below.
a.Spindle motor start
Starts the spindle motor and accelerates it to normal speed when power is applied.
4 - 12 |
|