Technical Reference Guide
Intel Pentium 4 Processor Intel 850 Chipset
Page
TRG
Page
Reader Feedback
Page
Technical Reference Guide
First Edition -- December
Table of Contents
Parallel Interface Connector
Power Supply and Distribution
Appendix B Ascii Character SET
Appendix D COMPAQ/NVIDIA TNT2 PRO AGP Graphics Card
Appendix H COMPAQ/MATROX Millennium G450 AGP Graphics Card
Appendix L COMPAQ/ADAPTEC Scsi Host Adapter
List of Figures
Figure C-1. Keystroke Processing ELEMENTS, Block Diagram
Figure L-3. External Ultra Scsi Connector 50-PIN
List of Tables
Technical Reference Guide
Able H-3
This page is intentionally blank
Using this Guide
Introduction
About this Guide
Additional Information Sources
Signal Labels
Notational Conventions
Register Notation and Usage
BIT Notation
Common Acronyms and Abbreviations
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Acronym/Abbreviation Description
Dimm
DIN
DIP
DMA
LAN
LCD
LED
LIF
Scsi
Sdram
SEC
Secam
System Overview
Introduction
Features and Options
Standard Features
Standard Feature Difference Matrix
Deskpro EXS Deskpro Workstation
Options
Mechanical Design
Cabinet Layouts
Front Views
Deskpro EXS Deskpro Workstation
Shows the rear cabinet layout of the controls and connectors
Rear View
Chassis Layout
Back
Front
Board Layout
System Board Layout
System Architecture
MCH AGP Rdram
ICH2 LPC
FWH
Pentium 4 Processor
Chipset
Support Components
Chipset Comparison
Support Component Functions
System Memory
Mass Storage
SERIAL, Parallel Interfaces
Universal Serial BUS Interface
Graphics Subsystem
Standard AGP Graphics Card Comparison
Matrox
G450
Specifications
Environmental Specifications Factory Configuration
Electrical Specifications
Audio Subsystem
Physical Specifications
Diskette Drive Specifications
Parameter Desktop Configuration Minitower Configuration
Compaq SP#
48x CD-ROM Drive Specifications SP# 187217-B21
Hard Drive Specifications
Parameter Measurement
Parameter 18.0 GB 20.0 GB 40.0 GB
Processor Memory Subsystem
FSB I/F
AGP MCH
XMM1 XMM2 Rimm
Processor Overview
CPU FPU
FSB
Processor Upgrading
Memory Subsystem
Sdram Interface Rdram Interface Dual Channel
Dimm Rdram
Rambus Signal Attributes Each Channel
Signal Name
Rambus Attributes
Rambus Channel Transactions
Rdram Power Management
Rdram CONFIGURATION/CONTROL
State Power Refresh
Exit Rdram Functionality
Shows the system memory map
Subsystem Configuration
Host/PCI Bridge Configuration Registers MCH, Device
Reset
Config Register Value Egister
System Support
PCI BUS Overview
NIC Eide USB
Configuration Cycles
PCI BUS Transactions
1.1 I/O and Memory Cycles
PCI Component Configuration Access Data
Idsel
PCI Component Vendor/Device ID Bus # Device # Function #
PCI Configuration Space Type
Bist
PCI BUS Master Arbitration
PCI Bus Mastering Devices
REQ/GNT Line Device
PCI Power Management Support
Option ROM Mapping
PCI Interrupts
PCI SUB-BUSSES
PCI Configuration
LPC Bridge Configuration Registers ICH, Function 0, Device
Config Reset
Addr Register Value
PCI Connector
PCI Bus Connector Pinout
Pin Signal
AGP BUS Overview
BUS Transactions
Data Request
Data Transfers
CLK D1A D1B D2A D2B GNT Trdy
AGP 2X Transfers
GNT Trdy
AGP Configuration
Config Reset Addr Register Value
AGP Connector
AGP Bus Connector Pinout
Ovrcnt GND KEY
Trdy Devsel
System Resources
Interrupts
Maskable Interrupts
Apic Mode
Mode
Maskable Interrupt Priorities and Assignments
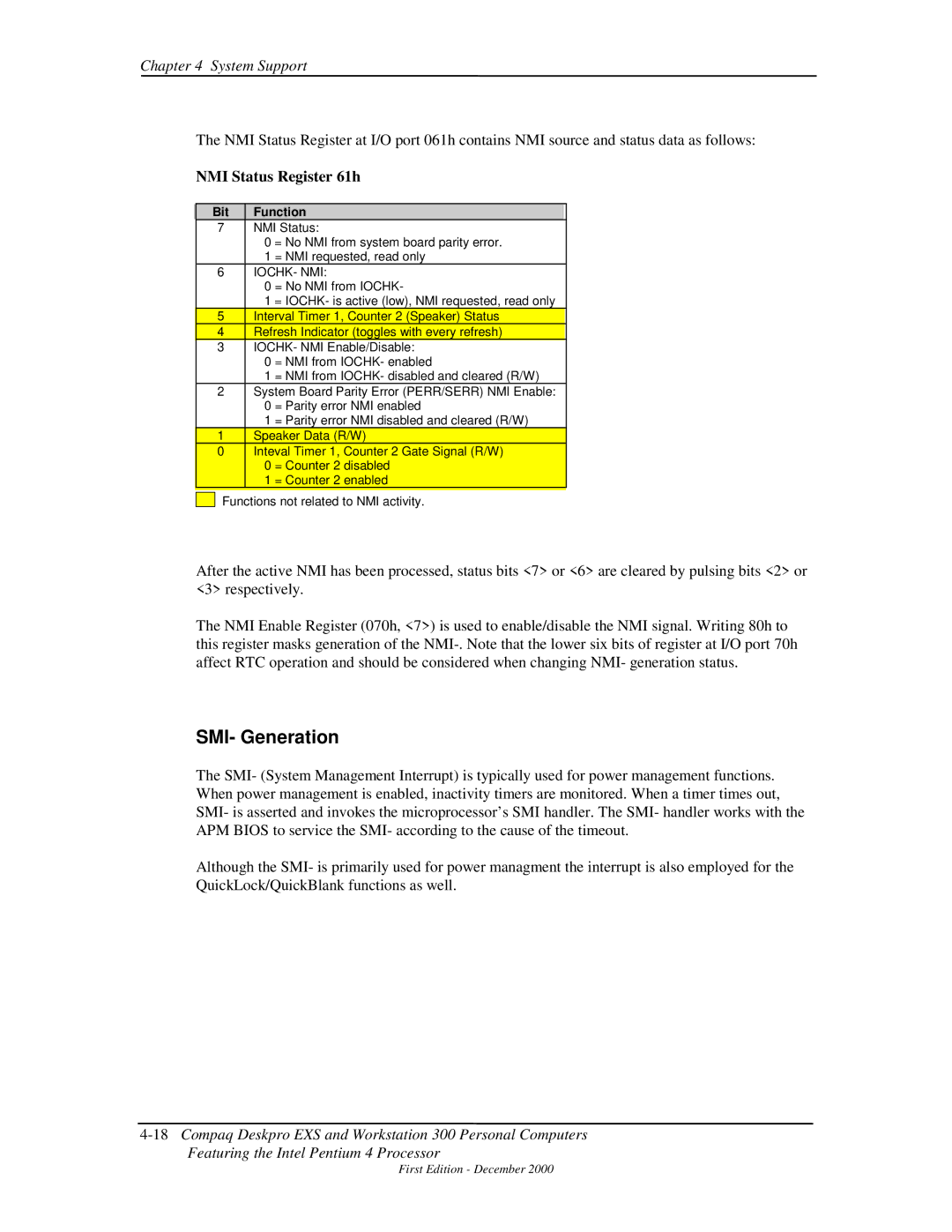
Non-Maskable Interrupts
NMI- Generation
Maskable Interrupt Control Registers
Port Register
SMI- Generation
IOCHK- NMI
Direct Memory Access
DMA Channel Assignments And Register Ports
DMA Channel Function Port
REAL-TIME Clock and Configuration Memory
System Clock Distribution
Clock Generation and Distribution
Frequncy Source Destination
Clearing Cmos
Cmos Archive and Restore
Configuration Memory Cmos Map
Standard Cmos Locations
Location Function
RTC Control Register A, Byte 0Ah
Configuration Byte 0Eh, Diagnostic Status
Configuration Byte 13h, Security Functions
Bit Function Reserved
Configuration Byte 24h, System Board Identification
Configuration Byte 27h, Speed Control/External Drive
Configuration Byte 2Ah, Hard Drive Timeout
Configuration Byte 2Eh, 2Fh, Checksum
Configuration Byte 35h, APM Status Flags
Power-On Password
Setup Password
System Management
Security Functions
Power Management
Cable Lock Provision
1.4 I/O Interface Security
Acpi Wake-Up Event System Wakes From
System Boot/ROM Flash Status LED Indications
System Status
System Operational Status LED Indications
NUM Lock CAPs Lock Scroll Lock Event
Temperature Sensing and Cooling
CMD
Register MAP and Miscellaneous Functions
System I/O MAP
System I/O Map
Port Function
2 82801 ICH General Purpose Functions
82801 ICH2 Gpio Register Utilization
Gpio Port # Function Direction
PS LED NIC REQ5 Irqe Irqf Irqg Irqh HD LED
Index Function Reset Value
3 I/O Controller Functions
Controller Control Registers
3.1 LPC47B357 Gpio Utilization
LPC47B357 Gpio Port Utilization
Function Direction
System Status Power LED
3.2 LPC47B357 I/O Controller Miscellaneous Functions
This page is intentionally blank
INPUT/OUTPUT Interfaces
Enhanced IDE Interface
IDE Programming
IDE Configuration Registers
Eide PCI Configuration Registers 82801, Device 31/Function
IDE Bus Master Control Registers
IDE Bus Master Control Registers
IDE Connector
Pin Primary IDE Connector Pinout
Pin Signal Description
