VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Page
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
October
First Edition October
Take Note
Contents
Key Documents and Other References
Job Control Language JCL Differences and Considerations
Disk and Tape Storage Considerations
Operating System Implementations
162
Advanced Function Printing and Print Services Facility/MVS
Defining MQSeries Object and Operating
Part 3. Converting VSE Languages to OS/390 Languages
Data Division File Description FD
VSE/ESA
Egcs VSE to Dbcs OS Version 2 Comments
349
VSE/Fast Copy and OS/390 DFSMSdss
Part 5. Setting Up the Migration Environment
Part 4. Converting VSE Utilities to OS/390 Utilities
Prepare the Migration Environment
Orienting Iccf Users to TSO/ISPF
Orientation to OS/390 Console Operation
Understanding Message Formats and Replies
Systems Management Philosophy and Methodology
495
Appendix B. Mapping ISV Products and Functions
List of Abbreviations 583
Appendix E. Related Publications
565
591
Figures
Xvii
Loading a Random Preformatted DAM File under VSE
Tables
Xix
Xx VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Preface
Team That Wrote This Redbook
Redbook Builders and Key Contributors
Authors and Significant Contributors
Comments Welcome
Http//w3.itso.ibm.com
Part 1. Planning the Migration An Introduction
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
What do I need to read?
Why Customers Migrate
Synopsis of This Book
System Programmers Read the following
Traditional Reasons for Migrating
Business Consolidation
Mergers/Acquisitions
Capacity Constraints
Virtual Storage
Cics
Supervisor
Unused
Cics TOR
Prod
VSE Vtam
Static Dynamic Partitions SVA 31-Bit 16MB VSE
ACF
C1 Y1 SVA 24- Bit
Task Quantity
Image
Way Processor Support
MVS Nucleus
Functional Reasons for Migrating to OS/390
Applications Availability
Systems Management
Connectivity
Systems Availability
Staff Availability
Sizing the Effort
Introduction to Sizing
Defining the Migration Project Objectives
Source Program Inventory
Areas of VSE and OS/390 Differences
Source Programs
Batch and Online Program Conversion
Job Control Language
Files
Iocp IOCP, HCD
Comparison of Basic VSE Functions & Components to OS/390
Operations
Erep Mshp SMP/E
Cobol PL/I
LE/VSE LE/MVS
A S M
RPG
OS/390 Components/Products/Subsystems
Comparison of VSE Functions & Components to OS/390
1.1 OS/390 Product Content
OS/390 Operating Environment
Unix System Services
Distributed Computing Services
Network Computing Services
LAN Services
MVS Subsystem and Component Terminology
∙ Systems Resources Manager SRM
∙ Interactive Problem Control System Ipcs
∙ Data Facility Storage Management Subsystem
∙ Systems Management Facility SMF
Supporting Products
Philosophical Changes
Subsystem Level Comparison/Affinity
What Changes Between VSE and OS/390?
Security
JCL Processing
Automation
Console Operator Interface
Management Disciplines
Activities
Who′ s Normal Activities are Affected?
Roles Activities
Approaches to Migration Disclaimer
Kernel/Progressive Approach
Single Switchover Mass Application Migration Approach
3 VM/ESA Guest Support in Your VSE to OS/390 Migration
Staffing Strategies
In-House Staff
Conversion Tools
Outside Consultants
CAP-GEMINI
Educational Requirements Introduction
System Programming
Application Programming
Scope of Work and Challenges
Application Inventory
Program Conversion
JCL Conversion
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
File Migration
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Project Management
Automated Operations
Cost Considerations
OS/390 Documentation Resources
Introduction References
Key Documents and Other References
Web URL
Recommendations
Developing the Plan
Overview References
Project Management
Migration Plan Guide and Outline
Two Phase Approach
Take Advantage Of Conversion Tools and Automation
Conversion Method
Project Staffing
Librarian
Migration Responsibilities
Migration Assignments
Plan Components Approach
Team
Project Manager
Systems Programmers
Tasks
Applications Programmers
Milestone Events
Education
Progressive versus Mass Conversion Approach Differences
Shared Application Code
Historical Perspective
Shared Application Files and Databases
Operations Support Staffing
Standardized Conversion Deliverables and Automation
Risk Management
Complexity of Implementation
Cobol
Mass Migration as a Conversion Method
Mass Migration Used as a Conversion Tool
RPG
Plan Examples
Estimated Schedule for CNV Responsibilities
Project Schedule
Estimated Project Schedule
Month Number Month Initial
ABC Responsibilities
Estimated Schedule for ABC Responsibilities
Estimated Schedule for SER Responsibilities
SER Responsibilities
Project Plan Example
Project Plan Summary
Task Name Projected Actual Start End
Task Name
1998 Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
Project Plan Details
PCL
Task Name Projected Actual Start End
Task ID
1998 Jan Feb Apr Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
Task ID
Conversion Software Install
Batch File Migration Procedures
JCL
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Copyright IBM Corp
