Americas Headquarters
Text Part Number OL-15498-01
Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved
N T E N T S
Network Requirements
Configuring Security on the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Vii
Port 1 Network, Port 2 Access, and Port 3 Phone Statistics
Viii
Cable Specifications E-2
D E
Organization
Overview
Audience
Xiii
Chapter Description
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration
Related Documentation
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7960G/7940G Series
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition
Document Conventions
Cisco Product Security Overview
Convention Description
Xvi
An Overview of the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Cisco Unified IP Phone 7960G
An Overview of the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Refer Cisco Unified Communications Manager
What Networking Protocols Are Used?
Networking Protocol Purpose Usage Notes
System Guide
UDP
Related Topics
Related Topic
Feature Overview
Configuring Telephony Features
Understanding Security Features for Cisco Unified IP Phones
Providing Users with Feature Information
Guide
Topic Reference
Refer to Cisco Unified Communications Manager Security
Refer to Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Communications Manager Security Guide
Overview of Supported Security Features
Feature Description
Phone section on page 3-10for more information
Understanding Security Profiles
Identifying Encrypted and Authenticated Phone Calls
Security Restrictions
Capf Interaction when the Phone Resets
Example
OL-15498-01
Refer to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration Guide, Directory Number
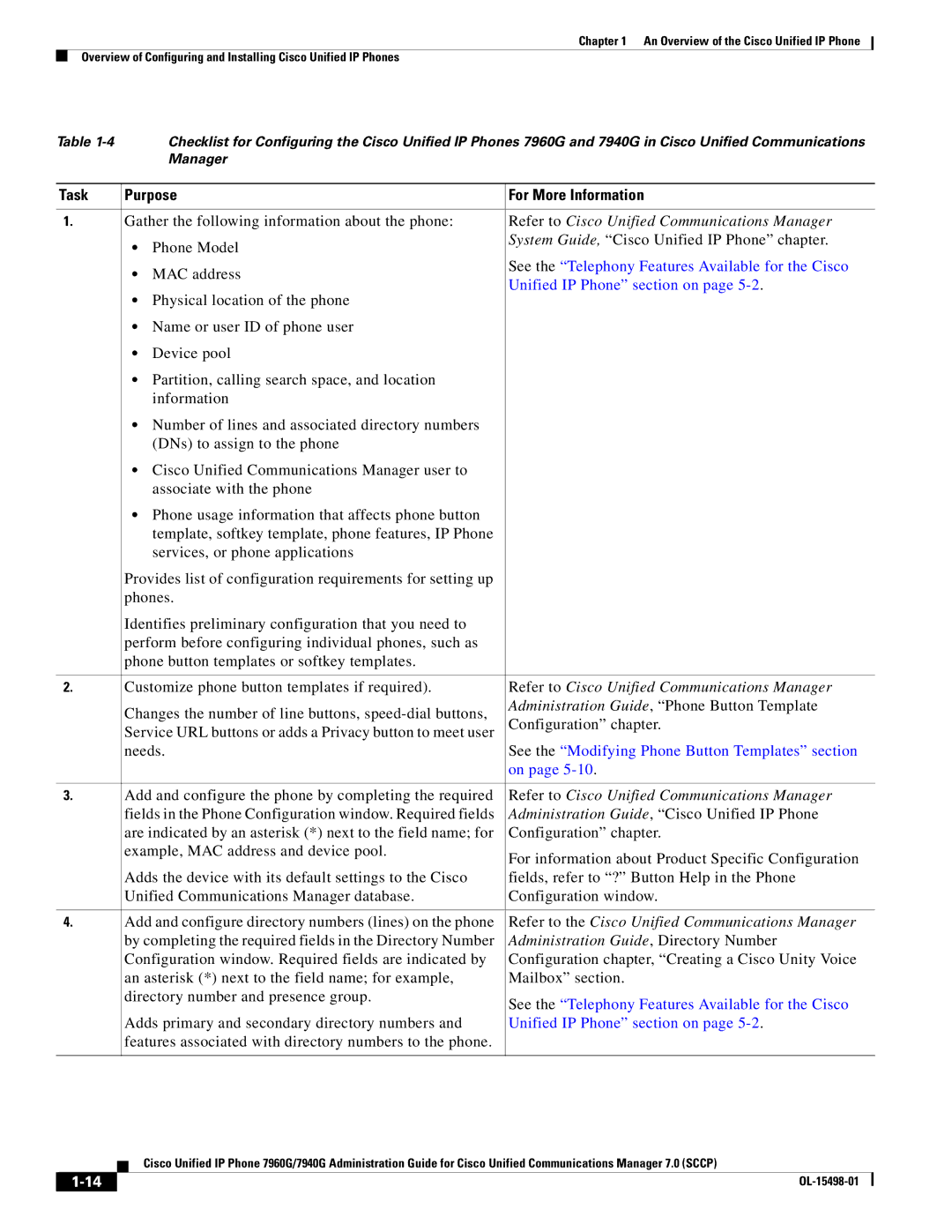
Purpose For More Information
Task Purpose For More Information
Administration Guide, Softkey Template
Administration Guide
URL
Installing Cisco Unified IP Phones
Series Phone Guide for Cisco Unified
Settings Network Configuration
Refer to Cisco Unified IP Phone 7960G/7940G
Communications Manager 7.0 Sccp
OL-15498-01
A P T E R
Related Topic
Providing Power to the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Obtaining Additional Information about Power
Power Guidelines
Power Outage
Power Type Guidelines
Understanding Phone Configuration Files
URL
Unified Communications Manager Security Guide
Understanding the Phone Startup Process
Description Related Topics
Request the configuration file
Taps
Adding Phones with Auto-Registration
Requires MAC Method Address?
Adding Phones with Auto-Registration and Taps
Unified Communications Manager System Guide
Adding Phones with BAT
Using Cisco Unified IP Phones with Different Protocols
Procedure
Converting a New Phone from Sccp to SIP
Deploying a Phone in an Sccp and SIP Environment
Converting an In-Use Phone from Sccp to SIP
Converting an In-Use Phone from SIP to Sccp
Determining the MAC Address for a Cisco Unified IP Phone
Parameters
Setting Up the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Before You Begin
Network Requirements
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Configuration
Network and Access Ports, Handset, Speakerphone, Headset,
Speakerphone
Network and Access Ports
Handset
Headset
Audio Quality Subjective to the User
Before You Begin
Installing the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Procedure Reference
