Maintenance & Service Guide
Maintenance & Service Guide
About This Book
Iv About This Book
Table of contents
Serial ATA Sata Drive Guidelines and Features
102
119
186
Page
Product Features
Feature Overview
Model
Microtower Components
1Microtower Components
Small Form Factor Components
2Small Form Factor Components
Installing the Operating System
Installing and Customizing the Software
Downloading Microsoft Windows Updates
Accessing Disk Image ISO Files
Installing or Upgrading Device Drivers Windows systems
Protecting the Software
Computer Setup F10 Utility
Computer Setup F10 Utilities
Using Computer Setup F10 Utilities
1Computer Setup F10 Utility
Computer Setup-File
2Computer Setup-File
Option Description Device Configuration
Computer Setup-Storage
3Computer Setup-Storage
Storage Options Sata Emulation
Shortcut to Temporarily Override Boot Order
Boot Order
DPS Self-Test
Computer Setup-Security
4Computer Setup-Security
USB Security
Network Boot
Slot Security
System IDs
System Security
Option Description Hardware Power
Computer Setup-Power
5Computer Setup-Power
Management
Computer Setup-Advanced
6Computer Setup-Advanced for advanced users
Recovering the Configuration Settings
Microtower Chassis Spare Parts
Illustrated parts catalog
Computer Major Components
Power supply, 300W
Description Spare part number Access panel
Front bezel
Description Spare part number
Cables
Chassis fan
Front I/O and USB assembly
Misc Parts
HP Business Digital Headset
Description Spare part number Hard drive
Drives
Misc Boards
Optical drive
Sequential Part Number Listing
Spare part Description Number
667727-001 Fan sink for use in models with Intel processors
Use only in HP Pro 3505 models
Intel Core i7 processor
Power supply
Small Form Factor SFF Chassis Spare Parts
Intel Core i5 processors
Intel Core i3 processors
Intel Pentium Dual-Core processors
Cables
Misc Parts
16X Sata DVD±RW drive 581600-001 DVD-ROM drive 581599-001
Illustrated parts catalog
Small Form Factor SFF Chassis Spare Parts
Sata Hard Drives
Serial ATA Sata Drive Guidelines and Features
Serial ATA Hard Drive Characteristics
Sata Hard Drive Cables
Smart ATA Drives
Hard Drive Capacities
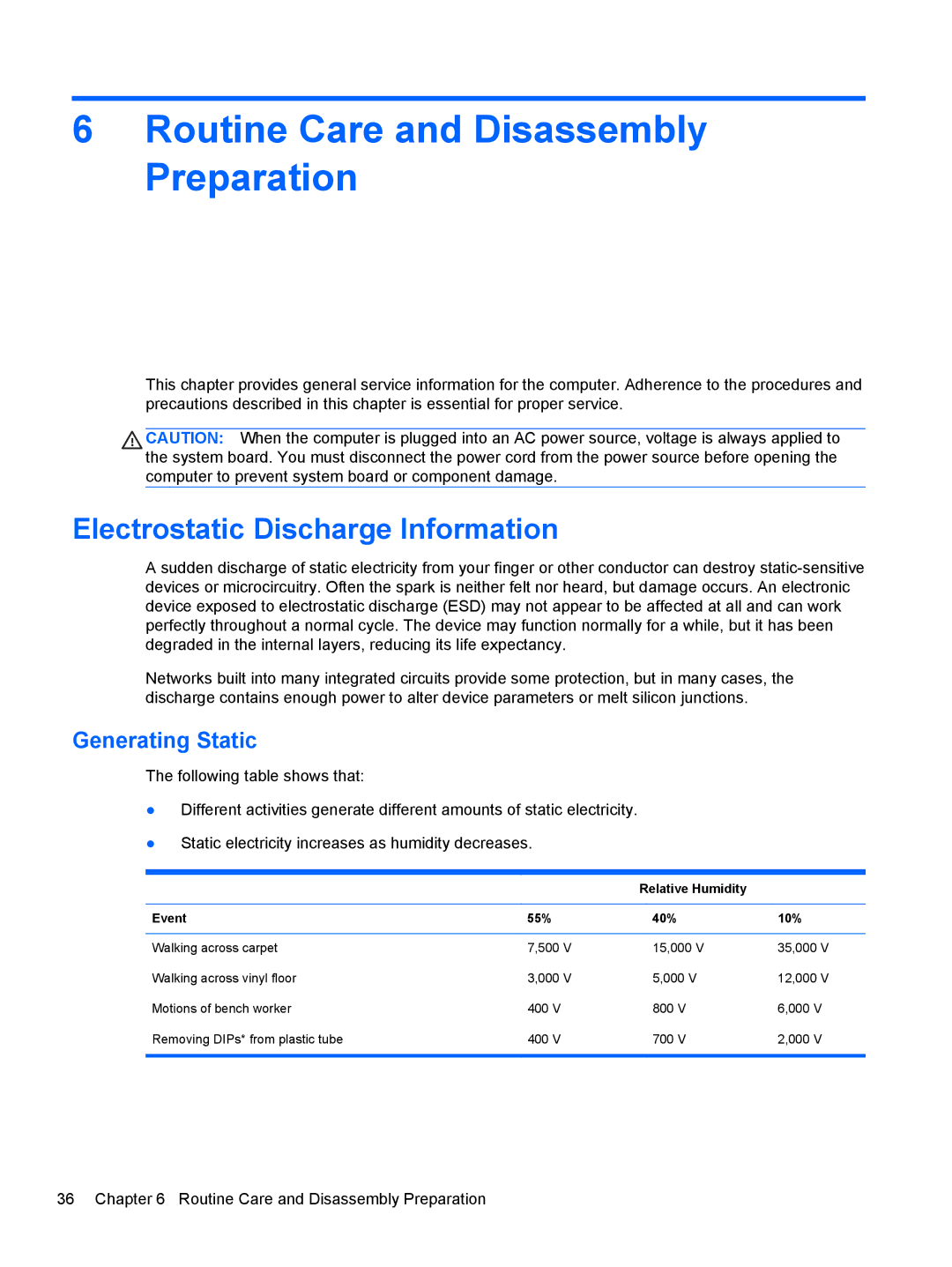
Generating Static
Routine Care and Disassembly Preparation
Electrostatic Discharge Information
Relative Humidity Event 55% 40% 10%
Static Shielding Protection Levels
Preventing Electrostatic Damage to Equipment
Personal Grounding Methods and Equipment
Method Voltage
Grounding the Work Area
Recommended Materials and Equipment
Operating Guidelines
General Cleaning Safety Precautions
Cleaning the Computer Case
Routine Care
Cleaning the Keyboard
Cleaning the Monitor
Power Supply Fan
Service Considerations
Cleaning the Mouse
Tools and Software Requirements
Lithium Coin Cell Battery
Cables and Connectors
Hard Drives
Serviceability Features
Removal and Replacement Procedures Microtower Chassis
Preparation for Disassembly
Access Panel
Description Spare part number Access panel 674373-001
Front Bezel
Memory
DDR3-SDRAM DIMMs
1DIMM Sockets
Populating Dimm Sockets
Description Socket Color Insertion Order
Removing Memory Modules
Page
2Expansion Slots
Expansion Cards
Slot Type Number of Slots
3Expansion Slots
6Expansion Slot Locations HP Pro
4Expansion Slots
8Removing an Expansion Slot Cover Expansion Cards
Page
Page
Cable Management
Connector Name Connector Color Description