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Job Control Language JCL Differences and Considerations
Philosophy of JCL in System/390
1 VSE/ESA′s Job Control Language Philosophy
2 OS/390′s Job Control Philosophy
Job Control Language JCL Differences and Considerations
High Level Similarities
JCL Statement and Job Layout
Spooling
JCL Differences Between VSE and MVS
Job Input
Multiple Instream Data Set Input
VSE Example
$$ LST CLASS=J,DEST=DANJ,DISP=H
Data Driven Segmentation of Output
JCL Parameter Handling
$$ EOJ
JCL Expansion
Operator Flexibility and Intervention
Comment Lines in the JCL
Pause Statement
Assgn SYS005,CUU
Resource Allocation at Open Time
Allocation of Resources
Hidden JCL
Partition and System Standard Labels
Permanent Assignments and Power Defaults
Help for the Hidden JCL Problem
5.3 ²Carry-Over²
SYS010 DD SYSOUT=
Device Address Specifications
Assgn SYS010,FEF
REPORT1 DD SYSOUT=
Catalogs
Partition Dependent Codes in JCL
Communication Region Date and Upsi
Job Statement
VSE Job Control Statements
Upsi
Exec Statement
Assgn Statement
Reset Statement
MTC Statement
Dlbl and Extent
Output JCL Statement
MVS Job Control Statements
DD Statement
MVS Conditional JCL
Cond Parameter on the Exec Statement
Comparison of VSE and MVS JCL a Summary
1 of 2. VSE Job Control Statements Summary
Function MVS Equivalent Statement
2 of 2. VSE Job Control Statements Summary
Summary of MVS JCL Statements
MVS Job Control Statements
JCL Statement Purpose
Jecl
Comparison of Power and JES2 Jecl a Summary
2. Overview of Power Jecl Statements
List Card * $$ LST
Summary of JES2 Jecl a Table
1 of 2. JES2 Control Statements
Statement Purpose Comments
VSE and MVS JCL Comparison Example
2 of 2. JES2 Control Statements
Sample VSE JCL
Sample MVS JCL
Myjob JOB ACCT#,′ Report by PLANT′ , CLASS=F,REGION=4M
Sysin DD * 01 Endicott Boeblingen
Extent DISK14,0,600,500
Sample VSE plus Carry-Over
Extent DISKO1,0,100,500
Outfil BLKSIZE=4350 Sort Ended
Exec PROGRAM2,SIZE=300K
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Access Method Similarities and Differences Access Methods
Disk and Tape Storage Considerations
Operating System Implementations
DAM or Bdam
Miscellaneous Functions
Data Set Naming Considerations VSE Considerations
2 OS/390 Considerations
Storage and Space Management VSE Considerations
System Managed Storage
Disk and Tape Storage Considerations
Implementing Dfsms
Tape Similarities and Differences Volume Interchangeability
Standard Labels
VOL1
VOL1 HDR1 TM Data Records TM EOV1 TM
VOL1 HDR1 TM Data Records TM EOF1 TM TM
UHL1 UHL8
No Labels
Standard User Labels
Nonstandard Labels
Bypass Label Processing Facility in OS/390
Use should be controlled
VSE With Tapemark Before Data Records
OS/390 Single Data Set-Single Volume
OS/390 Single Data Set-Multiple Volumes
VSE Without Tapemark Before Data Records
Dasd Similarities and Differences Volume Interchangeability
Dasd Vtoc Processing
Indexed Vtoc Considerations OS/390
Vsam Differences Introduction
2 OS/390 Catalogs
Integrated Catalog Facility ICF
Vsam Catalogs
Vsam Catalog and Cvol Support Ends in YR2000
Part 1 of 2. Extract from WSC Flash
3 OS/390 Catalog Management
3.1 OS/390 Master Catalog
LOADxx Prompt Nucleus Device Suffix Feature
3.2 OS/390 User Catalogs
Payroll
DEPT4
DEPT1 & Jones
DEPT2 DEPT3
4 OS/390 VSE/VSAM Catalog Compatibility
Do not use Jobcat or Stepcat statements in OS/390
Accessing a VSE/VSAM Catalog from an OS/390 System
Converting VSE/VSAM Catalogs to OS/390 ICF Catalogs
Moving a Vsam Catalog to a Different Dasd Type
− Delete Ignoreerror
Vsam Functional Differences
Areas of Consideration
Catalog Structures
Shared Volume Ownership
FBA Dasd
Noimbed Option
XXL Ksds New in VSE/ESA 2.3, greater than 4GB Ksds
AMS Commands
Synchk Parameter
Compress New in VSE/ESA 2.2, Vsam Record Compression
Vsam CISIZEs and Record Sizes
VSE/VSAM-managed SAM Files
JCL Implicit Define
Default Models
Noallocation Data Sets
Reusable Data Sets
VSE/VSAM BACKUP/RESTORE and VSE Fastcopy
Ikqvdu Volume Cleanup
Partition Independent File Names
Data Sharing and Integrity
Ikqvchk Catalog Check
Space Classes
Cross-Region Sharing Single CPU Environment
OS/390 Vsam Integrity Provided by Cross-Region Shareoptions
OS/390 Vsam Cross-Region SHR4
Single Region Data Set Sharing
Single ACB Open Multiple String Processing
Intra-Region Data Set Name Sharing
Cross-System and Dasd Sharing
OS/390 Definitions for Dasd Sharing Support
OS/390 Vsam Cross-System Shareoptions
Dasd Sharing Considerations
Alternatives to Vsam Data Set Sharing
Vsam Error and Reason Code Compatibility
Programming Languages and Vsam Support
Dfsort and Vsam Considerations
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Cics
Overview Cics Transaction Server
133
Cics TS
Key Prerequisites
General Compatibility Comments
Virtual Storage Considerations for MVS
Data Bases
Cics General System Considerations
Appl
TOR AOR1 AOR2
Btam devices and controllers
Journaling to tape service
Macro-level programs
Cics internal security and signon table
Access to Cics system control blocks
Message domain Monitoring domain
Enqueue domain
Kernel domain Domain
Cics Domains
Cics Macro Resource Definition Table Changes
Cics
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
CSD and RDO Considerations
7.1 CSD
System initialization modifications SIMODs are obsolete
7.2 RDO
CONNECTION/SECURITYNAMEMRO
Cics System Data Sets Requirements
TYPETERM/RECOVNOTIFY
Shows MVS data sets used by Cics
Exits
System Programming Commands
Cics System Program Interface and Exits
Collect Statistics
All exits
Command Exit points
Exec Cics Abend
Exec Cics Return
Cics Transaction Security
Cics Upsi
Application Programming
Spool Interface restrictions
SAA AD/Cycle COBOL/370 SAA AD/Cycle C/370 SAA AD/Cycle PL/I
Testing and Problem Determination Considerations
CICS/VSE and TS Coexistence Considerations
Vendor Applications
Cics with DL/I
User Profiles
Iccf and TSO
Preparing to Use the System
155
Permit JCL
Adduser Aaaa PASSWORDsecret Special
Permit Parmlib Classtsoauth Idaaaa Accessread
Permit Oper
Logon Procedures
Message Facilities
Security
Using the System
Summary
Accessing the System
Descriptive Qualifier Data Set Contents
Entering and Manipulating Data
Edit Payrollprtchk NEW Cobol
Executing Programs at a Terminal
Ready
Submitting Jobs for Batch Execution
Using Command Procedures
Migrating from VSE/ICCF to MVS and TSO/E
Converting Iccf Libraries
Sample Iccf Procedure
Sysin DD Data TOP Stack 13 Quit
Save Iebupdte Edit Iebupdte Next
Options
Load Dtsprocs
DEL
Iccf Procedures and Macros
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Databases
DL/I and IMS/VS DB Differences Introduction
169
Primary Index of Hidam DB
MVS System Requirements
Data Base Descriptor DBD
Secondary Index for HD DB
Batch Programming
Program Specification Block PSB
Interactive Macro Facility IMF Command-Level Coding Hlpi
5.1 RPG
PCB after GE Status
Statement Compatibility
Field Level Sensitivity
NI Status Codes
Utilities
Operations
Backout Utility/Disk Logging
7.4 DL/I Parameter Statement
Alternate DL/I and IMS/ESA Access
Database Portability
Unloading and Reloading the Database
Unload DB IMS GEN
Changes Utilities Operations Tuning
DL/I DBD
Yes
9 DL/I Multiple Partition Support
Additional Information
End Users
Application Developers
SQL/DS Dbsu UNLOAD/RELOAD
Database Administrators DBAs
System Administrators
SQL/DS Dbsu Load
Security Administrators
Other Comparison Areas
Year
Drda Considerations
Data Replication and Data Access
Summary of Migration Task
Transaction Management
Databases
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Telecommunications Subsystems
185
ACF/VTAM
Product Installation
Vtam Data Sets
PGM=ISTINM01,REGION=6000K,TIME=1440,DPRTY=15,13
Resource Definition and Operation
NET Proc PERF=13 Exec
PERFORM=&PERF
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Telecommunications Subsystems
Operation
Customization and Programming
Resource Definition
Vtam Tables
Network Configuration
Programming
ACF/NCP
Program Generation
Usage
Btam Product Installation
Backlevel Hardware Support
Migrating TCP/IP
Network Definitions
4 TCP/IP Batch Jobs
2 TCP/IP Configuration
3 TCP/IP Related User Data
User Written TCP/IP Applications
5.3 TCP/IP Applications using the BSD/C Sockets
5.1 TCP/IP Applications using the Sockets API for Assembler
5.2 TCP/IP Applications using the Preprocessor API
5.4 TCP/IP Applications using the LE/VSE C Socket API
Bibliography
MQSeries
OS/390
MQSeries in Your Operating System Environment
Prerequisites
Telecommunications Subsystems
Installation and Customization
PL/I
Cics Considerations
Data Sets
Networking Definitions
Defining MQSeries Object and Operating
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
MQSeries-based Applications
SC33-0807
Major Differences
Power and JES2
10.1 JES2 Introduction
Keep Disposition for Pre-Execution Jobs
Tape Spooling
Printer Forms Alignment via Psetup
Time Event Scheduling for Jobs
Separator Page Difference
End-of-page Sensing
Setting Up the Required Resources
Implementing JES2
FCB Incompatibilities
Starting JES2
10.2.1.2 JES2 Spool Volumes
Power JES2
10.2.1.1 JES2 Checkpoint
10.3 JES2-POWER Functional Comparison
Tailoring JES2
Multiple System Support
Input Service
JES2 Input Sources compared to Power
Input From
OS/390 Solution
Job Scheduling
Job Stream Disposition
Serializing Job Execution
Time Event Scheduling
Additional Job Scheduling Functions with MVS/JES2
Output Service
1 of 2. POWER/JES2 Output Service Comparison
Output Service
Output Segmentation
2 of 2. POWER/JES2 Output Service Comparison
Printers Supported
NEWPAGE=1
FCB Naming Differences
Separator Page Differences
Output Disposition
FCB Prefixes
FCB Specification
Interactive User Interfaces ICCF/CMS/TSO
UCS Naming Conventions
Remote Workstation Definitions
Remote Job Entry
Functional RJE Differences
Interactive
Network Job Entry
RJE Operations
RJE Exits
Application Interfaces
Job Information Services
Output Retrieval
Other Interfaces
Accounting Comparisons
Job Accounting
JES2 SMF Accounting Records
NJE Accounting
RAS Characteristics
NJE Activity VSE/POWER Account MVS/JES2 SMF Record
Accounting Records for NJE Activities
Mapping Power Parameters to JES2 Init Parms
10.3.11 JES2 Testing Techniques
POWER/JES2 Detailed Comparisons
Equivalent JES2 Parms for Power Macro
1 of 2. Power Macro to JES2 Parameter Mapping
