Programming Guide
Agilent Part No Microfiche Part No Update April
Safety Guidelines
Contents
Abor
Status Reporting
Error Messages
Synchronizing Power Module Output Changes
About This Guide
Introduction
Documentation Summary
External References
Downloading and Installing the Driver
VXIplug&play Power Products Instrument Drivers
Accessing Online Help
Supported Applications
Introduction To Programming
Gpib Capabilities Of The Power Module
Module Gpib Address
Introduction To Scpi
RST *IDN? *SRE
Voltlev 8.0 Prot 8.8 CURR?
Volt LEV Prot Curr
Outpprotdel
Effect of Optional Headers
Traversing the Command Tree
OUTPUTPROTECTIONCLEARSTATUSOPERATIONCONDITION?
Outputprotectionclear STATUSOPERATIONCONDITION?
Voltagelevel 7PROTECTION 8CURRENTLEVEL 3MODE List
Volttrig 7.5INIT*TRG Outp OFF*RCL 2OUTP on
Numerical Data Formats Talking Formats
Symbol
Listening Formats
Suffixes and Multipliers Class Unit Unit with Multiplier
Assign @PM3TO
System Considerations
Agilent Basic Controllers
Error Handling
Using the National Instruments Gpib Interface
Sending the Command Volt 5 in C
Sending the Command Volt 5 in Basic
Receiving Module Data with Basic
Receiving Data from the Module
Receiving Module Data with C
Introduction
Language Dictionary
CLS
Description Of Common Commands
Meaning and Type
Description
ESE
Bit Configuration of Standard Event Status Enable Register
ESE
ESR?
OPC?
IDN?
OPC
PSC
OPT?
RST
RCL
RCL
SRE
SAV
SRE
TRG
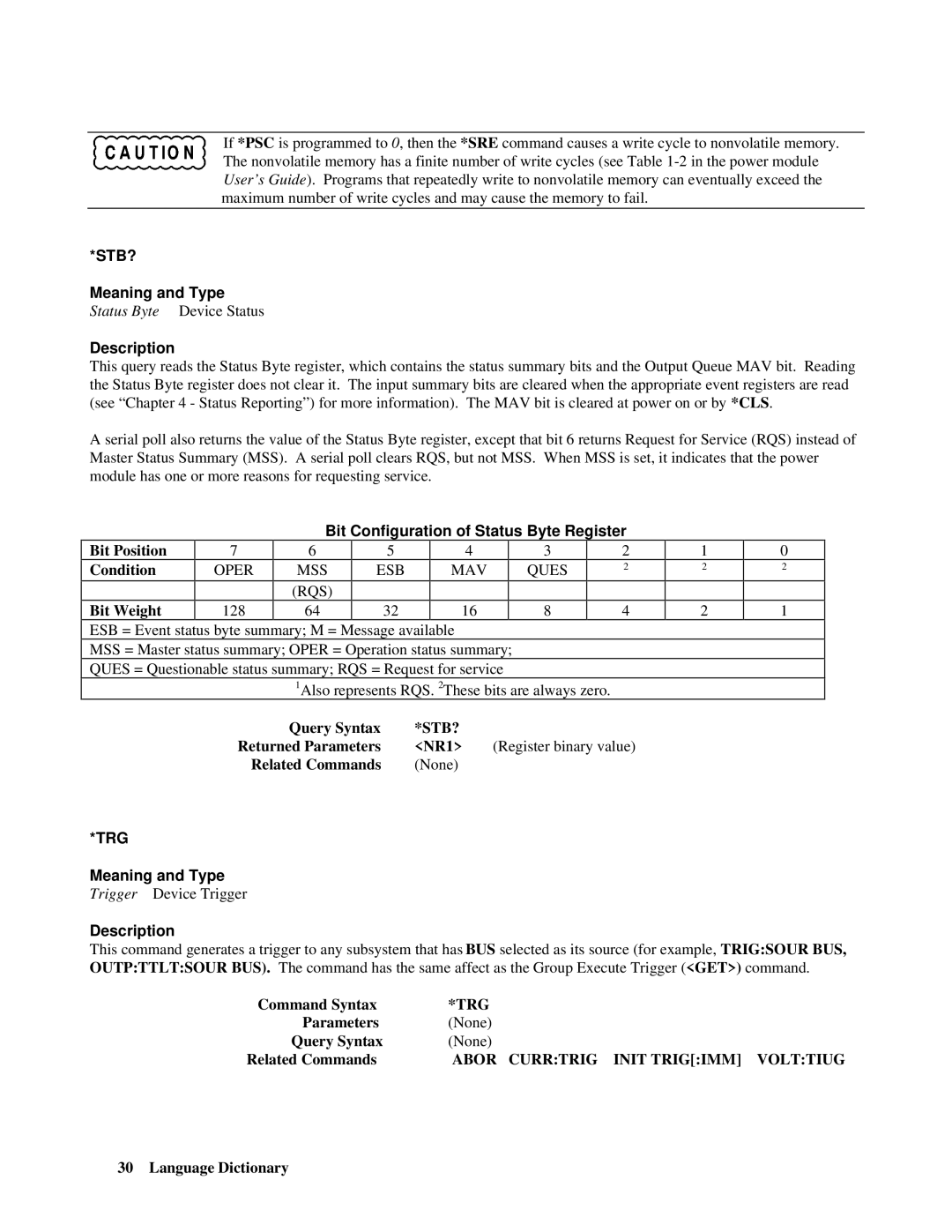
Bit Configuration of Status Byte Register