Diskette Drive Interface
Diskette Drive Interface Configuration
Diskette Drive Interface Configuration Registers
Index Reset
Diskette Drive Programming
Diskette Drive Interface Control Registers
Pri
Diskette Drive Connector
Pin Diskette Drive Connector Pinout
DB-9 Serial Connector Pinout
Serial Interface
1 RS-232 Interface
Serial Interface Configuration
Serial Interface Configuration Registers
Serial Interface Programming
Serial Interface Control
Serial Interface Control Registers
Addr Register
Standard Parallel Port Mode
Parallel Interface
Enhanced Parallel Port Mode
Extended Capabilities Port Mode
Parallel Interface Configuration
Parallel Interface Configuration Registers
Parallel Interface Programming
Parallel Interface Control
Parallel Interface Control Registers
Address Register
Parallel Interface Connector
DB-25 Parallel Connector Pinout
Pin Signal Function
KEYBOARD/POINTING Device Interface
Keyboard Interface Operation
To-Keyboard Commands
Command
3.1 8042 Configuration
Keyboard Interface Configuration Registers
Pointing Device Interface Operation
KEYBOARD/POINTING Device Interface Programming
3.2 8042 Control
Port 60h
Port 64h
CPU Commands To
Value Command Description
KEYBOARD/POINTING Device Interface Connector
Keyboard/Pointing Device Connector Pinout
Data
USB Data Formats
ICH2 USB
Endp
USB Configuration
USB Interface Configuration Registers
USB Programming
USB Control
USB Connector
USB Connector Pinout
USB Cable Data
USB Cable Length Data
Functional Analysis
CD ROM
TDA
Audio Controller
3 AC97 Link BUS
Sync
SD OUT
Slot Description
Audio Codec
Audio Configuration
AC’97 Audio Controller PCI Configuration Registers
Audio Programming
Audio Control
Audio Specifications
Audio Subsystem Specifications
Paramemter Measurement
Network Support
PCI VER .2 Support
ALERT-ON-LAN Support
AOL Events
Input/Output Interfaces
Remote System Alert Support
AOL/SOS
SOS
Remote System Alert Events
Power Supply ASSEMBLY/CONTROL
Distribution
AUX
Power Supply Assembly
Watt Power Supply Assembly Specifications P/N
Range Min. Current Max Surge
Power Control
Power Button
System State Pressed Power Button Results
System Board LED Indications
Power LED Indications
Power Management Event
Wake Up Events
Wake-On-LAN
Power Distribution
1 3.3/5/12 VDC Distribution
Conn Pin
RTN
LOW Voltage PRODUCTION/DISTRIBUTION
VID0
AGP PWR Rimm
VID1 VID2 VID3 VID4
Signal Distribution
System
Board
IDE I/F CD-ROM
Power Button/LED Header P5
CD ROM Audio Header P7
AOL/SOS Header P12
Bios ROM
Bios ROM
Boot Block Codes
ROM Flashing
Upgrading
Num Lock Cap Lock Scroll Lock
Changeable Splash Screen
\Flashi.exe ImageFilename BackgroundColor ForegroundColor
Boot Functions
