TE-PLAQUINDUCTION-NC00127885_Q7_final 12/9/14 11:37 Page 20
EN
Specification
Model | Maximum | Power Adjustment | Display | Applicable Power | |
Input Power | Range | Type | Supply | ||
| |||||
|
|
|
|
| |
IH2018 | 2100W | Digital | |||
Display | 50Hz | ||||
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Product Structure |
A. | Ceramicglass | H. | Stew Button |
B. | Air entry | I. | Fry Button |
C. | Air exit | J. | Deep fry Button |
D. | Controlpanel | K. | Boil water Button |
E. | Digital Display Screen | L. | Timer Button |
F. | Manual Heat button | M. | |
G. | Hot Milk button | N. | On/off Button |
Principle and Characteristics
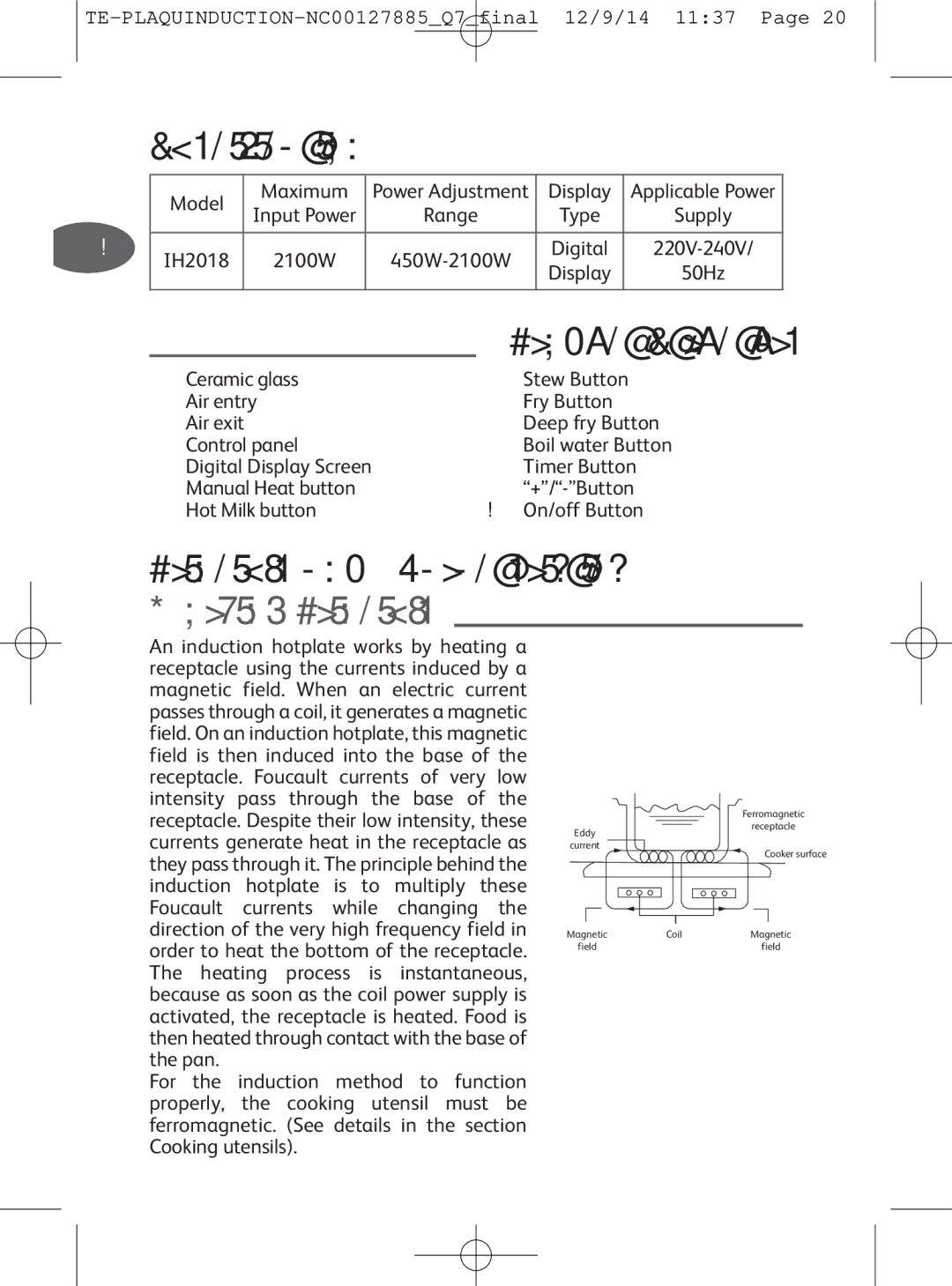
Working Principle
An induction hotplate works by heating a receptacle using the currents induced by a magnetic field. When an electric current passes througha coil, it generatesa magnetic field. On an induction hotplate, this magnetic field is then induced into the base of the receptacle. Foucault currents of very low intensity pass through the base of the receptacle. Despite their low intensity, these currents generate heat in the receptacle as they pass through it. The principle behind the induction hotplate is to multiply these Foucault currents while changing the direction of the very high frequency field in order to heat the bottom of the receptacle. The heating process is instantaneous, because as soon as the coil power supply is activated, the receptacle is heated. Food is then heatedthroughcontactwith the base of the pan.
For the induction method to function properly, the cooking utensil must be ferromagnetic. (See details in the section
Cooking utensils).
20
Eddy
current
Magnetic | Coil |
field |
|
Ferromagnetic
receptacle
Cooker surface
Magnetic
field