9. Appendix
bCalculating the polarization
MPrinciple
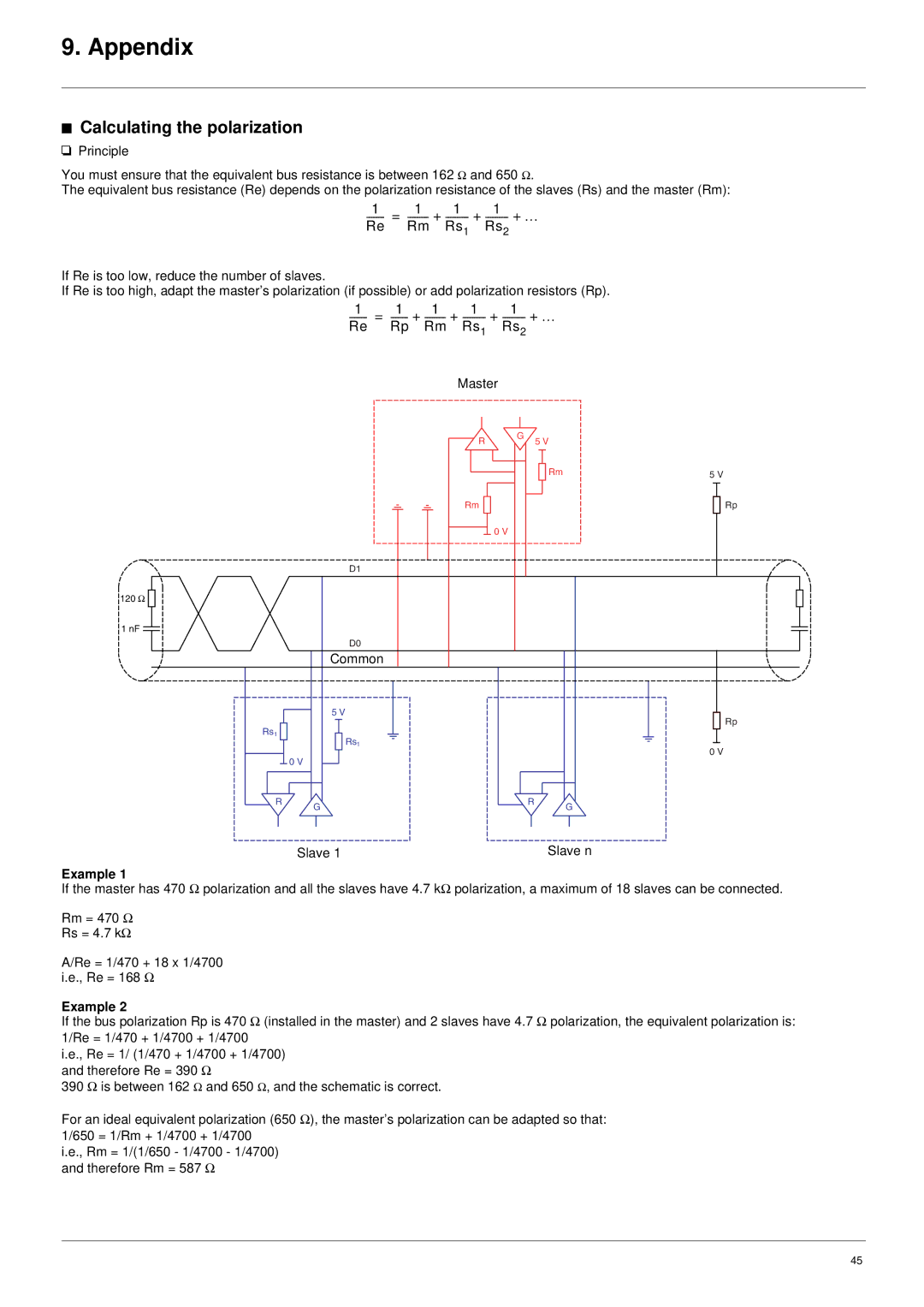
You must ensure that the equivalent bus resistance is between 162 Ω and 650 Ω.
The equivalent bus resistance (Re) depends on the polarization resistance of the slaves (Rs) and the master (Rm):
1 1 1 1 …
------- = --------- + --------- + --------- + Re Rm Rs1 Rs2
If Re is too low, reduce the number of slaves.
If Re is too high, adapt the master’s polarization (if possible) or add polarization resistors (Rp).
1 | = | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| … |
|
+ | + |
| ||||||
Re |
| Rp | Rm | Rs1 | Rs2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Master |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| R | G | 5 V |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rm | 5 V |
|
|
|
| Rm |
|
|
| Rp |
|
|
|
|
| 0 V |
|
|
|
D1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
120 Ω |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 nF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
5 V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rp |
Rs1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Rs1 ![]()
![]()
![]() 0 V
0 V
0 V
R
G
R
G
Slave 1 | Slave n |
Example 1
If the master has 470 Ω polarization and all the slaves have 4.7 kΩ polarization, a maximum of 18 slaves can be connected.
Rm = 470 Ω
Rs = 4.7 kΩ
A/Re = 1/470 + 18 x 1/4700 i.e., Re = 168 Ω
Example 2
If the bus polarization Rp is 470 Ω (installed in the master) and 2 slaves have 4.7 Ω polarization, the equivalent polarization is: 1/Re = 1/470 + 1/4700 + 1/4700
i.e., Re = 1/ (1/470 + 1/4700 + 1/4700) and therefore Re = 390 Ω
390 Ω is between 162 Ω and 650 Ω, and the schematic is correct.
For an ideal equivalent polarization (650 Ω), the master’s polarization can be adapted so that: 1/650 = 1/Rm + 1/4700 + 1/4700
i.e., Rm = 1/(1/650 - 1/4700 - 1/4700) and therefore Rm = 587 Ω
45