www.ti.com
Peripheral Architecture
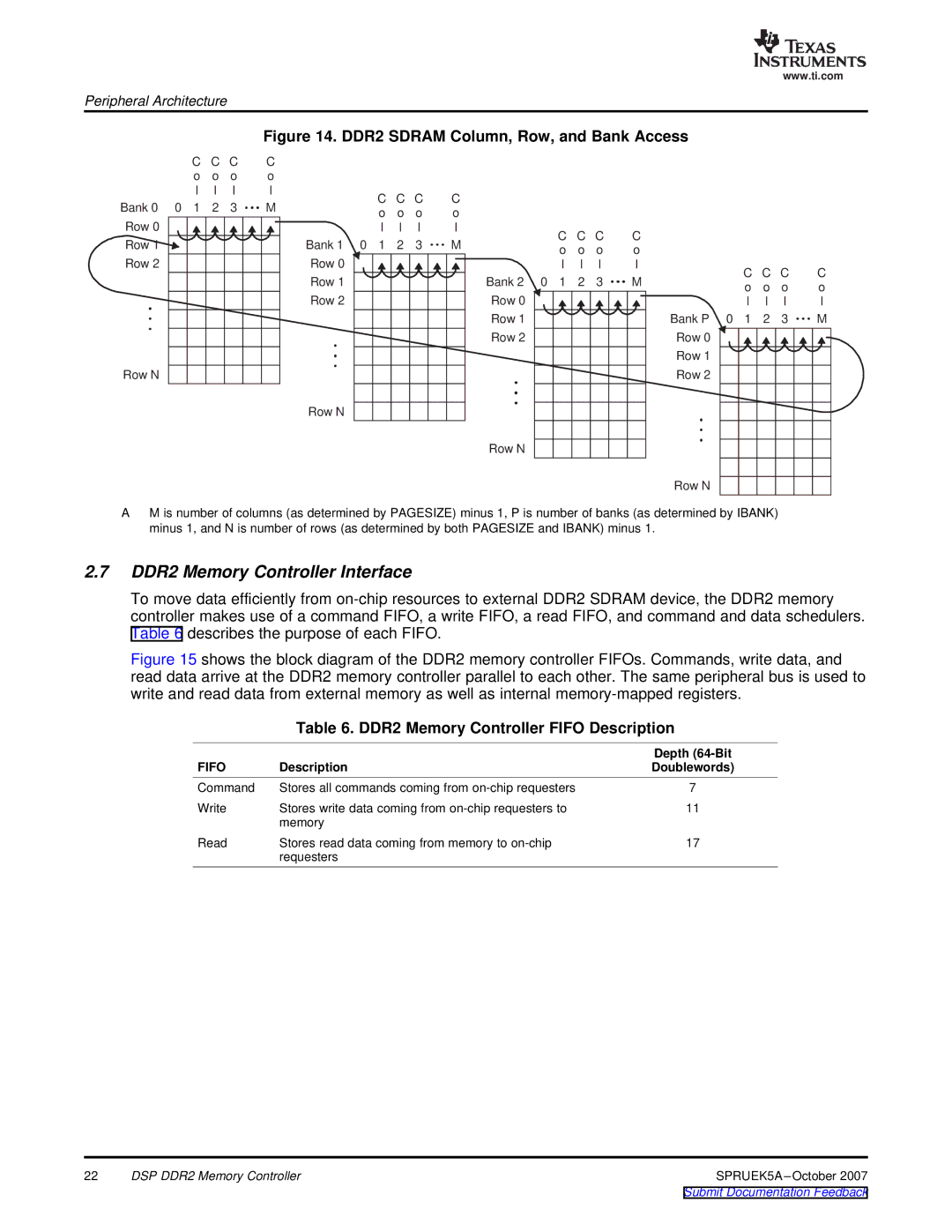
Figure 14. DDR2 SDRAM Column, Row, and Bank Access
Bank 0
Row 0
Row 1
Row 2
Row N
| C | C C | C | |
| o | o | o | o |
| l | l | l | l |
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | M |
|
| C C C | C | ||
|
| o | o | o | o |
|
| l | l | l | l |
Bank 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | M |
Row 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Row 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Row 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
Row N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| C | C C | C | |
|
| o | o | o | o |
|
| l | l | l | l |
Bank 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | M |
Row 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Row 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Row 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
Row N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| C C C | C | ||
|
| o | o | o | o |
|
| l | l | l | l |
Bank P | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | M |
Row 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
Row 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Row 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
Row N |
|
|
|
|
|
AM is number of columns (as determined by PAGESIZE) minus 1, P is number of banks (as determined by IBANK) minus 1, and N is number of rows (as determined by both PAGESIZE and IBANK) minus 1.
2.7DDR2 Memory Controller Interface
To move data efficiently from
Figure 15 shows the block diagram of the DDR2 memory controller FIFOs. Commands, write data, and read data arrive at the DDR2 memory controller parallel to each other. The same peripheral bus is used to write and read data from external memory as well as internal memory-mapped registers.
Table 6. DDR2 Memory Controller FIFO Description
|
| Depth |
FIFO | Description | Doublewords) |
Command | Stores all commands coming from | 7 |
Write | Stores write data coming from | 11 |
| memory |
|
Read | Stores read data coming from memory to | 17 |
| requesters |
|
22 | DSP DDR2 Memory Controller | SPRUEK5A |