Cisco Unified IP Phones 7960G and 7940G Cable Connections
Attaching the Cisco Unified IP Phone Expansion Module
Expansion Module
Configuring Softkey Templates,
Adjusting the Placement of the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Adjusting Cisco Unified IP Phone Footstand and Phone Height
Mounting the Phone to the Wall
Verifying the Phone Startup Process
Parts Used in Wall Mounting the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Configuring Startup Network Settings
Configuring Security on the Cisco Unified IP Phone
From the phone, choose Settings Security Configuration
OL-15498-01
Configuring Network Settings on the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Displaying the Network Configuration Menu
Unlocking and Locking Options
Editing Values
Overview of Network Configuration Options
Network Configuration
Category Description Menu Option
Option Description To Change
Network Configuration Menu
PC Vlan
Configuration Menu section on
Communications Manager Security Guide. For information
Manager, choose System Enterprise
Communications Manager Options section on
System Device Pool
Manager, choose Device Phone Phone
Configuration
Choose System Enterprise Parameters
Including language, font, date and time formatting,
Disabling the phone’s ability to accept Gratuitous ARP will
Blank
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Options
State
Device Pool
Communications Manager Administration Guide
Designation Description
To Cisco Unified Communications Manager Security Guide
OL-15498-01
Configuring Features, Templates, Services, and Users
Communications Manager Features and Services
Feature Description Configuration Reference
Administration Guide, Cisco Unified IP
Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Administration Guide, Configuring
Features and Services Guide, Barge
Features and Services Guide, Call Display
Specifying Options that Appear on the User
Communications Manager System Guide, Call
Administration Guide, Configuring Cisco
Unified Communications Manager Features
Communications Manager System Guide
DND
Unified Communications Manager
Mcid
Features and Services Guide, Malicious
Administration Guide, Message Waiting
Mlpp
Services menu on a phone
Administration Guide, Conference Bridge
Administration Guide, Time Period
Manager Administration Guide
Cisco VT Advantage Administration Guide
Configuring Personal Directory
Configuring Corporate and Personal Directories
Configuring Corporate Directories
Creating Custom Phone Rings
Modifying Phone Button Templates
Synchronizer
Configuring Softkey Templates
Setting Up Services
Managing the User Options Web Pages
Giving Users Access to the User Options Web Pages
Adding Users to Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Procedure
OL-15498-01
A P T E R
Model Information Screen
Status Menu
Message Description Possible Explanation and Action
Status Messages Screen
Select Status Messages
Address. See the Network Configuration Menu
Communications Manager Administration
Network Configuration Menu section on
Adding Phones with Cisco Unified
Configuration Menu section on page 4-4section for
Configuration Menu section on page 4-4for
See the Firmware Versions Screen section on
Message Component Description
Network Statistics Screen
Select Network Statistics
Firmware Versions Screen
Select Expansion Module Stats
Expansion Module Stats Screen