2 of 2. Power Macro to JES2 Parameter Mapping
Pline Mapping to JES2 Line Parameters for RJE and NJE
Define BSC Remotes
Pline Macro to JES2 Parameter Mapping
1 of 2. Prmt Macro to JES2 Parameter Mapping
Define SNA Remote Workstations
2 of 2. Prmt Macro to JES2 Parameter Mapping
Prmt Macro to JES2 Parameter Mapping
Define Compaction Tables
Exit Comparisons
Define NJE Nodes
Pnode Macro to JES2 Parameter Mapping
Source Code Modifications
POWER-JES2 Command Equivalences
Power Exit to JES2 Exits
JES2 Patching Facility
Task Management Commands
Command Short Code Form Verb
NJE Operator Commands
Network Management
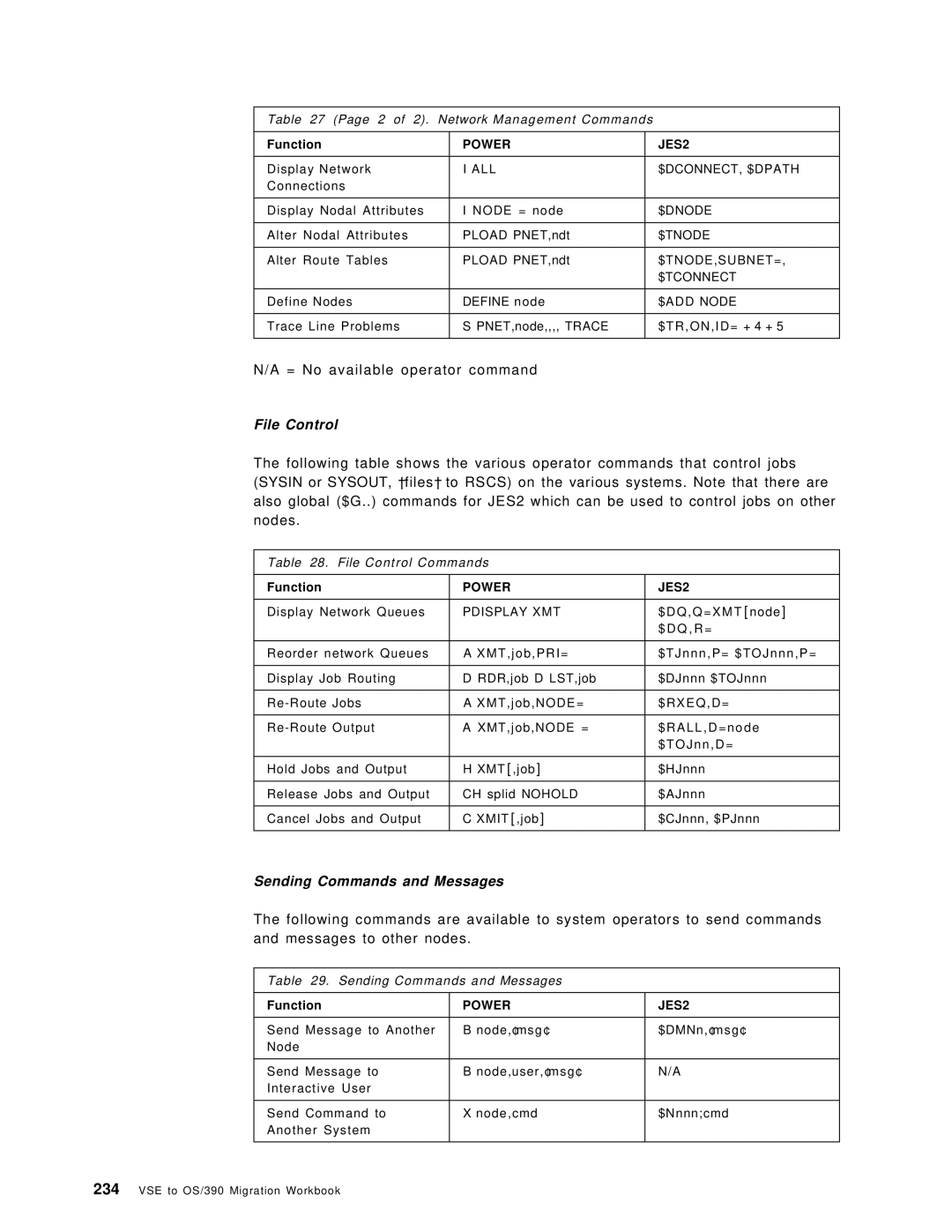
File Control Commands
Sending Commands and Messages
2 of 2. Network Management Commands
Sending Commands and Messages
Functional Comparison between PSF/VSE and PSF/MVS
Advanced Function Printing and Print Services Facility/MVS
Introducing PSF/MVS
Migration Effort
Defining Network Printers
Installing and Configuring PSF/MVS
Defining Channel-attached Printers to MVS
Attachment Options
PSF Startup Procedures
Defining Printers for PSF Printing
11.2.2.2 TCP/IP Attached Printers
FSS Procedure and Printdev Statements
Comparison of Printdev Statement Parameters
Printdev Parameter Comparison
Remote-Resident Resources
Setting up AFP Resources
Migrating Resources from VSE to OS/390
Defining Resources
JCL and Jecl Differences
Transferring Print Streams VSE and OS/390 Coexistence
Migrating Print Applications
Printing from TSO
Starting and Stopping PSF
Command Comparison
Understanding Operational Differences
High Level Language Programming Interfaces
Installation Exits
2 of 2. VSE OS/390 Command Comparison
Other Differences Performance
11.6.2 PSF/MVS Publications
Accounting
References 11.6.1 PSF/VSE Publications
Redbooks
Services
Internet Locations
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Part 3. Converting VSE Languages to OS/390 Languages
247
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Cobol
General Comments on Cobol for OS/390 and VM
249
Comparison of IBM Cobol Compilers
VSE to OS/390 Migration Considerations
DOS/VS Cobol
Deck
Migrating Object Code
Useful Publications
Outdd
Converting from DOS/VS Cobol
12.3.1 DOS/VS Cobol Cics Programs
Useful Cobol Publications
Common Cobol Coding Problems
PRIMARY-FIELD PIC
FIELD1 Values are 60 61 FIELD2 Values are 50 51
RECA-FIRST PIC RECA-SECND
RECORD-A
Filler Redefines RECORD-A
Move 0 to RETURN-CODE
Is ACCEPT-SYSIN
Configuration Section SPECIAL-NAMES Paragraph
SPECIAL-NAMES Sysin
UPSI-0 Is CBL232B on Status is CBL232-BASE UPSI-1
Linage Clause and END-OF-PAGE Phrase
Procedure Division Input/Output
Assign Clause
Close Statement for Tapes
File Status Codes
File Handling Considerations
Program Termination
Exit Program Goback Stop RUN
File Attribute Mismatches
PROCEDURE-POINTER Function
Converting from VS Cobol
Isam
Some Conversion Considerations for all VSE Cobol Compilers
VS Cobol II Cics Programs
Converting from Cobol for VSE/ESA
Vsam
Compiler Options
12.8.1 RES/NORES
Compiler Option Considerations for VS Cobol
Pgmnamecompat
Rmodeauto
Wordnooo
FDUMP/NOFDUMP
Reserved Words
Reserved Word Considerations for DOS/VS Cobol
Flagsaa
EMI Printing
Cbltitle
FUNCTIONPROCEDURE-POINTER
Reserved Word Considerations for VS Cobol II and Cobol for
Compiling and Running Your Converted Cobol Programs
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
General Assembler Conversion Comments
Assembler
Assembler Products
267
System Interface and Macros
MVS Register Conventions
Initiation
Termination
Register Conventions
Application Program Logic
LA 13,SAVEA LA 13,SAVEB Call Progb Call Progc
Save Areas
Call Progb Call Progc
Proga Start Progb Csect Progc Csect MVS
11,SAVEA 11,SAVEB 11,SAVEC
Savea DC
MVS Call
Larex Csect Using
VSE Call
Call SUBRTN1
13,413 Get backward chain pointer
1213 Restore the registers
1213,X′ FF′ Set return indicators Return
Caller′ s save area
Communication Region
Job Name
Upsi User Program Switch Indicators
Problem Program Area Addresses
User Program Communication Bytes
Communications Region Simulation
15,1 Pass address
Load the phase
Progb
Call
EP=PROGB
VSE Phasenm
EPLOC=PHASENM
Cdload
MVS BIN
VSE Standard HM MS S MVS DEC
VSE Binary
Time DEC,OUTAREA,DATETYPE=YYYYMMDD,LINKAGE=SYSTEM
VSE Jdump
Dump
MVS Abend Dump ,STEP
Unlock DTL1
VSE Cancel ALL MVS Abend
VSE Lock DTL1
MVS ENQ MF=E,DTL1
VSE Chkpt
Resar address
End address Poiner
′ S′
Multitasking Macros
ATTACH/DETACH Macros
Cb locaion address
Entrypoint
WAIT/POST Macros
Ecb1,ecb2 VSE Wait Lisname
Number of evens,ECB = address ECBLIST=address
Step Systems
13.2.2.3 RCB/ENQ/DEQ Macros
System
System Systems
Interval Timer Interrupts
Interrupt Handling Routines
Tecb Setime
VSE Ttimer Cancel MVS Ttimer Cancel ,TU
Operator Communication Interrupts
Exit
Virtual Storage Macros
Getvis and Freevis Macros
Vsam Macros
Exlst Macro and Excpad Routines
RPL Macro Additional MVS Parameters
∙ M a C R F =
Showcb Macro
Vsam Error and Reason Code Compatibility
Data Management Macros
MVS Vsam Check Macro
List and Execute Macro Forms
Definition of Blksize
Ioreg
13.2.6.4 I/O Error Checking
Liocs Card File Definition
Ctlchr = YES
Mode = E O Devd = ..,MODE=E O
Bufno =