Cable Connections
Drives
Drive locations
Installing Additional Drives
System Board Connector System Board Label Color
6System Board Drive Connections
14System Board Drive Connections HP Pro 3405 shown
7System Board Drive Connections Model
15System Board Drive Connections HP Pro 3505 shown
8System Board Drive Connections Model
Removing an Optical Drive
Page
Front I/O and USB Panel Housing Assembly
9Front I/O connectors
Page
Power Switch/LED Assembly
Remove the optical drive Removing an Optical Drive on
Page
System Fan
Page
Fan Sink Assembly
Description Spare part number Intel Core i7 processors
Processor
Intel Celeron processors
Remove the fan sink Fan Sink Assembly on
Page
Page
Power Supply
System Board
Battery
Page
Preparation for Disassembly
Description Spare part number Access panel 656832-001
Page
Description Spare part number Front bezel 656835-001
GB, PC3-10600 585157-001 635803-001 635802-001
1DIMM Socket Locations
Description Socket Color
Removing DIMMs
Page
Page
Expansion Card
Description Spare part number Graphics cards
2Expansion Slots
Page
Page
Cable Management
Sysfan
Drive Positions
3Drive Positions
Removing Drives
Page
Removing the Hard Drive
Page
Page
Page
Power Switch
Page
Front USB Assembly
28Removing the front USB assembly screw Front USB Assembly
Page
Fan Assembly
Description Spare part number Fan 656834-001
Page
Fan Sink
Description Spare part number Fan sink 657402-001
Page
2600S 2.7 GHz, 8-MB L3 cache, 65W 638419-001
Page
Power supply, 220W 656722-001 Power supply, 270W 665224-001
Page
System Board
Page
Battery
Page
Connector and Icon 1/8 miniphone Pin Signal
Connector Pin Assignments
Connector and Icon Pin Signal
Ethernet BNC
Line-in Audio
Pin Power for CPU
Headphone
Line-out Audio
Serial Interface, Powered and Non-Powered
Monitor
DVI Connector
Connector Pin Signal
Pin Power
Signal Pin
X1, x4, x8, and x16 PCI Express Connector Pin a Signal
PCI Express
X1, x4, x8, and x16 PCI Express Connector Pin B Signal
GND PRSNT2# Rsvd
Japanese Power Cord Requirements
Power Cord Set Requirements
General Requirements
Country-Specific Requirements
Country Accrediting Agency
Post Error Messages
Post Numeric Codes and Text Messages
Table C-1Numeric Codes and Text Messages
Appendix C Post Error Messages
Verify monitor is attached and turned
Replace diskette drive
Select File Save Changes and Exit
Test under Storage DPS Self-test
Options Sata Emulation to IDE,
Security Drivelock Security. For each
Appendix C Post Error Messages
Bios
Occurred prior to the ME firmware update
Table C-2Diagnostic Front Panel LEDs and Audible Codes
Activity Beeps Possible Cause Recommended Action
Desktop Management Guide for more
Appendix C Post Error Messages
Troubleshooting Without Diagnostics
Safety and Comfort Before You Call for Technical Support
Helpful Hints
Refer to Helpful Hints on page 142 in this guide
Page
Table D-1Solving General Problems
Solving General Problems
Computer date and time display is incorrect Cause Solution
There is no sound or sound volume is too low Cause Solution
Poor performance is experienced Cause Solution
Cause Solution
Table D-2Solving Power Problems
Solving Power Problems
Power supply shuts down intermittently Cause Solution
Solving Diskette Problems
Table D-3Solving Diskette Problems
Diskette drive cannot read a diskette Cause Solution
Cannot format diskette Cause Solution
