PRIMUSr 880 Digital Weather Radar System
TILT MANAGEMENT
The pilot can use tilt management techniques to minimize ground clutter when viewing weather targets.
Assume the aircraft is flying over relatively smooth terrain which is equivalent to sea level in altitude. The pilot must make adjustments for the effects of mountainous terrain.
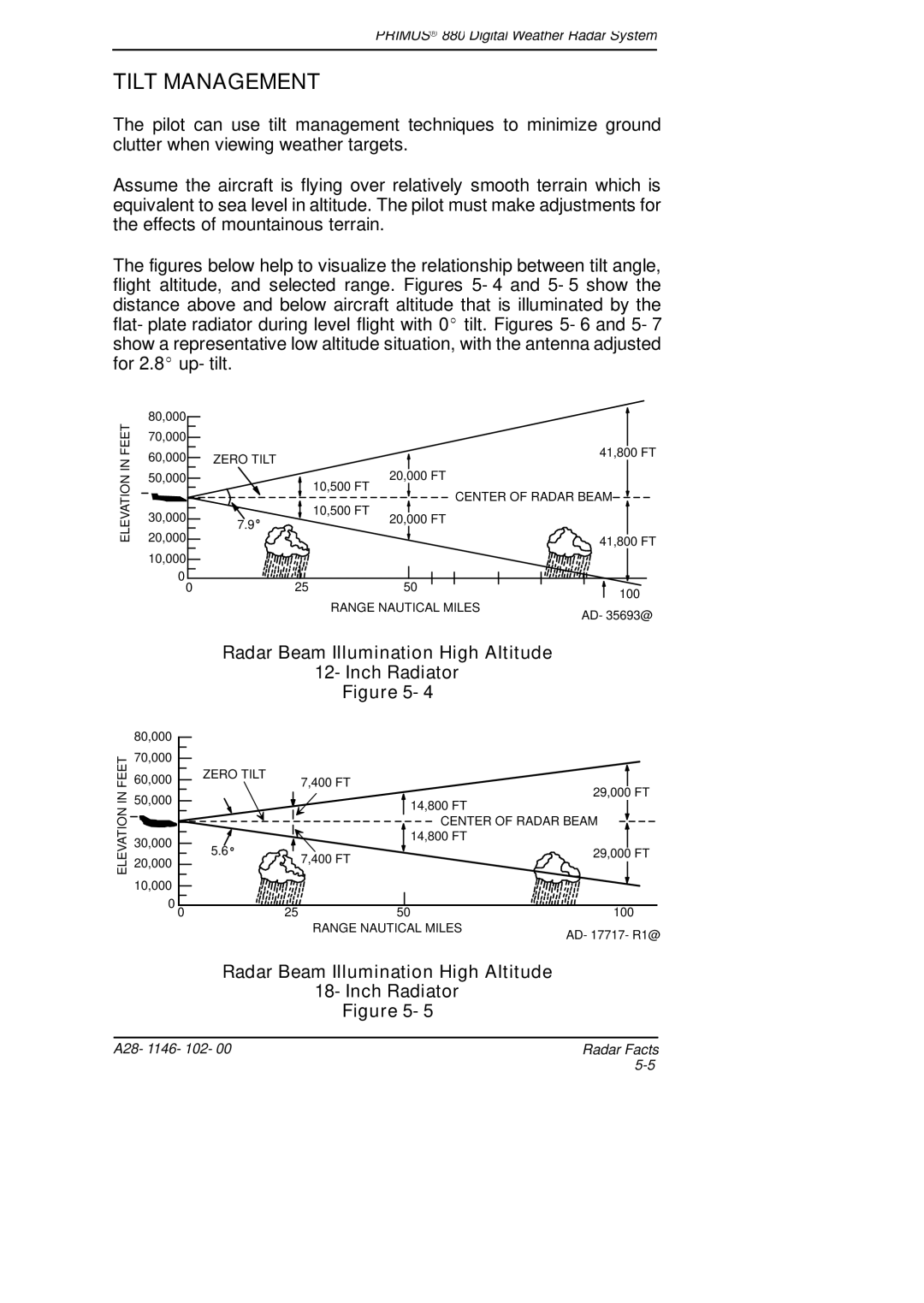
The figures below help to visualize the relationship between tilt angle, flight altitude, and selected range. Figures 5- 4 and 5- 5 show the distance above and below aircraft altitude that is illuminated by the flat- plate radiator during level flight with 0_ tilt. Figures 5- 6 and 5- 7 show a representative low altitude situation, with the antenna adjusted for 2.8_ up- tilt.
ELEVATION IN FEET
80,000 |
|
|
|
|
70,000 |
|
|
| 41,800 FT |
60,000 | ZERO TILT |
|
| |
20,000 FT |
|
| ||
50,000 |
|
|
| |
|
| 10,500 FT | CENTER OF RADAR BEAM | |
|
| 10,500 FT | ||
30,000 |
|
|
| |
7.9 | 20,000 FT |
|
| |
20,000 |
|
| 41,800 FT | |
|
|
| ||
10,000 |
|
|
|
|
0 | 25 | 50 |
|
|
0 |
| 100 | ||
|
| RANGE NAUTICAL MILES | ||
|
| AD- 35693@ | ||
|
|
|
| |
Radar Beam Illumination High Altitude
12- Inch Radiator
Figure 5- 4
ELEVATION IN FEET
80,000 |
|
|
| |
70,000 | ZERO TILT |
|
| |
60,000 | 7,400 FT |
| ||
| 29,000 FT | |||
50,000 |
|
| ||
|
| 14,800 FT | ||
|
|
| ||
|
|
| CENTER OF RADAR BEAM | |
30,000 | 5.6 |
| 14,800 FT | |
7,400 FT | 29,000 FT | |||
20,000 | ||||
|
| |||
10,000 |
|
|
|
0 0 | 25 | 50 | 100 |
RANGE NAUTICAL MILES | AD- 17717- R1@ |
|
Radar Beam Illumination High Altitude
18- Inch Radiator
Figure 5- 5
A28- 1146- 102- 00 | Radar Facts |
|