ASA
Prtov Macro
Liocs Printer File Definition
Cntrl Macro
Card File Programs in VSE and MVS
Printov = YES
Liocs Tape File Definition
Control = YES Macrf = PC Ctlchr = YES
Sepasmb = YES
Close Macro
Reread Leave Rewind Disp
BSR, number of blocks
VSE MVS Bsam only
No equivalen. The opion specified in he Disp
FSR, number of blocks
Points Macro
Relse Macro
Trunc Macro
Feov Macro
GET / PUT Macros
Eropt = ACC SKP ABE
Skip
Optcd = Q
MACRF=RP,WP
Liocs Device-independent File Definition
Open Tape VSE PUT Close Tape
Close TAPE,LEAVE
Erropi = Ignore Eropi = ACC Skip SKP ABE
Liocs Sequential File Definition on Direct Access Devices
Liocs Console File Definition
Recfm = FA
Bsam Inout Disp Updat Leave Outin Outinx
Qsam Input
Output Leave Updat Disp Extend Input
Reread Leave Free Disp
Eret Macro
Write
Read Macro
Write Macro
Check Macro
Filename Address
Feovd Macro
Eropt = ACC
Errext = YES Feovd = YES Hold = YES
WORKA= YES
Optcd = W
Liocs Direct Access File Definition
General Considerations
Sequential Dasd File Program in VSE and MVS
Readid = YES
After = YES
Errext = YES
Readkey = YES
Error VSE MVS
VSE Error Bytes and MVS Exception Code Bits
WAITF, Open and Close Macros
Record Addressing
Track and Record Addressing
Track Addressing
Record Addressing by ID
Record Addressing by KEY
Reference Methods
Record Reference by ID
Record Reference by KEY
Reference Method
OPTCD=R,BUFL=58
Direct Access File Processing
DCB DSORG=DA,MACRF=RISC,WIC
Reference
Damfile DCB MACRF=WICS,DSORG=DA,OPTCD=R
Open DAMFILE,OUTPUT
Decbadd
Open DAMFILE,TAPE WRITER0
DCB
Specified in the DD statement
Open DAMFILE,UPDAT,TAPE,INPUT
Loading a Sequential DAM File under MVS
DECBR0 CLI
Open R0FILE,OUTPUT,TAPE WRITER0
DECBR0,SZ,R0FILE STC
Open DAMFILE,OUTPUT CLI
DISP=OLD DCB=BLKSIZE=50,RECFM=F GO.R0DD DD DSN=UDAM
Count
Three
DCB=DSORG=DA DISP=,KEEP GO.DAMDD DD DSN=UDAM
Loading a DAM File Fixed-Length Records without keys
Loading a DAM File Undefined or Variable-Length Records
AFTER=YES,ERREXT=YES,RELTRK=YES
Open Damfile Read DAMFILE,KEY
Damfile Addition Write DAMFILE,AFTER
Processing a DAM File under VSE
Multiple Search / Feedback
Loading a Random Preformatted DAM File under VSE
Liocs Indexed Sequential Definition
Type or Reference
Piocs
Overview of Programming Elements
CCB Macro
Comparison of Physical Iocs Elements
Dtfph Macro
Device Information
RPG
Migration from VSE to OS/390
Print Files
Extent Exit
File Access Methods
Tape Labels
Processing Options
Calling PL/I Subprograms
Direct access method files are processed with Bdam
Calling Cobol Subprograms
Year
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
PL/I
333
Dynamic Loading of Dependent Programs
Extended Precision
Multitasking
File Organization
Compiler Options Options Specific to the DOS Compiler
Parameters Passed to a Main Program
15.1.7 %INCLUDE
Catalog
Options Specific to the MVS Compiler
Execution Options
Linkages not Supported
Exec and Process Cards
Linkages Between Languages Linkages Supported
Environment Attributes
Not Supported in MVS
SIS Option Sequential Insert Strategy
Supported but to be Avoided
²TOTAL² Option
Calling Sort from PL/I Interfaces Offered
Storage
Sort Fields
Record
Return Code
Call Plickpt pl,p2,p3,p4 DOS and MVS
Checkpoint-Restart in PL/I Plickpt
Plirest
If ONCODE= xxx then do
Options Specific to DOS
Plicanc
Dump in PL/I Optimizer Output File
² File Plidump could not be Opened Ddname MISSING²
Compatibility
Return Codes in PL/I Setting Return Codes
Options Specific to MVS
Return Code Values
Conversion
Automatic Restart
Overlay Structures
Overlay in MVS
CALLing Dump
15.12 PL/I and Cics File Support
Statements not Supported
15.12.6 PL/I-CICS/VS Transaction Abend Codes
PL/I
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Fortran Conversion Considerations
Fortran
VS Fortran in OS/390
349
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Few Words about Cobol and PL/I
Language Environment LE
General Comments on Language Environment
351
17.2.1 LE/VSE-conforming Languages
Migrating from LE/VSE-Conforming Languages
For VSE/ESA
Useful Publications
Migrating from Non-LE/VSE Run-time Environments
Cobol for VSE/ESA
17.3.3 PL/I for VSE/ESA
Options Mapping
Report and Isasize Options, C/370 and DOS PL/I
17.4.2 C/370
VS Cobol
370 Migration Considerations
DOS PL/I
VS Cobol II Migration Considerations
DOS/VS Cobol Migration Considerations
Migration Comments Consideration
Default setting for the Depthcondlmt option, both for
DOS PL/I Migration Considerations
Depthcondlmt
To Migrate You Need To
Migrating Interlanguage Communications Applications
1 of 2. ILC Migration Considerations
DOS PL/I
Run-time Options
Migrating Assembler Applications
Migrating from LE/VSE
2 of 2. ILC Migration Considerations
Shh Ihh Udddd
Syslst
Run-time Options and LE/VSE
Cblqda Flow Interrupt Simvrd Vctrsave
Run-time Options and LE/VSE 1.4 and Later Releases
Argparse
Recommended Settings for Options
Language Environment
Language Option Recommendation
High-Level Language Exits
User Exits and Abnormal Termination Exits
Assembler User Exits
Ceecxita Cics
Callable Services and Math Services
Abnormal Termination Exits
Cobol and Cics
17.5.4 LE/VSE 1.4 Locales
Cics
Ceetdli