Select Firmware Versions
Call Statistics Screen
Select Call Statistics
Monitoring the Voice Quality of Calls section on
Voice Quality Metrics
MOS LQK
Security Configuration Menu
CTL File Menu
Certificate Icon
Trust List Menu
Monitoring the Cisco Unified IP Phone Remotely
Accessing the Web Page for a Phone
Http//IPaddress
Choose Device Phone
Disabling and Enabling Web Page Access
Device Information
Network Configuration
Vlan ID
Description
Network Statistics
Ethernet Statistics
Port 1 Network, Port 2 Access, and Port 3 Phone Statistics
Description
Device Logs
Status Messages
Streaming Statistics
Stack Statistics
Streaming Statistics Area Items
Description
OL-15498-01
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Resolving Startup Problems
Troubleshooting and Maintenance Resolving Startup Problems
Identifying Error Messages
Verifying IP Addressing and Routing
Creating a New Configuration File
Choose Tools Control Center Feature Services
Verifying Physical Connection
Cisco Unified IP Phone Resets Unexpectedly
Symptom Cisco Unified IP Phone Unable to Obtain IP Address
Verifying Voice Vlan Configuration
Verifying Dhcp Settings
Checking Static IP Address Settings
Identifying Intermittent Network Outages
Verifying that the Phones Have Not Been Intentionally Reset
Eliminating DNS or Other Connectivity Errors
Troubleshooting Cisco Unified IP Phone Security
Problem Possible Cause
Options section on page 4-2for details
General Troubleshooting Tips
Summary Explanation
Summary Explanation
Problem Solution
Halfduxcollisionexceedthreshold
Restore softkey
Resetting or Restoring the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Performing a Basic Reset
Default softkey
Performing a Factory Reset
Using the Quality Report Tool
Monitoring the Voice Quality of Calls
Metric Change Condition
Where to Go for More Troubleshooting Information
Cleaning the Cisco Unified IP Phone
OL-15498-01
Providing Information to Users Via a Website
How Users Get Copies of Cisco Unified IP Phone Manuals
How Users Access a Voice Messaging System
How Users Configure Personal Directory Entries
Programs Cisco Systems TabSync
Installing the Synchronizer
Configuring the Synchronizer
Page
OL-15498-01
Features
Sccp SIP
SIP
QRT
Services Guide
Cisco Unified IP Phone Service Application
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Features
Development Notes for Release 4.13 or later
OL-15498-01
Supporting International Users
Adding Language Overlays to Phone Buttons
OL-15498-01
Physical and Operating Environment Specifications
Specification Value or Range
Network Port Connector
Cable Specifications
Network and Access Port Pinouts
Access Port Connector
Pin Number Function
OL-15498-01
Basic Phone Administration Steps
Example User Information for these Procedures
Choose System Ldap Ldap Directory
Proceed to Configuring the Phone, page F-3
Adding a User From an External Ldap Directory
Click Perform Full Sync Now
Procedure to Configure Phone
Configuring the Phone
Procedure To Select Phone Model and Protocol
Example johndoe
OL-15498-01
Page
OL-15498-01
Choose User Management End User
Click Device Associations
Performing Final End User Configuration Steps
Click Save
OL-15498-01
Numerics
IN-1
IN-2
Capf
CDP
IN-3
External power
IN-4
Mlpp B-2
IN-5
CDP Dhcp Http RTP Sccp SIP TCP Tftp UDP
IN-6
QRT B-2
IN-7
See Srst
IN-8
Dhcp DNS
IN-9
Vlan
IN-10