Problem has occurred with a disk transaction Cause Solution
Invalid system disk message is displayed Cause Solution
Solving Hard Drive Problems
Table D-4Solving Hard Drive Problems
Advanced Power-On Options
Power-On
Nonsystem disk/NTLDR missing message Cause Solution
Computer will not boot from hard drive Cause Solution
Computer seems to be locked up Cause Solution
Table D-5Solving Media Card Reader Problems
Solving Media Card Reader Problems
Can not write to the media card Cause
Table D-6Solving Display Problems
Solving Display Problems
Blank screen no video Cause Solution
Personalization, select Adjust screen resolution
Image is not centered Cause Solution
Dim characters Cause Solution
Select ImageControl/ Horizontal Position or Vertical
Out of Range displays on screen Cause
No Connection, Check Signal Cable displays on screen Cause
Clicking noise coming from inside a CRT monitor Cause
Certain typed symbols do not appear correct Cause Solution
Symbol. Click Start All Programs Accessories
Solving Audio Problems
Table D-7Solving Audio Problems
There is no sound or sound volume is too low Cause
Sound from headphones is not clear or muffled Cause
Line-in jack is not functioning properly Cause
Solving Printer Problems
Table D-8Solving Printer Problems
Table D-9Solving Keyboard Problems
Solving Keyboard and Mouse Problems
Table D-10Solving Mouse Problems
Solving Keyboard and Mouse Problems
Computer will not start Cause Solution
Solving Hardware Installation Problems
Table D-11Solving Hardware Installation Problems
Security USB Security
Solving Hardware Installation Problems
Solving Network Problems
Table D-12Solving Network Problems
Solving Network Problems
Diagnostics reports a failure Cause Solution
Solving Memory Problems
New network card will not boot Cause Solution
Memory count during Post is wrong Cause Solution
Table D-13Solving Memory Problems
Out of memory error Cause Solution
Insufficient memory error during operation Cause Solution
Table D-14Solving Processor Problems
Solving Processor Problems
Solving CD-ROM and DVD Problems
Table D-15Solving CD-ROM and DVD Problems
Solving CD-ROM and DVD Problems
Movie will not play in the DVD drive Cause Solution
Table D-16Solving USB Flash Drive Problems
Solving USB Flash Drive Problems
Cannot eject compact disc tray-load unit Cause
USB flash drive not found identified Cause Solution
Solving Front Panel Component Problems
Table D-17Solving Front Panel Component Problems
System will not boot from USB flash drive Cause Solution
Unable to connect to the Internet Cause Solution
Solving Internet Access Problems
Table D-18Solving Internet Access Problems
Click Network and Internet
Internet takes too long to download Web sites Cause
Cannot automatically launch Internet programs Cause
Double-clickAgere Systems PCI-SV92PP Soft Modem
Solving Software Problems
Table D-19Solving Software Problems
Contacting Customer Support
Password Security and Resetting
Cmos
Resetting the Password Jumper
Clearing and Resetting the Cmos
Page
Windows 7 Backup and Recovery
Backup and Recovery
Backing Up Your Information
Select Start All Programs Maintenance Backup and Restore
Performing a Recovery
Using the Windows Recovery Tools
Using F11
Select Repair your computer
Specifications
Table G-1Specifications
SFF Specifications
Table G-2Specifications
Symbols/Numerics
Index
Page
Sata