User Exits and Abnormal Termination Exits
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Rexx and VSE/ESA
Procedure Language Rexx
Rexx and VM/ESA
Rexx and TSO/E
18.4.1 VSE/ESA Environment
Power
Environments
18.4.2 VM/ESA Environment
Rexx Exec Sample for the OS/2, TSO and CMS Environments
Migration Issues
18.4.3 TSO/E Environment
Rexx
Rexx and SAA
Rexx Bibliography
Part 4. Converting VSE Utilities to OS/390 Utilities
373
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Sort
JCL Statements
375
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Control Statements
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Additional DFSORT/VSE Migration Considerations
Icetool
381
Ditto
Compatibility with Previous Releases of Ditto
MVS/ESA VSE/ESA VM/ESA
Function Description Replacement
Ditto Functions that are No Longer Supported
Ditto Functions that are Not Recommended
Batch Keywords that are No Longer Supported
Functions Keyword Description Replacement
Ditto Function Code Synonyms
Function Synonyms Description
Batch Keywords that are Not Recommended
DITTO/ESA Security
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
21.1.1 OS/390 Vsam Backup/Restore
Vsam Backup/Restore
Vsam Backup/Restore
21.1.2 VSE/VSAM Backup/Restore
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Librarian
Overall Library Support
389
22.1.1 OS/390 Ispf Overview
∙ Interactive usage
22.1.2 OS/390 Library Management
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
VSE Listlog Utility Program
LISTLOG/PRINTLOG Printing Log Streams
VSE Printlog Utility
23.3 OS/390 Hardcopy Processing
Syslog
Printing Syslog
Printing Operlog
23.5 JES2 System Data Sets Job Log and System Messages
Systems Management Recording
Printing SMF Records
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
VSE/Fast Copy and OS/390 DFSMSdss
24.1 VSE/Fast Copy Online and Stand-Alone
397
∙ Compress
∙ DUMP/RESTORE
DFSMSdss OS/390 Component
∙ Release
Part 5. Setting Up the Migration Environment
399
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Prepare the Migration Environment
401
Devices Supported by OS/390
Install and Configure Required Hardware
Processor Requirements
Dasd Requirements
Other Hardware Requirements
403
Shared Dasd
Terminal Access
Inter-Systems Connectivity
Tape Drives
SoftwareXcel Installation Express SIE
Order and Install the OS/390 Software
Fee-based Methods of Installing OS/390
Data Transfer and NJE
Other Offerings
Entitled Methods of Installing OS/390
SoftwareXcel SystemPac/MVS
ServerPac
Cbpdo
Set Up Standards, Procedures, and Documentation
Installation Standards
Data Management Standards
Related Redbooks
Dasd and Tape Volume Serials
MVS Naming Standards
Data Sets
409
Systems Management Procedures
JCL Standards
Other MVS Names
Implementing System Security
Enforcing Installation Standards
Creating an Emergency Backup System
Backing Up Your System
Managing Change
Setting Up Critical Operations Procedures
Managing Problems
411
Your Softcopy Library
Documentation
Your Hardcopy Library
Printing Softcopy Books
Customize Your New OS/390 System
Verifying the New OS/390 System
413
Applying Preventive Service
Providing Terminal Access to the OS/390 System
Providing NJE Connection to the OS/390 System
NetView FTP Access
MVS BCP Customization
25.5.2.1 SYS1.PARMLIB Parameters
Tailoring Other Components
Optional Features for Release
Other OS/390 Elements
Base Elements for Release
Independent Software Vendor Products
417
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Terminology
Differences in Testing ²Philosophy²
Test Environments
419
Application Development & Test System
Production Maintenance Backup Sand-box
Test Systems in the Life of the Migration
Application Program, JCL, and Data Conversion
OS/390 Production Stand-By Maintenance
OS/390 VSE Backup Production Maintenance
26.3 VM, LPAR, or Standalone Systems
Logical Partitioning
Software Partitioning
Our Recommendation
New Users of VM
Advantages of Guest Support in VM/ESA
System Simulation
Performance Benefits
Reduced Hardware and Migration Cost
Operations Management
Recovery Management
Access to VM/ESA CMS Applications
Interactive Computing, Application Development and Support
Models 3 and 6 Fast Write Transparency
Use of CMS
DB2 Guest Sharing
Multiple 3270 Session Support
Building the Initial OS/390 Test System
Parallel Activities
Synchronizing VSE Applications with OS/390 Versions
26.3.3.5 OS/390 Guest Considerations
26.5.1 OS/390 Maintenance Environment
26.5.2 OS/390 Test Logical Partition
Maintaining Your OS/390 Libraries and SMP/E Zones
Shared Dasd vs. Cloned Dasd
Shared Dasd between OS/390 Test Systems vs. Cloned Dasd
Shared Dasd between VSE and OS/390 vs. Cloned Dasd
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Part 6. Running Your OS/390 System
435
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Orienting Iccf Users to TSO/ISPF
27.1 TSO/ISPF and Sdsf
437
Editing Data Sets
Using Ispf Utilities
Submitting Jobs
Creating and Executing Ispf Applications
Managing Projects
Using Sdsf for Operators
Tracking Jobs
Retrieving Output
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Understanding the Operator Interfaces