STB?
TST?
Description of Subsystem Commands
WAI
Abor
Calauto
Subsystem Tree Diagram Calibration Subsystem
Calcurr
Calauto 1 Calauto Once
Calcurrlev
Calpass
Calstat
Calsave
Calvolt
Calvoltlev
Curr
Calvoltprot
Curr 500 MA Currlev
Currmode
Currprotstat OFF
Currprotstat
Currtrig
Currtrig 1200 MA Currlevtrig
Listcoun
Init Initcont 1 Initcont on
Listcoun Listcoun INF
Listcurr
Listdwel
LISTCURRPOIN?
LISTDWELPOIN?
Liststep
Listvolt 2.0,2.5,3.0 Listvolt MAX,2.5,MIN
Listvolt
LISTVOLTPOIN?
MEASCURR? MEASVOLT?
Outpprot
Outp Outpstat ON,NORELAY
Outprel
Outpprotcle Outpprotdel 75E-1
Outprelpol
Norm
Outpttlt 1 Outpttlt OFF
Outpttlt
Outpttltlink
Outpttltsour Link
STATOPEREVEN?
STATOPER?
STATOPERCOND?
Statoperenab
Statpres
Stat Oper NTR 32 Stat Oper PTR
STATQUESEVEN?
STATQUES?
STATQUESCOND?
Stat Ques COND?
SYSTVERS?
SYSTERR?
Trigger Subsystem
Trig
Trigdel
Trig Trig IMM
Trigdel .25 Trigdel MAX
Triglink
Voltlev
Volt
Voltmode
Voltmode List Voltmode FIX
Volttrig 1200 MV Voltlevtrig
VOLTSENSSOUR?
Volttrig
Link Parameter List
Power Module Programming Parameters
Status Register Bit Configuration
Power Module Status Structure
Status Reporting
Operation Status Group
Questionable Status Group
Bit Signal Bit Configurations of Status Registers Meaning
Status Questionable Commands Query
Standard Event Status Group
Power Module Status Model
Location Of Event Handles
Status Byte Register
Output Queue
Examples
Initial Conditions At Power On
Statquesptr 18ENAB
Statoperptr 5376ENAB
STATOPEREVEN?QUESEVEN?
Statoperptr 1024NTR Statoperenab 1024*SRE
Model of Fixed-Mode Trigger Operation
Synchronizing Power Module Output Changes
Trigger Subsystem
Initiated State
Delaying State
Idle State
INITiateCONTinuous Command
Model of List Mode Trigger Operation
Trigger Status and Event Signals
Output Change State
Outpttltsour
List Subsystem
Automatically Repeating a List
Listvolt 3.0,3.25,3.5,3.75 Listdwel 10,10,25,40
Listcurr 2,3,12,15
Triggering a List
Timing diagrams of Liststep Operation
RI Remote Inhibit Subsystem
DFI Discrete Fault Indicator Subsystem
Scpi Command Completion
Power Module Hardware Error Messages
Error Messages
System Error Messages
Standard Event Status Register Error Bits
222 -223 -241 -310 -330 -350 -400 -410 -420 -430
Scpi Approved Commands
Scpi Confirmed Commands
Scpi Conformance Information
Scpi Version
Non-SCPI Commands
Application Programs
Application 1. Sequencing Multiple Modules During Power Up
Variations On This Implementation
Figure B1-1. Block Diagram of Application #1
Figure B1-2. Timing Diagram of Application #1
Enable Backplane TTL Trigger Drive
Reset and Clear Module
Enable Output
Enable Response to Trigger
Implementation Details How The MPS Implements The Solution
MPS Set Up
Figure B2-1. Block Diagram of Application #2
Enable TTL Trigger Drive
When a CV-TO-CC Transition Occurs
Enable Response to TTL Trigger
Start AT 15
Application 3. Controlling Output Voltage Ramp Up at Turn On
Figure B3-1. Simulating a Slow Voltage Ramp
Generating the Desired Voltage Ramp for Application #3
Start Voltage for Ramp
Option Base
Stop Voltage for Ramp
Seconds
Figure B4-1. Voltage Waveform for Application #4
Application 4. Providing Time-Varying Voltages
Module set up
Variations On This Implementation
No Delay Before Protection Occurs
Enable OCP
Enable Detection of OC Condition
Enables Detection on Positive TRANSITION, I.E
Application 5. Providing Time-Varying Current Limiting
Figure B5-1. Typical DUT Current vs. Time
Implementation Details How The MPS Implements The Sequence
Current Limit Data
GO to 12 V When Triggered
Dwell Time Data
SET to GET Current from List
Nominal 12
Application 6. Output Sequencing Paced by the Computer
MPS Set Up
Figure B6-1. Block Diagram of Application #6
Supply Limit Conditions
These are the Bias
To be Tested
Number of Bias Supply Limit C0MBINATIONS
Return
Overview Of Application
Advantages/Benefits Of The MPS Solution
Figure B7-1. Block Diagram of Application #7
When IT Completes the LIST. OPC Generates SRO
When the Module Indicates SIC Step Completed
Enable SRQ Interrupt
Enable Intr Identify Handler Subroutine
Supplemental Information
CMD$ = Initiate ‘ Enable Trigger to Start List
CMD$ = Output on ‘ Enable Output
‘ Conversion to Send Real Numbers Over the BUS
CMD$ = Voltmode List ‘ SET to GET Voltage from List
Waiting for Trigger BIT 5 of the Operation Status Register
Call Iooutputs SLOTO, CMDS, L
CONDITION.DATA =
Wend
If IBSTA% 0 then Goto ‘ AS Part of the Command String
‘ Disable Auto Serial Poll
‘ Program N3.BAS
‘ INSTRUMENT.NAME$ = Sloto
Stop
‘ General Error Handler
If IBSTA% 0 then Goto Selected AS a Trigger Source
Dwell = ramptime
Application #3 Controlling Voltage Ramp UP AT Turn on
To terminate the iooutputa
Int error Char *badstring If error !=
EOl enabled for both read and write
Strcatvlist, vpoint
This is a generalized error checking routine
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
United States Latin America
Agilent Sales and Support Offices
Manual Updates