KX-P7100
1.9.Laser Scan Unit ( Exposure )
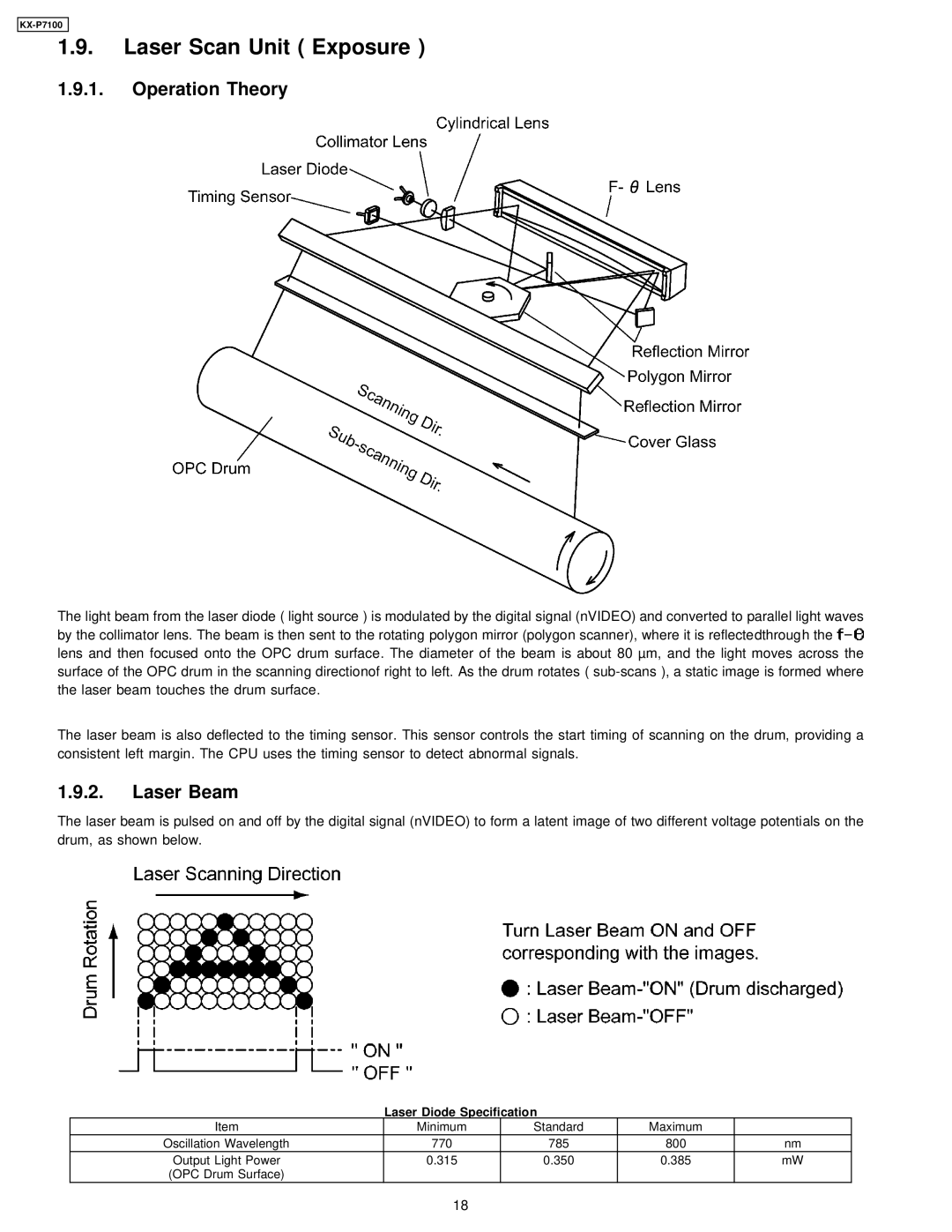
1.9.1.Operation Theory
The light beam from the laser diode ( light source ) is modulated by the digital signal (nVIDEO) and converted to parallel light waves by the collimator lens. The beam is then sent to the rotating polygon mirror (polygon scanner), where it is reflectedthrough the ![]() lens and then focused onto the OPC drum surface. The diameter of the beam is about 80 µm, and the light moves across the surface of the OPC drum in the scanning directionof right to left. As the drum rotates (
lens and then focused onto the OPC drum surface. The diameter of the beam is about 80 µm, and the light moves across the surface of the OPC drum in the scanning directionof right to left. As the drum rotates (
The laser beam is also deflected to the timing sensor. This sensor controls the start timing of scanning on the drum, providing a consistent left margin. The CPU uses the timing sensor to detect abnormal signals.
1.9.2.Laser Beam
The laser beam is pulsed on and off by the digital signal (nVIDEO) to form a latent image of two different voltage potentials on the drum, as shown below.
Laser Diode Specification
Item | Minimum | Standard | Maximum |
|
Oscillation Wavelength | 770 | 785 | 800 | nm |
Output Light Power | 0.315 | 0.350 | 0.385 | mW |
(OPC Drum Surface) |
|
|
|
|
18