Orientation to OS/390 Console Operation
Operating Hardware Consoles
443
Console Modes
Controlling Consoles
Managing Display Consoles
DEL=R,SEG=28,CON=N,RNUM=14,RTME=001,MFORM=T,J
Display Areas
Using the TSO/E Functions
Extended MCS Consoles
PFKeys
Using Sdsf for System Operation
Understanding Message Formats and Replies
Controlling the OS/390 System
Starting the System
Displaying System Status
Displaying the Status of Devices
Stopping the System
Controlling Devices
Understanding Device Allocation
Controlling TSO Users, Jobs and Started Tasks
28.4.3 JES2 Devices
Sdsf Device Panels
Displaying Work on Your System
Sdsf Panels
MVS Commands
28.5.1.2 JES2 Commands
RMF and Other Monitors
Controlling Time Sharing Users
Controlling Batch Jobs
Controlling Started Tasks
Host Operations
Managing Remote Operations
28.6.1 JES2 RJE Operations
Remote Workstation Operations
NJE Operations
Using Sdsf Panels for RJE
Command Authority for Remote Operators
Remotes Without Consoles
$D Nxx.′$D NODEyy′
Using Sdsf Panels for NJE
$D PATHnodename
$D MNn,′Please drain your session′
Orientation for Utilities
IEBxxx or IEHxxx
455
DFSMSdss Storage Administration Reference, SC26-4929
DFSMSdss
Systems Management Philosophy and Methodology
457
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Systems Management Scope What Needs to be Managed?
Role of Automation
Change Management Overview
Problem Management Overview
Methodology
Tasks
Performance Management Overview
Methodology
Operations Management Overview
Methodology
Automating Operational Procedures
Security Management Overview
Configuration Management Overview
Methodology
Asset Management Overview
Accounting Management Overview
Summary
Dumps
Diagnosing System Problems
Problem Determination Tools
Ipcs
Using Ipcs
Traces
Analyzing Traces
31.4 JES2 Diagnosis
Slip
Performance Tools
DFSMS/MVS Diagnosis
Analyzing Catalogs for Errors and Synchronization
Catalog Recovery
DFSMSdfp
Checking a Vsam Ksds for Structural Errors
DFSMShsm
Diagnostic Reference Publications
DFSMSrmm
Part 7. Converting your Applications
479
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Conversion Process
481
Conversion Process Introduction
∙ Refer to MVS MS Production Standards, LB11-8080
Conversion Process
Prerequisites
Manuals
Secure OS/390 Skills
32.1.3.6 24x7 Installations
Migrate the SNA Network Early
Assumptions
Mass Conversion Overview / Benefits
Automated Conversion
Repetitive Conversion
Mass Conversion Switchover
Mass Conversion Tools
Automation Limits
DMT DOS/OS/390 Translator
Automated Conversion Process
Cortex MS
INT File Integration
Prep Preparation
Switch Switchover
EZ-PCL Easy PCL
ENV Environment
JCL Conversion Tools
Inventory Validation
Translate the Languages/Programs
File Transfer
Mass Conversion Phase Overview
Preparation Phases
Phase 0 Project Management and Technical Leadership
Project Planning and Orientation
∙ Implement System Managed Storage Dfsms
Phase 1 Application Inventory
Collection
Analysis and Resolution of Exceptions
Determination
Supply
32.4.3 OS/390 Standards and Naming Conventions
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Phase 2 Conversion Specifications
Analyze the VSE Source Material
Phase 3 Customization or Development of Conversion Tools
Design the MVS Target Output
Determine the Method to Get from Source to Target
VSE Positioning
Manual OS/390 Conversion
Conversion Phases
Program Conversion Considerations
Common VSE Coding Practices Causing Conversion Problems
Phase 4 Initial Trial Conversion
Objectives of testing
Phases of testing
Responsibilities
Testing Priorities
Personnel Involvement in Testing
Recommendations
Dasd Requirements
MVS Tools Testing
Test Plan
Subsystem Storage Protect
Conversion Process
32.5.4.4 OS/390 Automated Operations Tools
Initialization Testing
Unit Testing
Data Migration in Unit Testing
Online Unit Testing
Batch Unit Testing
Timing between Online and Batch Testing
System Testing
Online
Batch
Parallel/Production Simulation Testing
Data Migration in System Testing
Data Migration in Parallel Testing
Implementation Phases
Date Concerns during Parallel Testing
Job Simulation
Phase 6 Actual Conversion and Switchover
Converting the Development Material
Final JCL Conversion
Switchover
Final Program Conversion
Data/File Migration
Phase 7 Initial OS/390 Operations
Additional Switchover Tasks
Automated Migration Services AMS
Conversion Services and Tools
Conversion Services IBM Global Services
519
Conversion Tools 33.2.1 VSE/ESA Facilities
IBM OPTI-AUDIT for VSE
Product Highlights
Product Details
IBM Cobol and Cics Command Level Conversion Aid Ccca
Product Positioning
Technical Description
Sisro CORTEX-Migration System CORTEX-MS
CA-Convertor
Source Recovery Company
Computer Associates
CA-DUO
Rename/SRC
Recovery/SRC
Cobol Recovery Example
Reconcile/SRC
Part 8. Migration Experience
527
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Environment
Customer Migration Example
Background
Hardware
Inventory
Resources
Phase One
Phase Two
Duration
Benefits
Part 9. Appendixes
533
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Appendix A. Education Information
535
When are Courses Scheduled and When are they Needed?
Custom Classes
OEM Product Education
Where will the Training Take Place?
Who will Provide the Training?
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
VSE ISV System Management Products and OS/390 Compared
Appendix B. Mapping ISV Products and Functions
IBM Software Migration Project Office Smpo
539
Idms
Appendix B. Mapping ISV Products and Functions
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Appendix C. Dfsms Naming Conventions
Data Set Naming Guidelines
543
Components of a Data Set Name
High-Level Qualifier HLQ
Appendix C. Dfsms Naming Conventions
File Contents
Relative Importance
Things Not to Include in the Data Set Name
User Name
Data Set Level
Department Number
Output Device Type
Application Location
Management Criteria
Expiration Date
Common Applications Naming Conventions
Access Method
Job Name
TSO Naming Conventions
Hlq.DSNDBx.dbname.tblspacename.I0001.A00n
Vsam Data Set Naming Conventions
3 DB2 Naming Conventions
DSNDBx is
Generation Data Sets
C.GnnnnV00
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Appendix D. Special Notices
553
AFP
ACF/VTAM
Adstar
AIX
Following terms are trademarks of other companies
VM/ESA VM/XA VSE/ESA Vtam
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Other Redbooks
Appendix E. Related Publications
International Technical Support Organization Publications
OS/390 Product Publications
Book Title Publication Number
Planning Books
2 OS/390 Online Product Library
SK2T-6700
Redbooks on CD-ROMs
Other Publications
Other Sources Books on the Internet
Redbooks 1.2 OS/390 Books IBM Printing Systems
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
How to Get Itso Redbooks
How IBM Employees Can Get Itso Redbooks
561
∙ Mail Orders Ð send orders to
How Customers Can Get Itso Redbooks
∙ Telephone Orders
∙ Fax Ð send orders to
IBM Redbook Order Form
Please send me the following
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Glossary Numerics
565
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
O s s a r y
Customer Information Control System CICS. An
O s s a r y
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
File
Information Management System/Virtual Storage
Language/Product Days Since Dec-31
Language Environment Oct-14
Interactive Computing and Control Facility ICCF. An
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
O s s a r y
Ordinal Day of Year. See Julian Date
O s s a r y
Resource Access Control Facility RACF. An
Rolling window. Synonymous with sliding window
O s s a r y
System management facilities SMF. See SMF
O s s a r y
Year2000 support. The ability to provide Year2000 readiness
List of Abbreviations
583
Callable Services Library
Command List
Recovery
Control Volume
Environmental error Record
Data Set Services
Extended Common Service
External Symbol Dictionary
Interactive Problem Control
Interactive Command Facility
Service Facility
Indexed Sequential Access
Power END
Series
Print Service Facility/6000
Program Specification Block
Print Service Facility
Queued Sequential Access
System Services Program
Service Planning Guide
SQL Processor Using File
SYStem ADMinistrator
Vsam Volume Record
Volume Table of Contents
Vsam Volume Data Set Facility
EXtended Recovery Facility
Index Special Characters
591
ACF/VTAM
Apsrmark MVS
Ttimer
Cancel
Aptrmark VSE
Index
PSF/MVS
Batch TCP/IP 195 unit testing
Diagnostic reference 478 Language Environment 353 MQSeries
Plicanc Plickpt Plirest
Cics
Cobol
Conversion CA-Convertor
Courses locations 537 schedules 536 when needed
CORTEX-MS
Dadsm Dasd
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Device Ditto
Data Division File Description FD
E15 Exit Procedure
Entrypoint
Associate
Filesec
FBA Dasd
Gonumber
Fortran
Idcams Iebcopy Iebgener
Isasize
Ipcs
Isam
Ismf Ispf
JES2
Link
LE/VSE
Limsconv
Liocs
Cortex MS
Migration
356
VS Fortran
TCP/IP
Operlog
MVS device addresses 80 DFP
NJE
Printing Operlog 394 Opsys routine 349 OPTI-AUDIT 79
OS/390 NCP
Vtamlst 190 XCF
MVS BCP
Piocs PL/I
PL/I
394 SMF records 395 Softcopy books 412
Syslog
Racf
Project
RES/NORES
RDO
371 VM/ESA
Resources
TSO/E
370 Risk management Risky VSE coding practices 504
Fields
Rexx
Sort
Icetool
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook
Index
Vsam
BACKUP/RESTORE
VS Cobol II
Btam
OS/VS Cobol
Delete Ignoreerror
VSE/VSAM BACKUP/RESTORE & VSE
Compress
VSE Year2000
Vtamlst
Itso Redbook Evaluation
621
Please answer the following questions
VSE to OS/390 Migration Workbook SG24-2043-00
XRL/1
XRL/2
XRL/3
Jmacp
XRL/4
XRL/5
XRL/6
XRL/7
XRL/8
XRL/9
XRL/10
XRL/11
Dittind
XRL/12
Oploind
Operlog
XRL/13
Smfpind
ACB
DL/I
Power
XRL/14
NJE
XRL/15
XRL/16
XRL/17
XRL/18
Ctrind
XRL/19
Vosind
Csysind
XRL/20
XRL/21
XRL/22
MVS BCP
XRL/23
Cortex MS
XRL/24
XRL/25
XRL/26
XRL/27