Communications | PcOS Series 150 | Programmer's Guide |
Overview
In most cases, the host computer is capable of sending information to the printer much faster than the printer can print it. To prevent information from being lost, a flow control mechanism is provided. This mechanism is called the flow control protocol. The goal of the flow control protocol is to exchange as much information as possible as fast as possible without losing any data. The Series 150 Printer supports three flow control protocols, two in serial mode and one in parallel.
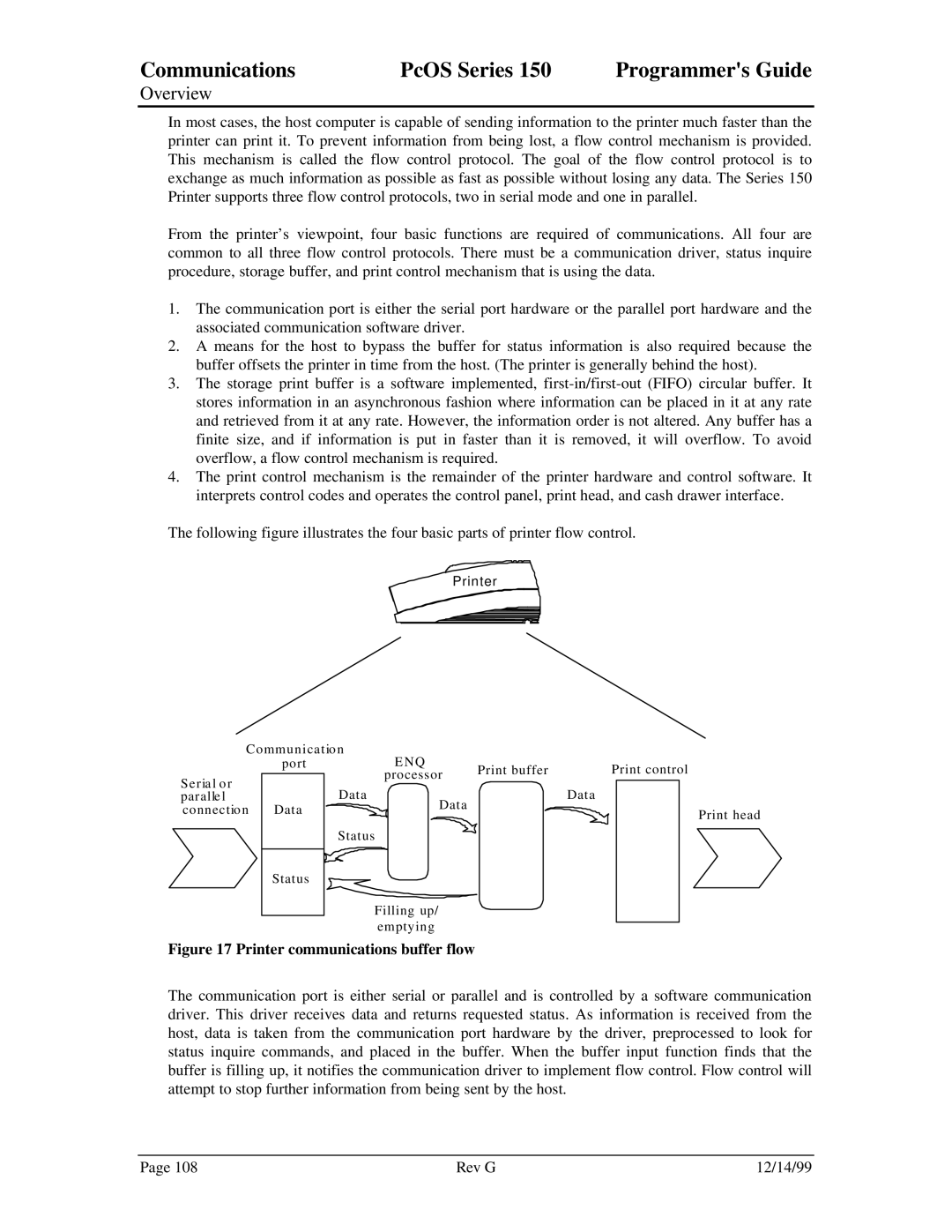
From the printer’s viewpoint, four basic functions are required of communications. All four are common to all three flow control protocols. There must be a communication driver, status inquire procedure, storage buffer, and print control mechanism that is using the data.
1.The communication port is either the serial port hardware or the parallel port hardware and the associated communication software driver.
2.A means for the host to bypass the buffer for status information is also required because the buffer offsets the printer in time from the host. (The printer is generally behind the host).
3.The storage print buffer is a software implemented,
4.The print control mechanism is the remainder of the printer hardware and control software. It interprets control codes and operates the control panel, print head, and cash drawer interface.
The following figure illustrates the four basic parts of printer flow control.
Printer
Communicatio n | E N Q |
|
| |
| port | Print buffer | Print control | |
Seria l o r |
| processor | ||
|
|
| ||
Data |
|
| Data | |
paralle l | Data |
| ||
connectio n | Data |
| Print head | |
|
| |||
|
|
|
| |
| Status |
|
|
|
Status
Filling up/ emptying
Figure 17 Printer communications buffer flow
The communication port is either serial or parallel and is controlled by a software communication driver. This driver receives data and returns requested status. As information is received from the host, data is taken from the communication port hardware by the driver, preprocessed to look for status inquire commands, and placed in the buffer. When the buffer input function finds that the buffer is filling up, it notifies the communication driver to implement flow control. Flow control will attempt to stop further information from being sent by the host.
Page 108 | Rev G | 12/14/99 |