EX2500 Ethernet Switch Configuration Guide
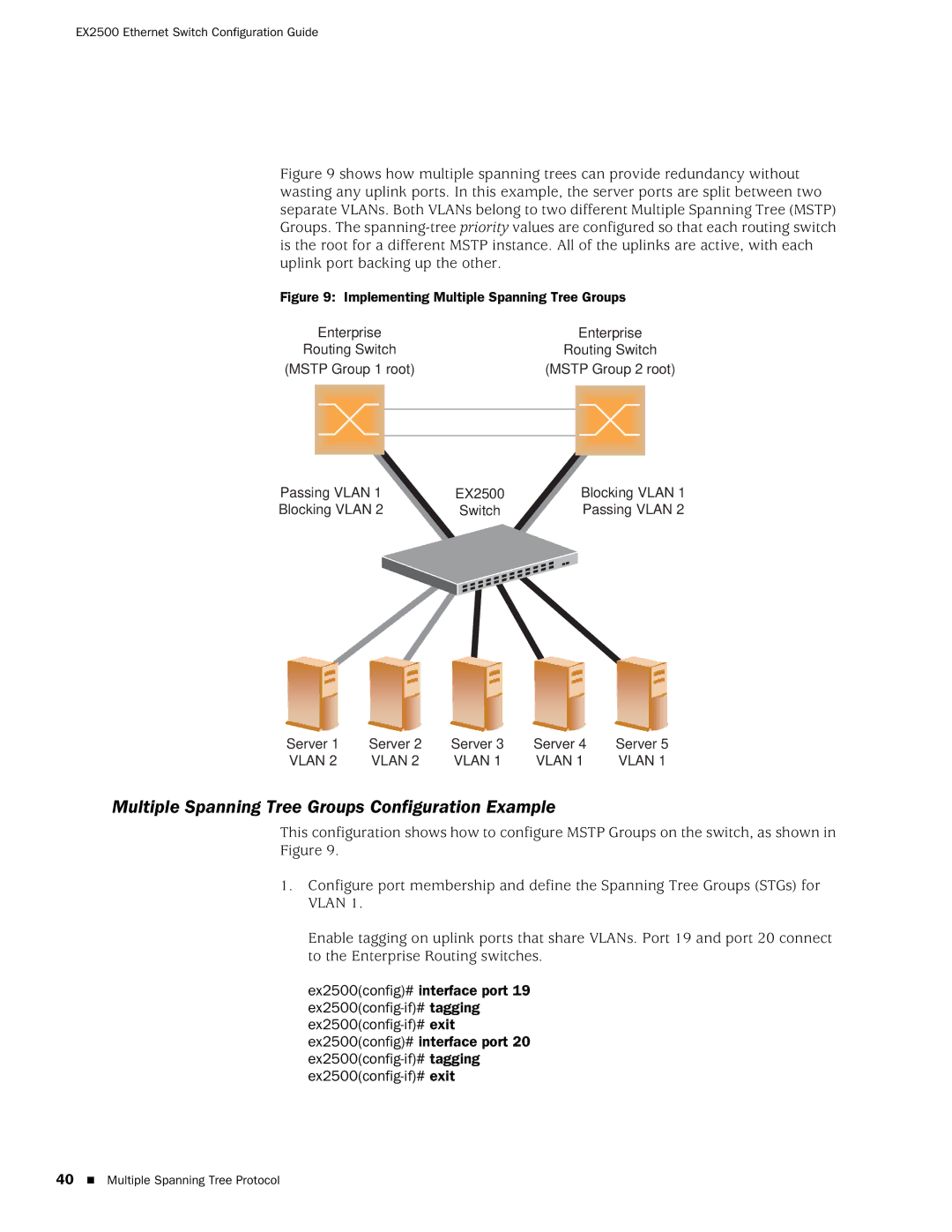
Figure 9 shows how multiple spanning trees can provide redundancy without wasting any uplink ports. In this example, the server ports are split between two separate VLANs. Both VLANs belong to two different Multiple Spanning Tree (MSTP) Groups. The spanning-tree priority values are configured so that each routing switch is the root for a different MSTP instance. All of the uplinks are active, with each uplink port backing up the other.
Figure 9: Implementing Multiple Spanning Tree Groups
| Enterprise |
| Enterprise | |
Routing Switch | Routing Switch | |||
(MSTP Group 1 root) | (MSTP Group 2 root) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Passing VLAN 1 | EX2500 | Blocking VLAN 1 |
Blocking VLAN 2 | Switch | Passing VLAN 2 |
Server 1 | Server 2 | Server 3 | Server 4 | Server 5 |
VLAN 2 | VLAN 2 | VLAN 1 | VLAN 1 | VLAN 1 |
Multiple Spanning Tree Groups Configuration Example
This configuration shows how to configure MSTP Groups on the switch, as shown in
Figure 9.
1.Configure port membership and define the Spanning Tree Groups (STGs) for VLAN 1.
Enable tagging on uplink ports that share VLANs. Port 19 and port 20 connect to the Enterprise Routing switches.
ex2500(config)# interface port 19
40 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol