AMD AthlonTM Processor
Trademarks
Contents
Instruction Decoding Optimizations
Cache and Memory Optimizations
Scheduling Optimizations
Floating-Point Optimizations
General x86 Optimization Guidelines 127
Appendix B Pipeline and Execution Unit Resources Overview
Appendix E Programming the Mtrr and PAT
List of Figures
Xii
List of Tables
Xiv
Revision History
Xvi
Introduction
About this Document
Source Level Optimizations. Describes optimizations that
AMD Athlon Processor Family
AMD Athlon Processor Microarchitecture Summary
AMD Athlon Processor Microarchitecture Summary
AMD Athlon Processor x86 Code Optimization
Top Optimizations
Memory Size and Alignment Issues
Optimization Star
Group I Optimizations Essential Optimizations
Use the 3DNow! Prefetch and Prefetchw Instructions
Group II Optimizations-Secondary Optimizations
Select DirectPath Over VectorPath Instructions
Load-Execute Instruction Usage
Use Load-Execute Instructions
Take Advantage of Write Combining
Use 3DNow! Instructions
Avoid Branches Dependent on Random Data
Avoid Placing Code and Data in the Same 64-Byte Cache Line
22007E/0 November
Source Level Optimizations
Use 32-Bit Data Types for Integer Code
Consider the Sign of Integer Operands
Example 1 Avoid
Example Preferred
Use Array Style Instead of Pointer Style Code
Example Avoid
Use unsigned types for
Use signed types for
Vertex
Example 2 Preferred
Completely Unroll Small Loops
Avoid Unnecessary Store-to-Load Dependencies
Avoid Unnecessary Store-to-Load Dependencies
Consider Expression Order in Compound Branch Conditions
Switch Statement Usage
Optimize Switch Statements
Use Prototypes for All Functions
Use Const Type Qualifier
Generic Loop Hoisting
Example
Generalization for Multiple Constant Control Code
Declare Local Functions as Static
Dynamic Memory Allocation Consideration
Introduce Explicit Parallelism into Code
Explicitly Extract Common Subexpressions
Language Structure Component Considerations
Example
Avoid
Preferred
Sort Local Variables According to Base Type Size
Original ordering Avoid
New ordering, with padding Preferred
Accelerating Floating-Point Divides and Square Roots
Improved ordering Preferred
Accelerating Floating-Point Divides and Square Roots
Avoid Unnecessary Integer Division
AMD Athlon Processor x86 Code Optimization
Instruction Decoding Optimizations
Overview
Select DirectPath Over VectorPath Instructions
Load-Execute Instruction Usage
Use Load-Execute Integer Instructions
TOP
Align Branch Targets in Program Hot Spots
Use Short Instruction Lengths
Avoid Partial Register Reads and Writes
Example 2 Avoid
Use 8-Bit Sign-Extended Immediates
Replace Certain Shld Instructions with Alternative Code
Use 8-Bit Sign-Extended Displacements
Code Padding Using Neutral Code Fillers
Recommendations for the AMD Athlon Processor
Code Padding Using Neutral Code Fillers
AMD Athlon Processor x86 Code Optimization
NOP6EDI
AMD Athlon Processor x86 Code Optimization
Memory Size and Alignment Issues
Cache and Memory Optimizations
Avoid Memory Size Mismatches
Align Data Where Possible
Use the 3DNow! Prefetch and Prefetchw Instructions
Example Multiple Prefetches
Code
MOV ECX, -LARGENUM
Determining Prefetch Distance
Prefetch Distance = 200 DS/C bytes
Take Advantage of Write Combining
Avoid Placing Code and Data in the Same 64-Byte Cache Line
Store-to-Load Forwarding Restrictions
Store-to-Load Forwarding Pitfalls -True Dependencies
Example 3 Avoid
Example 4 Avoid
Example 5 Preferred
Example 6 Avoid
Example 7 Avoid
Stack Alignment Considerations
Summary of Store-to-Load Forwarding Pitfalls to Avoid
Align Tbyte Variables on Quadword Aligned Addresses
Sort Variables According to Base Type Size
Branch Optimizations
Avoid Branches Dependent on Random Data
AMD Athlon Processor Specific Code
Blended AMD-K6and AMD Athlon Processor Code
Always Pair Call and Return
Example 6 Increment Ring Buffer Offset
Example 7 Integer Signum Function
Replace Branches with Computation in 3DNow! Code
Muxing Constructs
Sample Code Translated into 3DNow! Code
Code
3DNow! code
MM5
Pfsub
Psrad
Avoid the Loop Instruction
Avoid Far Control Transfer Instructions
Avoid Recursive Functions
Scheduling Optimizations
Schedule Instructions According to their Latency
Unrolling Loops
Complete Loop Unrolling
Partial Loop Unrolling
Without Loop Unrolling
With Partial Loop Unrolling
Deriving Loop
Control For Partially
Unrolled Loops
Example 1 rolled loop
Use Function Inlining
Overview
Avoid Address Generation Interlocks
Always Inline Functions if Called from One Site
Use Movzx and Movsx
Minimize Pointer Arithmetic in Loops
MOV ECX, Maxsize
Push Memory Data Carefully
Example 3 Preferred
Push Memory Data Carefully
Integer Optimizations
Replace Divides with Multiplies
Multiplication by Reciprocal Division Utility
Unsigned Division by Multiplication of Constant
Signed Division by Multiplication of Constant
Simpler Code for
Restricted Dividend
Signed Division By
Signed Division By 2n
Remainder of Signed
Integer 2 or
Use Alternative Code When Multiplying by a Constant
Integer 2n or -2n
ADD REG1, REG1 REG1, REG2 SHL
Use MMX Instructions for Integer-Only Work
Repeated String Instruction Usage
Latency of Repeated String Instructions
Guidelines for Repeated String Instructions
Using Movq
Ensure DF=0 UP
Align Source
Destination with
Use XOR Instruction to Clear Integer Registers
Efficient 64-Bit Integer Arithmetic
Example 4 Left shift
Example 5 Right shift
Example 6 Multiplication
Example 7 Division
EBX, ESP+12 Dividendlo
Example 8 Remainder
SHR EDX
Efficient Implementation of Population Count Function
Step
Bit field. Thus the following computation is performed
MOV EDX, EDX SHR
Derivation of Multiplier Used for Integer Division by
Utility sdiv.exe was compiled using the following code
MOV ECX EDX Imul ADD SHR SAR
Floating-Point Optimizations
Ensure All FPU Data is Aligned
Use Multiplies Rather than Divides
Floating-Point Compare Instructions
Use Ffreep Macro to Pop One Register from the FPU Stack
Avoid Using Extended-Precision Data
Use the Fxch Instruction Rather than FST/FLD Pairs
Minimize Floating-Point-to-Integer Conversions
Example 1 Fast
Example 2 Potentially faster
Example 3 Potentially faster
Example 4 Fastest
Floating-Point Subexpression Elimination
104
Take Advantage of the Fsincos Instruction
106
3DNow! and MMX Optimizations
Use 3DNow! Instructions
Use Femms Instruction
Use 3DNow! Instructions for Fast Division
Optimized 14-Bit Precision Divide
Optimized Full 24-Bit Precision Divide
Pipelined Pair of 24-Bit Precision Divides
Newton-Raphson Reciprocal
Optimized 15-Bit Precision Square Root
Optimized 24-Bit Precision Square Root
Newton-Raphson Reciprocal Square Root
3DNow! and MMX Intra-Operand Swapping
AMD Athlon
Specific Code
Blended Code
Fast Conversion of Signed Words to Floating-Point
Use MMX Pxor to Negate 3DNow! Data
Use MMX Pcmp Instead of 3DNow! Pfcmp
Both Numbers
Positive One Negative, One
Positive
Use MMX Instructions for Block Copies and Block Fills
AMD-K6and AMD Athlon Processor Blended Code
116
Processor Specific
Use MMX Pxor to Clear All Bits in an MMX Register
Optimized Matrix Multiplication
Use MMX Pcmpeqd to Set All Bits in an MMX Register
MOV EBX, RES
Optimized Matrix Multiplication 121
Data
Use 3DNow! Pavgusb for MPEG-2 Motion Compensation
MM0=QWORD1
Stream of Packed Unsigned Bytes
Complex Number Arithmetic
General x86 Optimization Guidelines
Short Forms
Dependencies
Register Operands
Stack Allocation
AMD Athlon Processor Microarchitecture
Introduction
AMD Athlon Processor Microarchitecture
Superscalar Processor
AMD Athlon Processor Microarchitecture 131
Predecode
Branch Prediction
Early Decoding
Instruction Control Unit
Data Cache
Integer Scheduler
Integer Execution Unit
Floating-Point Scheduler
Floating-Point Execution Unit
12 to
Load-Store Unit LSU
Load/Store Unit
L2 Cache Controller
Write Combining
AMD Athlon System Bus
140 AMD Athlon Processor Microarchitecture
Pipeline and Execution Unit Resources Overview
Fetch and Decode Pipeline Stages
C T L R O M
Cycle 1-FETCH
Cycle 2-SCAN
Cycle 3 DirectPath
Cycle 3 VectorPath
Integer Pipeline Stages
Integer Pipeline Stages
Cycle 7-SCHED
Cycle 8-EXEC
Cycle 9-ADDGEN
Cycle 10 -DCACC
Floating-Point Pipeline Stages
Floating-Point Pipeline Stages
Cycle 7-STKREN
Cycle 8-REGREN
Cycle 9-SCHEDW
Cycle 10 -SCHED
Execution Unit Resources
Terminology
Operands
Results
Integer Pipeline Operations
Integer Pipeline Operation Types
Integer Decode Types
Floating-Point Pipeline Operations
Floating-Point Pipeline Operation Types
Floating-Point Decode Types
Load/Store Pipeline Operations
Load/Store Unit Stages
Stage 1 Cycle Stage 2 Cycle Stage 3 Cycle
Code Sample Analysis
Imul EAX, ECX INC ESI MOV
ADD EDI, EBX SHL
INC EBX ADD ESI, EDX
Sample 2 Integer Register and Memory Load Operations
DEC EDX MOV EDI, ECX SUB
SAR
Appendix C
Implementation Write Combining
What is Write Combining?
Write-Combining Definitions and Abbreviations
Programming Details
Write-Combining Operations
Write Combining Completion Events
INIT, Halt
AMD Athlon System Bus Commands Generation Rules
Sending Write-Buffer Data to the System
160 Write-Combining Operations
Performance-Monitoring Counters
Performance Counter Usage
PerfEvtSel30 MSRs MSR Addresses C0010000h-C0010003h
PerfEvtSel30 Registers
Performance Counter Usage 163
Performance-Monitoring Counters
65h
73h
Snoop hits
74h
Event Source Event Description
Waited to use the L2
Instruction cache fetches
Instruction cache misses
PerfCtr30 MSRs MSR Addresses C0010004h-C0010007h
Event and Time-Stamp Monitoring Software
Starting and Stopping the Performance-Monitoring Counters
Monitoring Counter Overflow
170 Monitoring Counter Overflow
Programming the Mtrr
Memory Type Range Register Mtrr Mechanism
172 Memory Type Range Register Mtrr Mechanism
Fixed Ranges
FFFFFFFFh
100000h Kbytes each Fixed Ranges C0000h 80000h
Memory Types
Memory Type Encodings
Mtrr Capability
Register Format
Memory Type Range Register Mtrr Mechanism 175
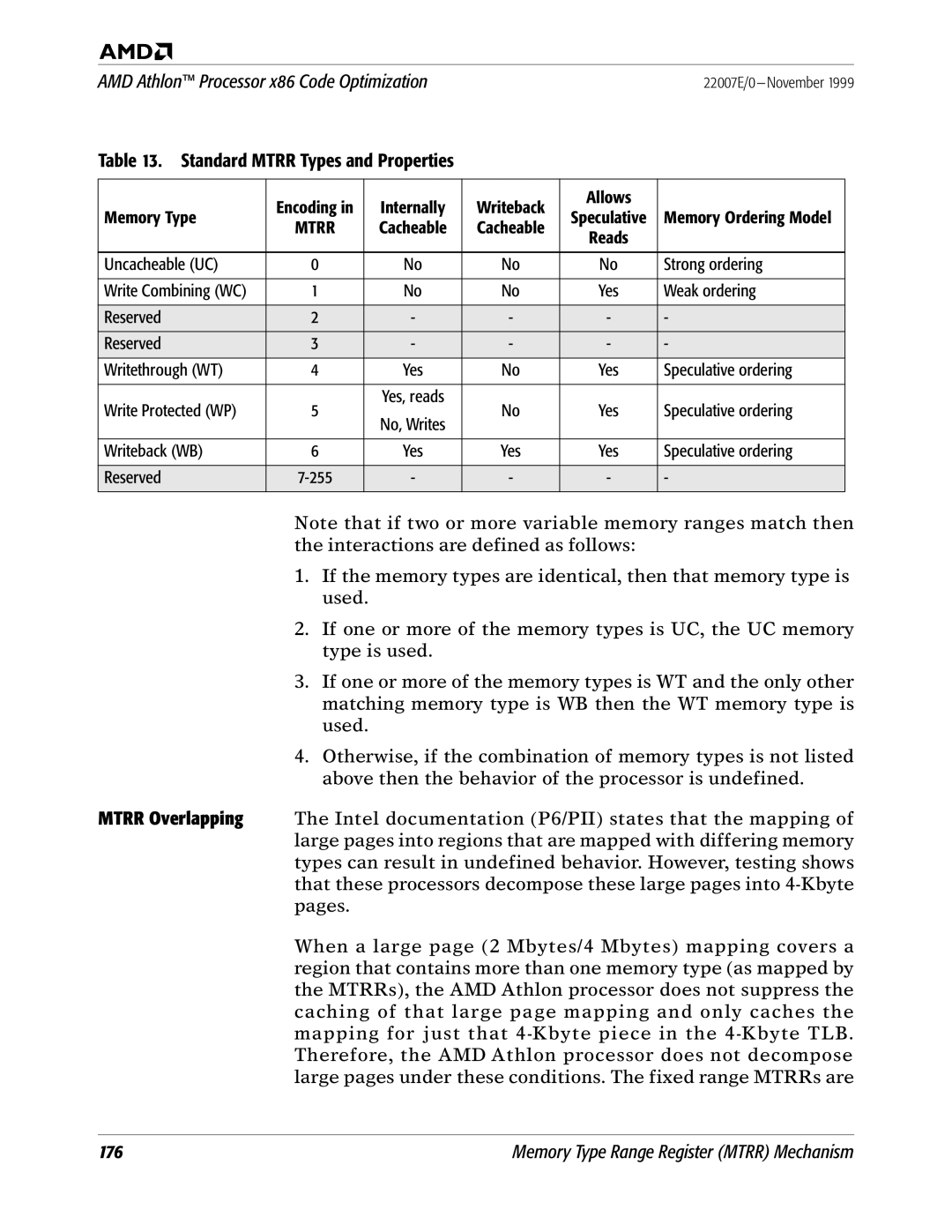
Standard Mtrr Types and Properties
Attribute Table PAT
Attribute Table MSR 277h
PAT Entry Reset Value
PATi 3-Bit Encodings
MTRRs and PAT
PATi
Effective Memory Type Based on PAT and MTRRs
PAT Memory Type Mtrr Memory Type
Final Output Memory Types
Input Memory Type
Attribute Table PAT 181
7FFFF 6FFFF 5FFFF 4FFFF 3FFFF 2FFFF 1FFFF 0FFFF
9FFFF 9BFFF 97FFF 93FFF 8FFFF 8BFFF 87FFF 83FFF
Bffff Bbfff B7FFF B3FFF Affff Abfff A7FFF A3FFF
C7FFF C6FFF C5FFF C4FFF C3FFF C2FFF C1FFF C0FFF
Attribute Table PAT 183
MTRRphysMaskn Register Format
MTRR-Related Model-Specific Register MSR Map
186
Appendix F
Instruction Dispatch Execution Resources
Integer Instructions
AAA
AAD
AAM
ModR/M Decode Byte
ADC mreg8, reg8
ADC mem8, reg8
ADC mreg16/32, reg16/32
Bound
Bswap EAX
Bswap ECX
Bswap EDX
CBW/CWDE
CLC
CLD
CLI
CMOVE/CMOVZ reg16/32, reg16/32 0Fh
CMOVE/CMOVZ reg16/32, mem16/32 0Fh
CMOVG/CMOVNLE reg16/32, reg16/32 0Fh
CMOVG/CMOVNLE reg16/32, mem16/32 0Fh
Cpuid
CWD/CDQ
DAA
DAS
Enter
AL, DX
AX, DX
EAX, DX
Invd
Invlpg
Lahf
Leave
LOOPE/LOOPZ disp8 E1h
LOOPNE/LOOPNZ disp8 E0h
LSL reg16/32, mreg16/32 0Fh 03h
LSL reg16/32, mem16/32 0Fh 03h
NOP Xchg EAX, EAX
OUT DX, AL
OUT DX, AX
OUT DX, EAX
POP ES
POP EBX
POP ESP
POP EBP
POP ESI
Rdmsr
Rdpmc
Rdtsc
Sahf
SBB mreg16/32, reg16/32
SBB mem16/32, reg16/32
SBB reg8, mreg8
SBB reg8, mem8
Sets mreg8
Sets mem8
Setns mreg8
Setns mem8
STC
STD
STI
Syscall
Sysenter
Sysexit
Sysret
Xchg EAX, EAX
Xchg EAX, ECX
Xchg EAX, EDX
Xchg EAX, EBX
MMX Instructions
Emms
Pandn mmreg1, mmreg2
DFh
Pandn mmreg, mem64
Pcmpeqb mmreg1, mmreg2
FADD/FMUL
MMX Extensions
FPU
Floating-Point Instructions
Fcompp
Fcos
Fdecstp
Fincstp
Finit
FLD1
FLDL2E
FLDL2T
FLDLG2
FLDLN2
Fstsw AX
Ftst
Fucom
Fucomp
DNow! Instructions
Femms
DNow! Extensions
DirectPath versus VectorPath Instructions
DirectPath Instructions
DirectPath Integer Instructions
BT mreg16/32, reg16/32 BT mreg16/32, imm8 BT mem16/32, imm8
CBW/CWDE CLC CMC
DEC mreg8 DEC mem8 DEC mreg16/32 DEC mem16/32
INC mreg8 INC mem8 INC mreg16/32 INC mem16/32 JO short disp8
222 DirectPath Instructions
DirectPath Instructions 223
224 DirectPath Instructions
Wait Xchg EAX, EAX
226 DirectPath Instructions
DirectPath MMX Instructions
DirectPath MMX Extensions
DirectPath Floating-Point Instructions
Fcompp Fdecstp
Fist mem16int
FLD1 FLDL2E FLDL2T FLDLG2 FLDLN2 Fldpi Fldz
Ftst Fucom Fucomp Fucompp Fwait Fxch
VectorPath Instructions
VectorPath Integer Instructions
AAA AAD AAM AAS
CLD CLI Clts
Instruction Mnemonic DIV EAX, mem16/32
AL, DX AX, DX EAX, DX Invd Invlpg
POP mreg 16/32 POP mem 16/32
Push mreg16/32 Push mem16/32
PUSHA/PUSHAD PUSHF/PUSHFD
Rdmsr Rdpmc Rdtsc
VectorPath MMX Instructions
VectorPath MMX Extensions
Syscall Sysenter Sysexit Sysret
Wbinvd Wrmsr
VectorPath Floating-Point Instructions
Fptan Fpatan Frndint
Fscale Fsin Fsincos
Fxam Fxtract FYL2X FYL2XP1
236
Index
238 Index
Index 239
240 Index