Boot Device Order
Network Boot F12 Support
Memory Detection and Configuration
Boot Error Codes
Boot Error Codes
Visual Audible Meaning
Setup Utility
Setup Utility Functions
Heading Option Description
Translation Mode IDE disks only
Removable Media Boot
Translation Parameters IDE Disks only
Multisector Transfers IDE ATA devices only
CTRL+ALT+DEL
See the Desktop Management Guide for more
Setup Utility Functions
Setup Utility Functions
Setup Utility Functions
Function Mode
Client Management Functions
Client Management Functions INT15
Input EAX
Output
EBX
ECX
Temperature Status
System ID and ROM Type
Edid Retrieve
System System ID ROM Family PnP ID
Drive Fault Prediction
PnP Bios Functions
PNP Support
Smart Hard Drive detects imminent failure
Smbios
Power Management Functions
System Timer
IDE Hard Drive Timer
Independent PM Support
Going to Sleep in Independent PM
System Standby
IDE Hard Drive Standby
Suspend
Acpi Support
APM 1.2 Support
APM Bios Functions
APM Bios Function Description
Staying Awake in APM
Going to Sleep in APM
System/Hard Drive Standby
System Suspend
Waking Up in APM
USB Legacy Support
This page is intentionally blank
Error Messages and Codes
BEEP/KEYBOARD LED Codes
Table A-1
Beep/Keyboard LED Codes
POWER-ON Self Test Post Messages
Power-On Self Test Post Messages
Error Message Probable Cause
Table A-2
System Error Messages
System Error Messages
Table A-3
Message Probable Cause
Memory Error Messages
Keyboard Error Messages
Table A-4
Table A-5
Printer Error Messages
Video Graphics Error Messages
Table A-6
Table A-7
Diskette Drive Error Messages
Serial Interface Error Messages
Table A-8
Table A-9
Modem Communications Error Messages
Table A-10
System Status Error Messages
Hard Drive Error Messages
Table A-11
Table A-12
Table A-13
Table A-14
Audio Error Messages
17 DVD/CD-ROM Error Messages
Network Interface Error Messages
Scsi Interface Error Messages 65xx-xx, 66xx-xx
Pointing Device Interface Error Messages
Table A-18
Table A-19
12Compaq Personal Computers
Dec Hex Symbol
Ascii Character SET
Table B-1
Ascii Character Set
Appendix B Ascii Character Set
Keyboard
Appendix C Keyboard
Keystroke Processing
1 PS/2-TYPE Keyboard Transmissions
Parameter Minimum Nominal Maximum
USB-TYPE Keyboard Transmissions
Keyboard Layouts
Standard Enhanced Keyboards
Windows Enhanced Keyboards
Figure C-6.National Windows 102W-Key Keyboard Key Positions
Easy Access Keyboards
Figure C-8.8-Button Easy Access Keyboard Layout
Keys
Special Single-Keystroke Functions
Multi-Keystroke Functions
Windows Keystrokes
Easy Access Keystrokes
Button # Description Default Function
Keyboard Commands
Keyboard-to-System Commands
Scan Codes
Table C-1
Key Make / Break Codes Hex Pos Mode
Table C-2
Keyboard Scan Codes
Table C-2. Keyboard Scan Codes
Key Make / Break Codes Hex Pos
7E/FE
2B/AB
Key
Connectors
Figure C-9.PS/2 Keyboard Cable Connector Male
COMPAQ/NVIDIA TNT2 PRO AGP Graphics Card
Sgram Nvidia TNT2
Bios ROM
Functional Description
2D/VGA
RAM DAC
Resolution Bits per pixel Color Depth
Display Modes
Table D-1
Nvidia TNT2 Pro Graphics Display Modes
Power Management and Consumption
Monitor Power Management Conditions
Software Support Information
Table D-2
Monitor Connector
DB-15 Monitor Connector Pinout
Table D-3
SDA
6Compaq Personal Computers
Appendix E Compaq/NVIDIA GeForce2 GTS AGP Graphics Card
Sdram Nvidia
Appendix E Compaq/NVIDIA GeForce2 GTS AGP Graphics Card
Table E-1
Nvidia GeForce2 GTS Graphics Display Modes
Table E-2
Table E-3
Video Feature Connector
Video In Connector Pinout
Table E-4
COMPAQ/LUCENT V.90 56K PCI Modem
Appendix F Compaq/Lucent V.90 56K PCI Modem
DSP DAA
Operating Parameters
Uart Transfer Rates
Transmission Modes
Table F-1
Connector
APM Environment
Acpi Environment
Programming
Appendix G COMPAQ/ELSA Gloria
Appendix G Compaq/ELSA GLoria II AGP Graphics Card
Table G-1
Elsa GLoria II Graphics Display Modes
Table G-2
Table G-3
Table G-4
Appendix G Compaq/Matrox Millennium G450 AGP Graphics Card
RAM MGA
Ramdac
MB Sdram
Table H-1
Matrox Millennium G450 Graphics Display Modes
Table H-2
Table H-3
Video Feature Connector
Network Interface Controller Adapters
WOL Bios
Controller Type Featured on
VDC
TX/RX PHY
AOL Function
Wake UP Functions
Ipsec Function
Power Management Support
Configuration
Adapter Programming
Control
Control Registers
Network Connector
Adapter Specifications
Adapter Specifications
DES/3DES, Hmac SHA-1, MD5
8Compaq Personal Computers
COMPAQ/NVIDIA QUADRO2 MXR AGP Graphics Card
Sdram Nvidia NV11GL
RAM DAC Sdram
Table J-1
Nvidia Quadro2 MXR Graphics Display Modes
Table J-2
Table F-3
6Compaq Personal Computers
Compaq PCI 10/100 Ethernet Adapter
AOL/SOS LED
GND VDC
SMB CS
TX/RX
AOL Function
RSA Function
Power Management Support
2 AOL/SOS Connector
Figure K-4.AOL/SOS Connector 7-pin Header
Smbus Connector
WOL Connector
Table K-1
COMPAQ/ADAPTEC 29160N Scsi Host Adapter
Appendix L Compaq/Adaptec Scsi Host Adapter
PCI Scsi
Scsi Adapter Programming Scsi Adapter Configuration
Scsi Adapter Control
Table L-1
Table L-2
Scsi Connectors
External 50-PIN Ultra Scsi Connector
External Ultra Scsi Connector Pinout
Table L-3
Internal 50-PIN Ultra Scsi Connector
Internal 50-Pin Ultra Scsi Connector Pinout
Table L-4
Internal 68-PIN ULTRA160 Scsi Connector
Ultra160 Scsi Connector Pinout
Table L-5
Index
Dimm support
Ipsec
Specifications
Electrical
Environmental
This page is intentionally blank